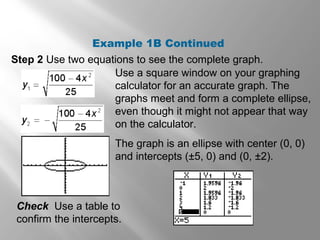
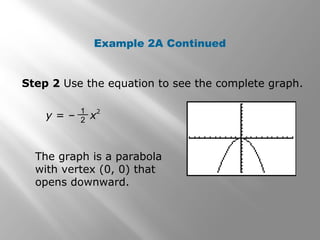
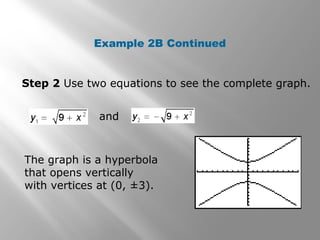
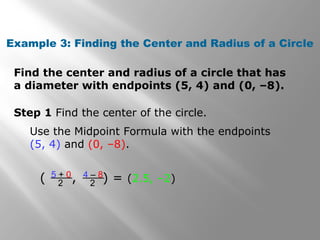
This document provides an overview of conic sections including circles, ellipses, hyperbolas, and parabolas. It discusses how conic sections are formed by the intersection of a double right cone and a plane. Examples are provided on graphing conic sections on a calculator and identifying their properties such as center, vertices, and intercepts. The document also covers using the midpoint and distance formulas to find the center and radius of a circle from its diameter endpoints.