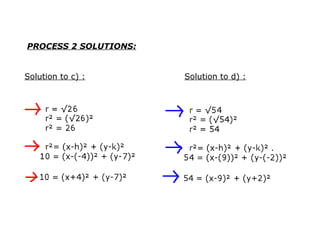
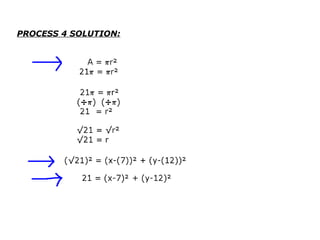
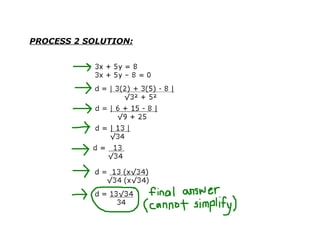
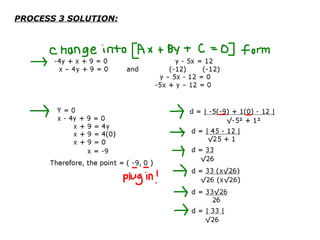
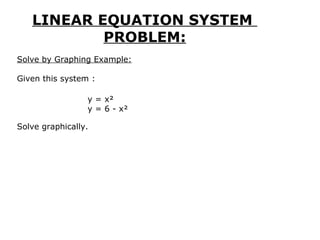
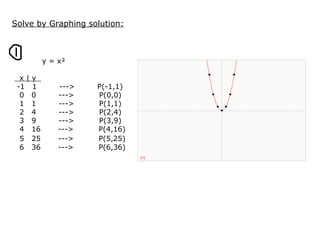
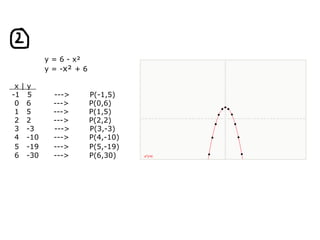
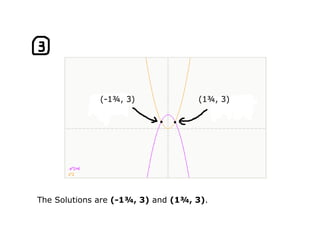
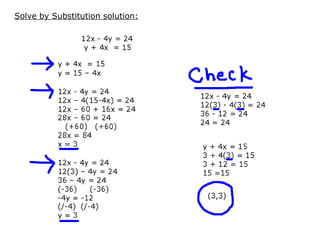
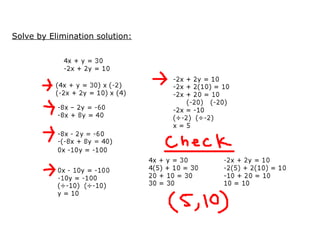
This document provides examples and solutions for solving various types of coordinate geometry problems. It covers changing coordinate equations into standard form, writing equations given a center and radius, finding perpendicular distance between points and lines, and solving systems of linear equations graphically and algebraically. Methods demonstrated include substitution, elimination, and graphing lines to find their point of intersection.