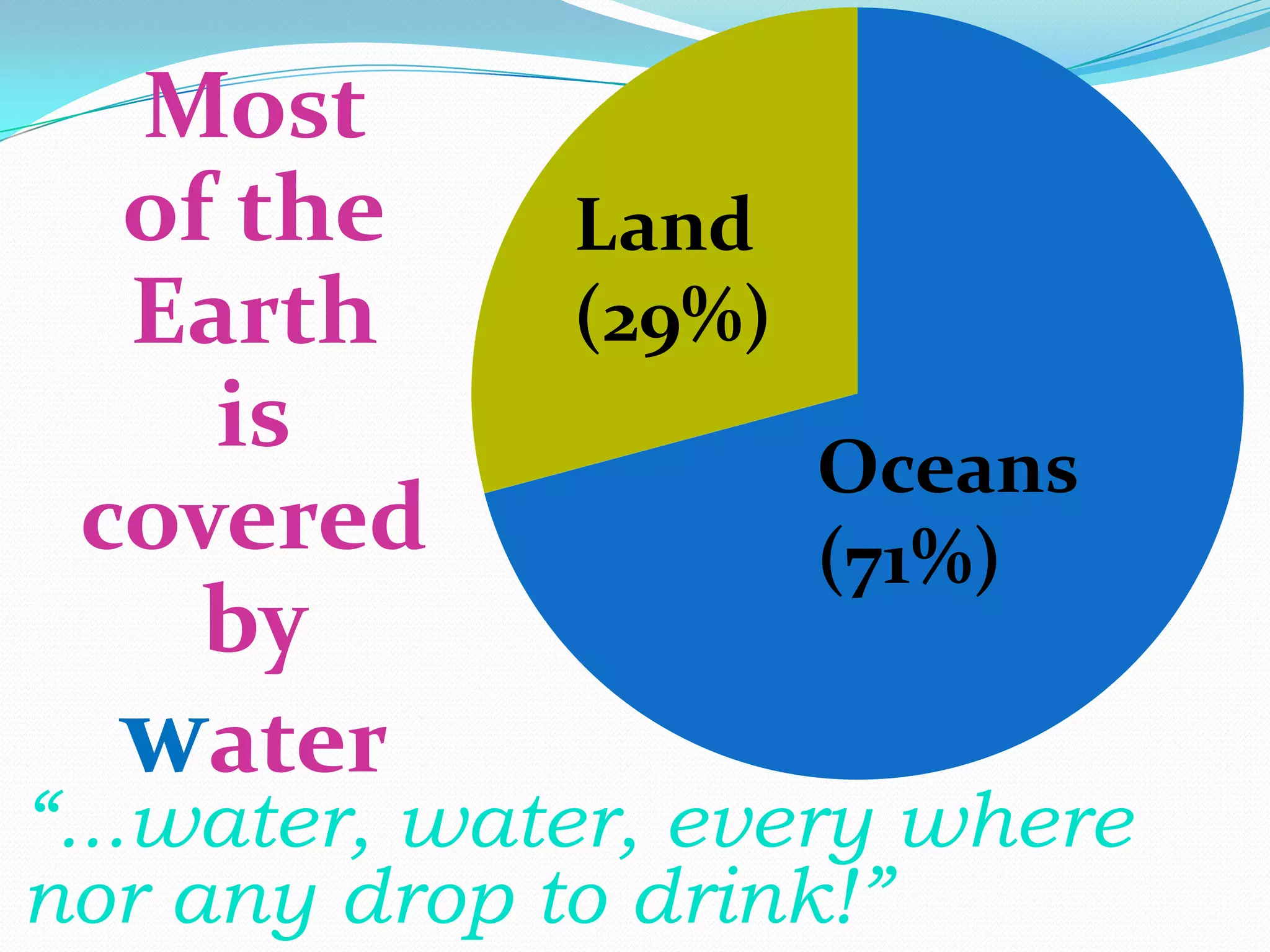
Natural resources are materials found in nature that are valuable in their relatively unmodified form. They are classified as biotic, coming from living organisms, and abiotic, coming from non-living material. Natural resources include forests, water, minerals, food, land, and energy. Many natural resources are under threat due to overconsumption, pollution, deforestation, and other human and natural impacts. Conservation efforts include sustainable harvesting, reforestation, reducing waste, and developing renewable resources to protect natural resources for future generations.