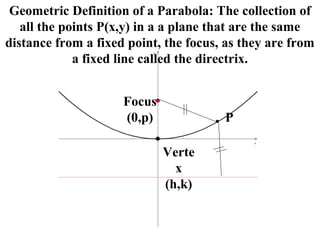
This summary combines slides from Melanie Tomlinson and Morrobea on the topic of parabolas. The key points covered include:
- The geometric definition of a parabola as the set of all points equidistant from a fixed point (the focus) and fixed line (the directrix).
- Parabolas can be represented using various equation forms including vertex form, standard form, and general form.
- Methods for graphing parabolas by identifying features like the vertex, axis of symmetry, x-intercepts, focus, and directrix.
- Applications of parabolas to model real-world situations like searchlights and radio telescopes.