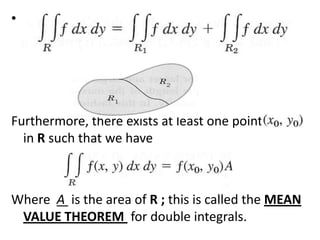
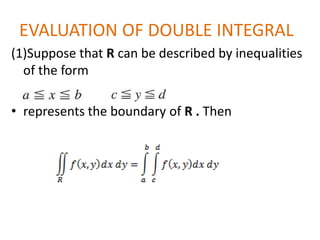
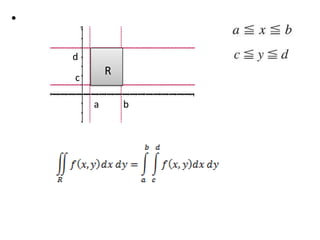
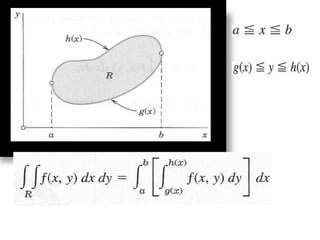
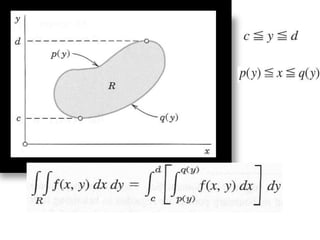
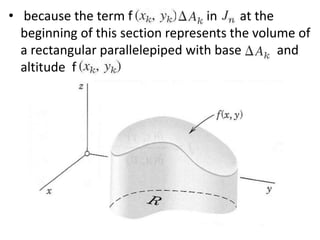
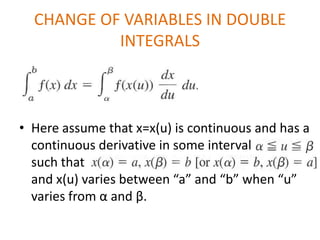
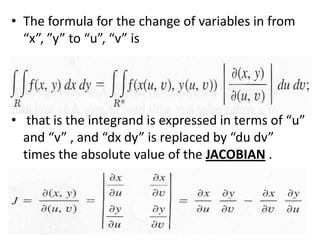
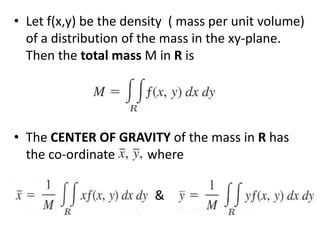The double integral of a function f(x,y) over a bounded region R in the xy-plane is defined as the limit of Riemann sums that approximate the total value of f over R. This double integral is denoted by the integral of f(x,y) over R and its value is independent of the subdivision used in the Riemann sums. Properties and methods for evaluating double integrals are discussed, along with applications such as finding the area, volume, mass, and moments of inertia. Changes of variables in double integrals using the Jacobian are also covered.