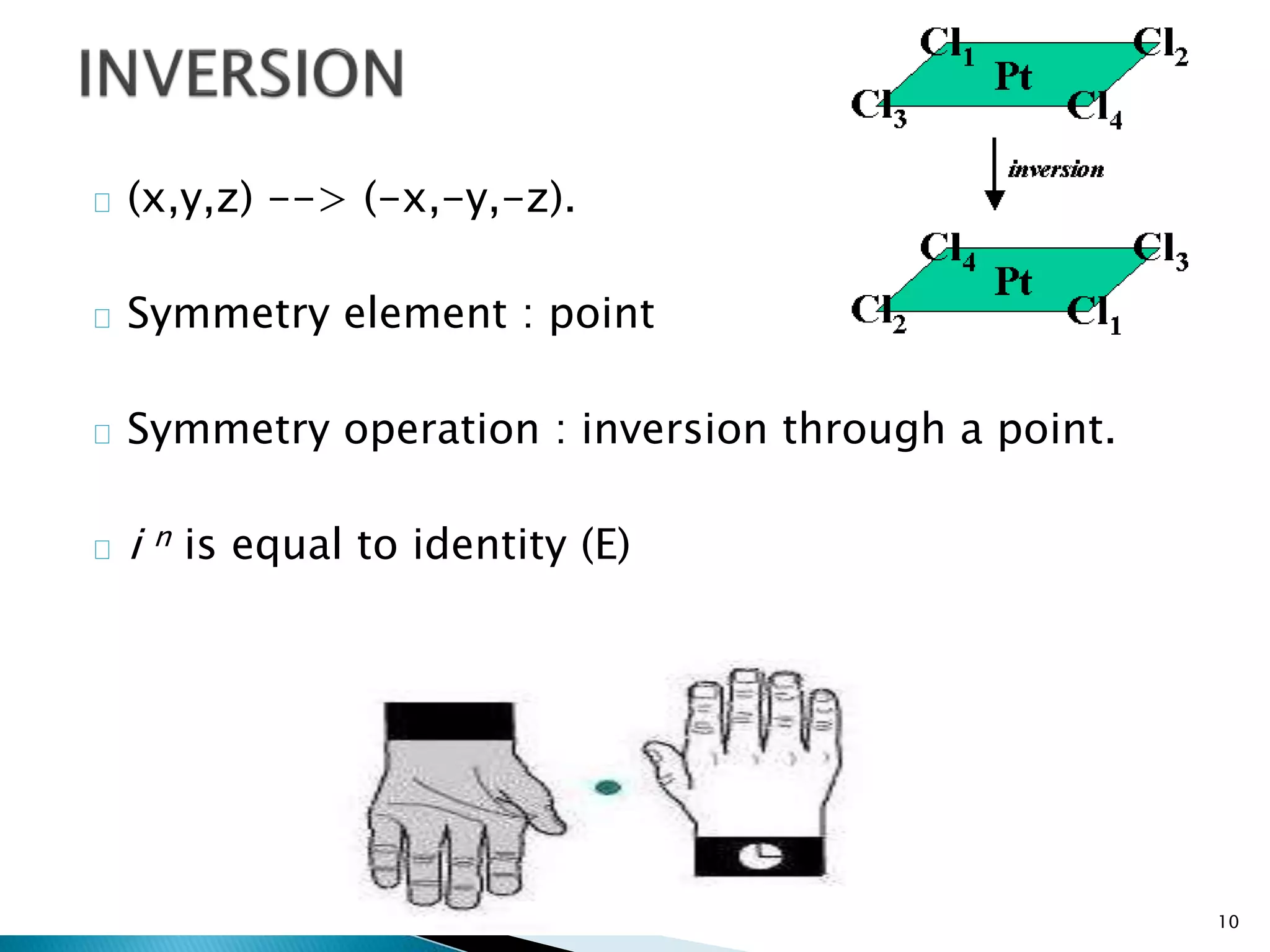
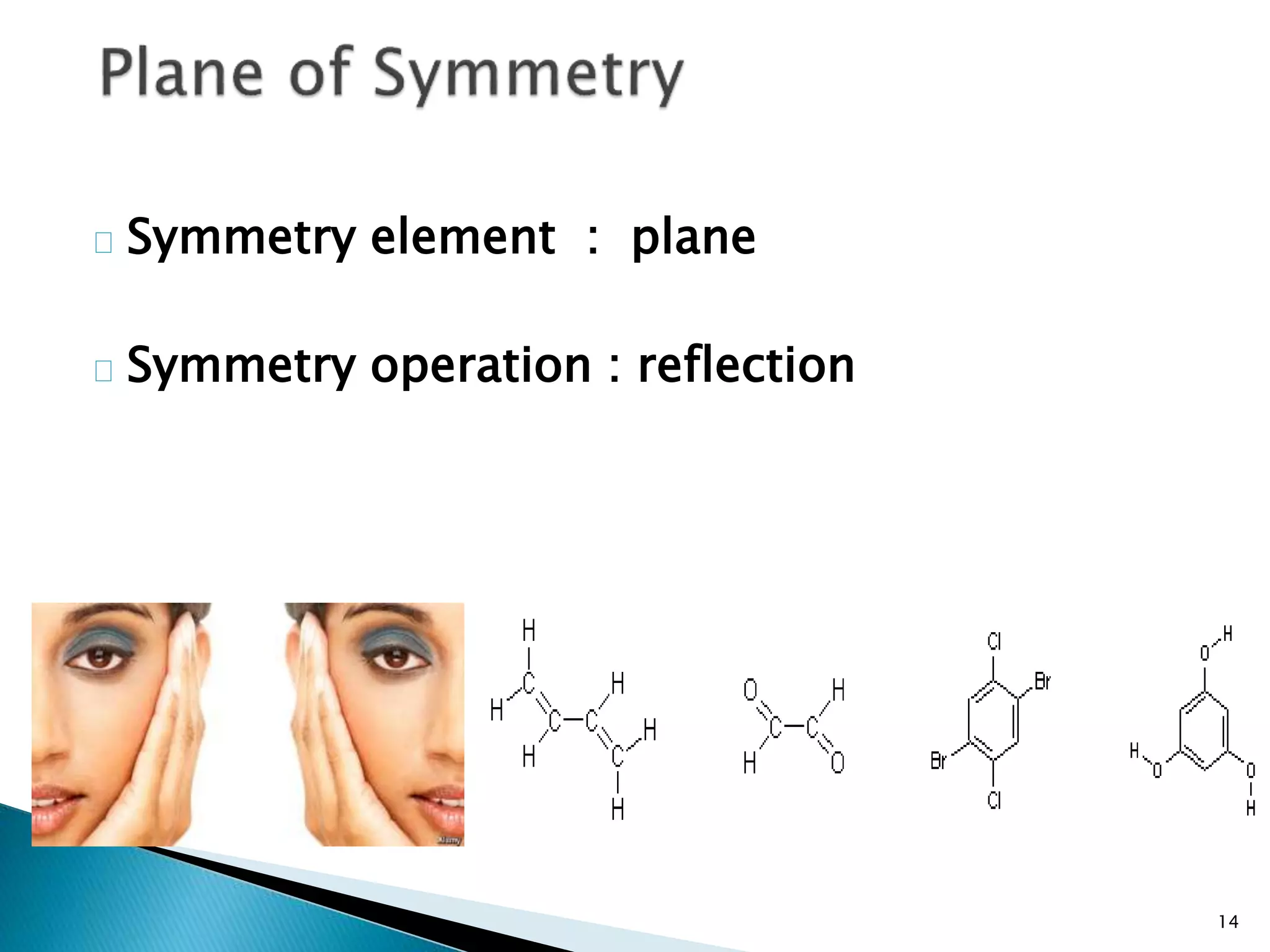
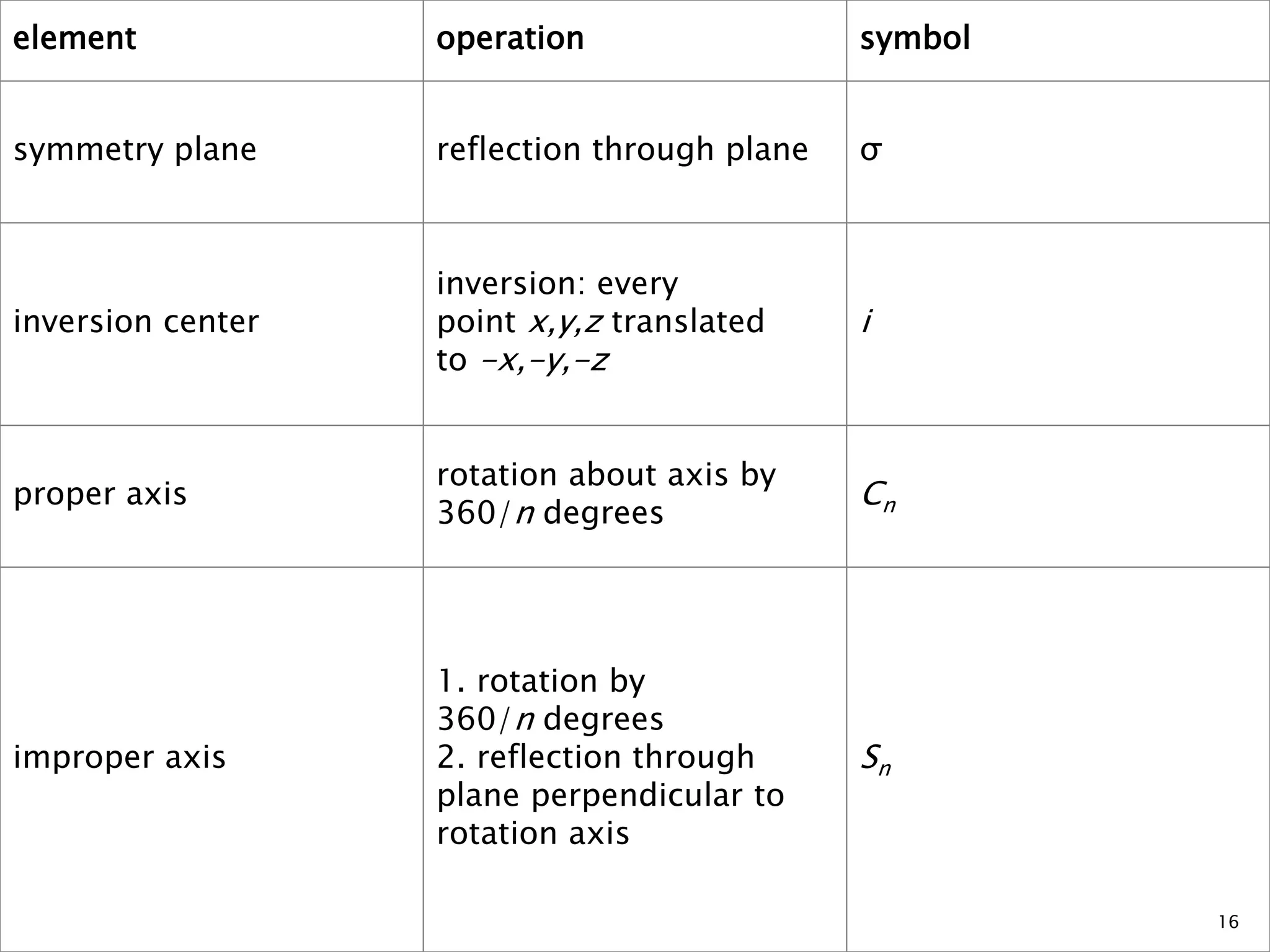
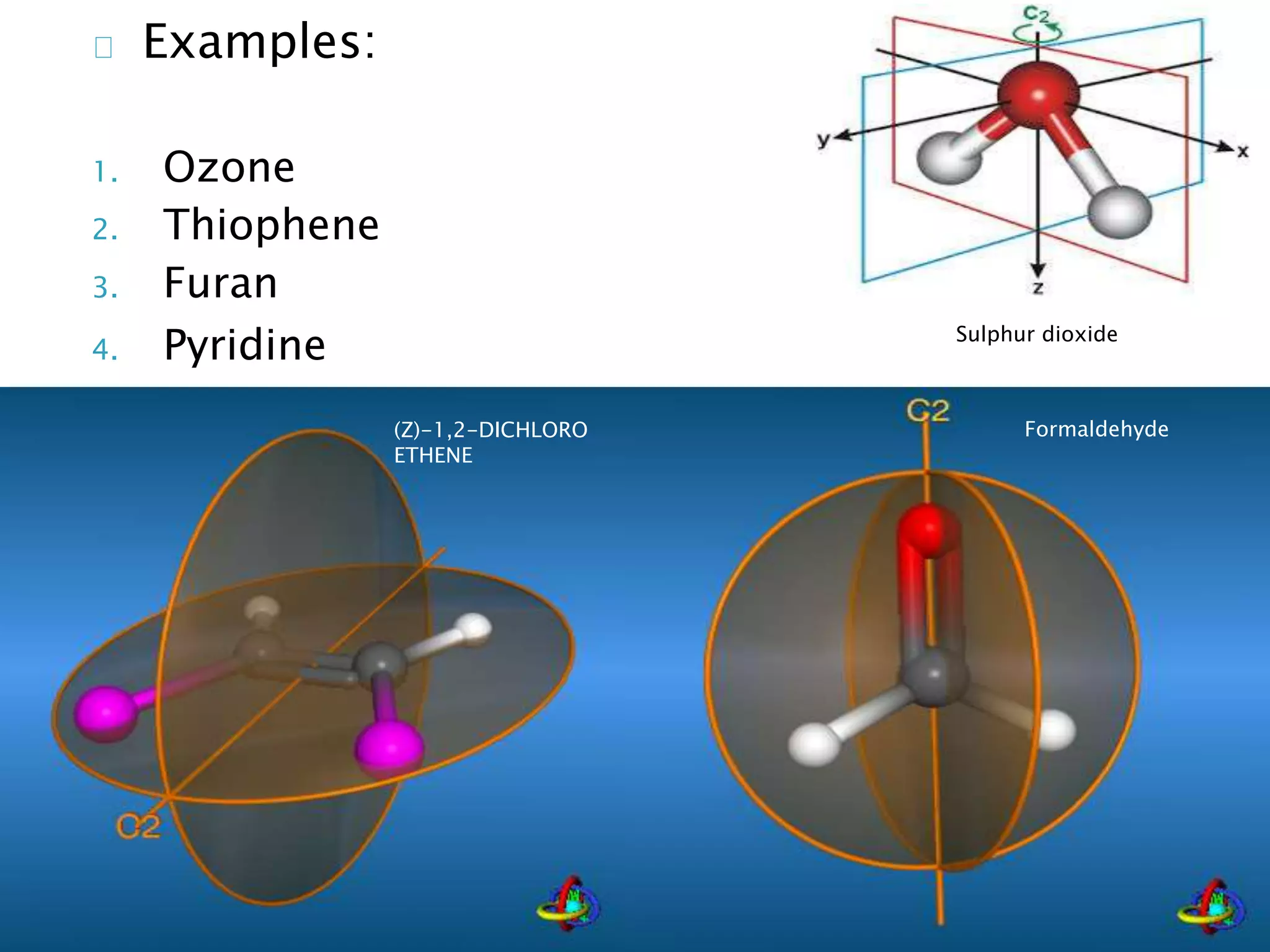
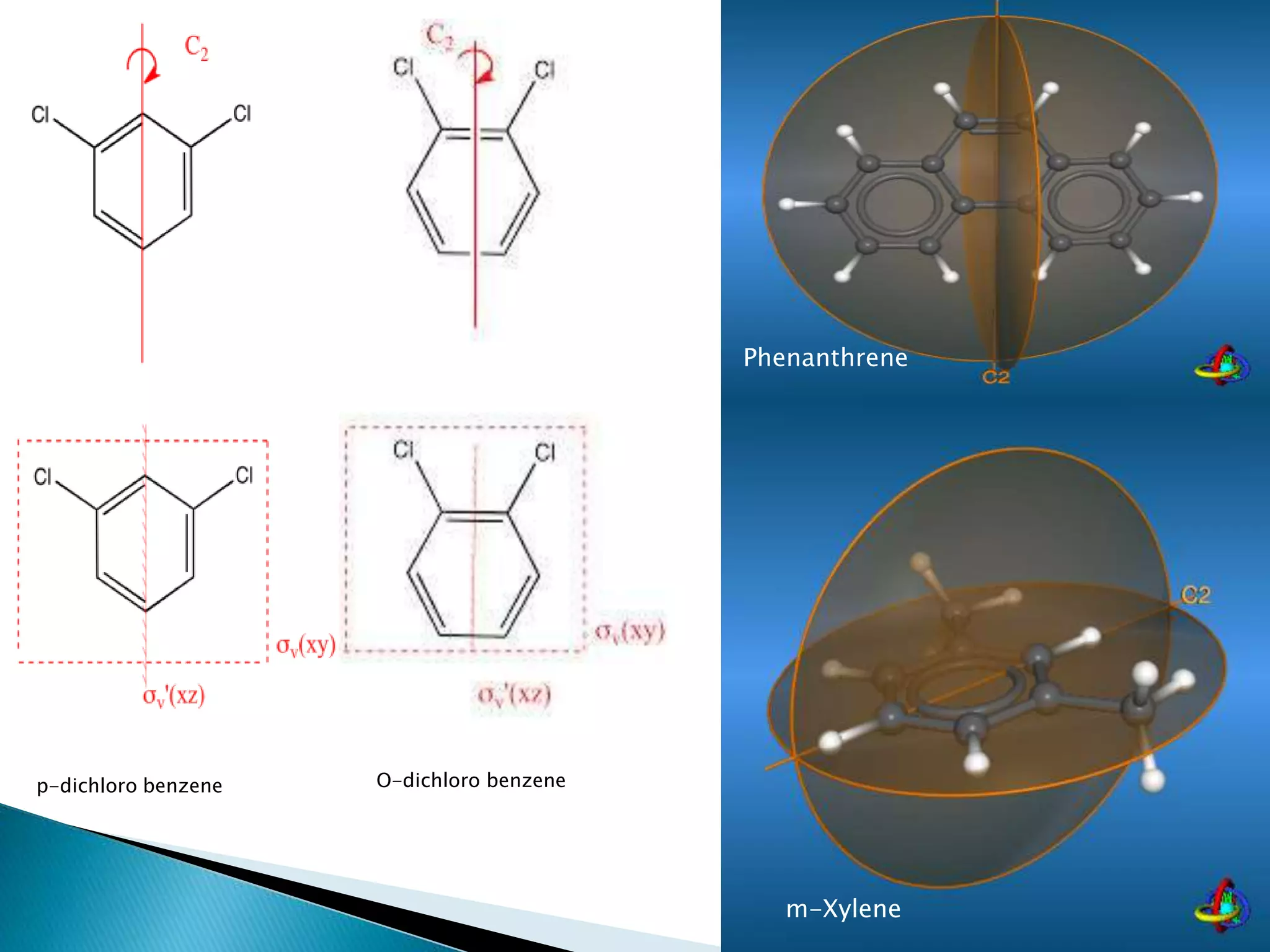
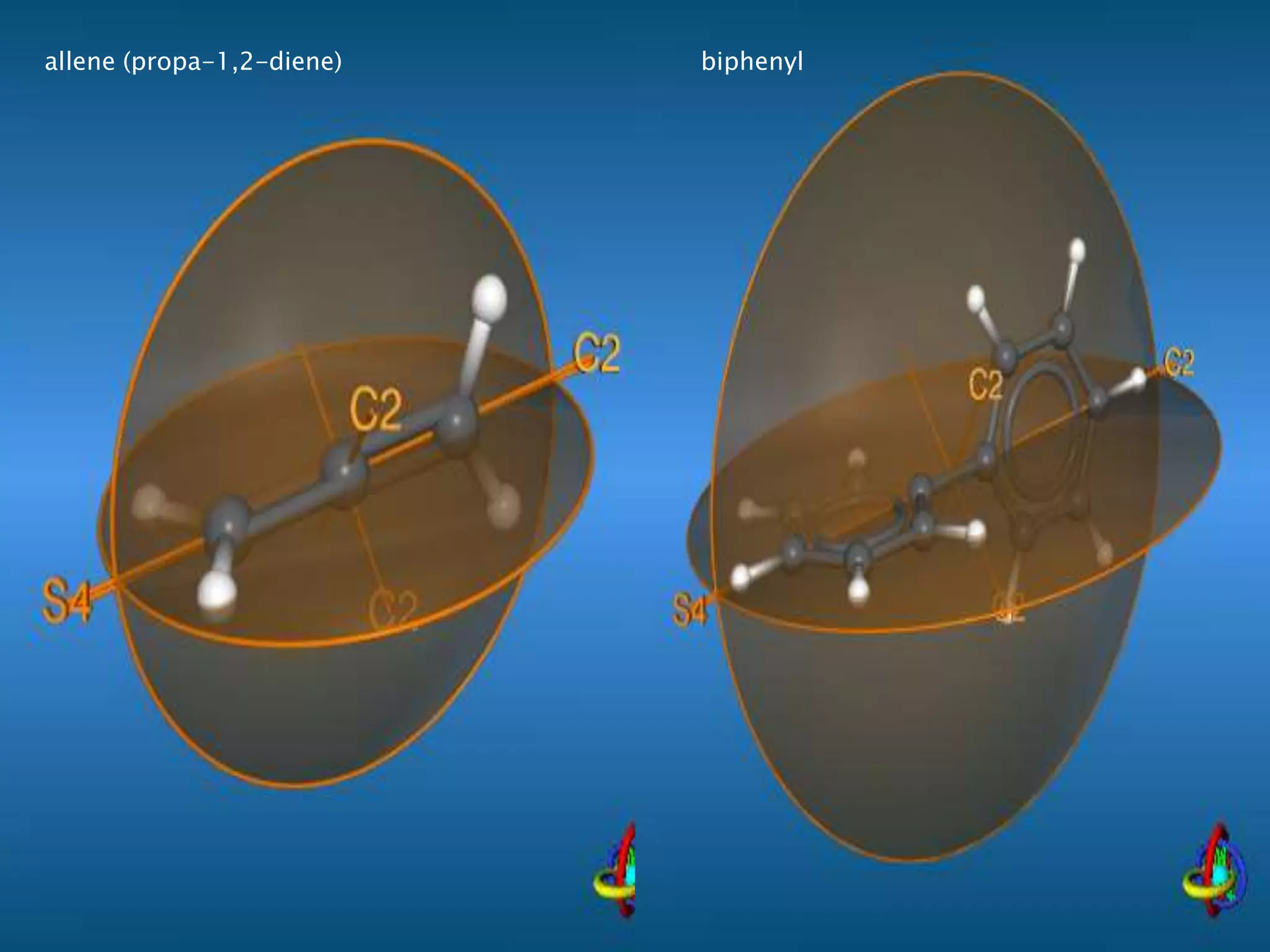
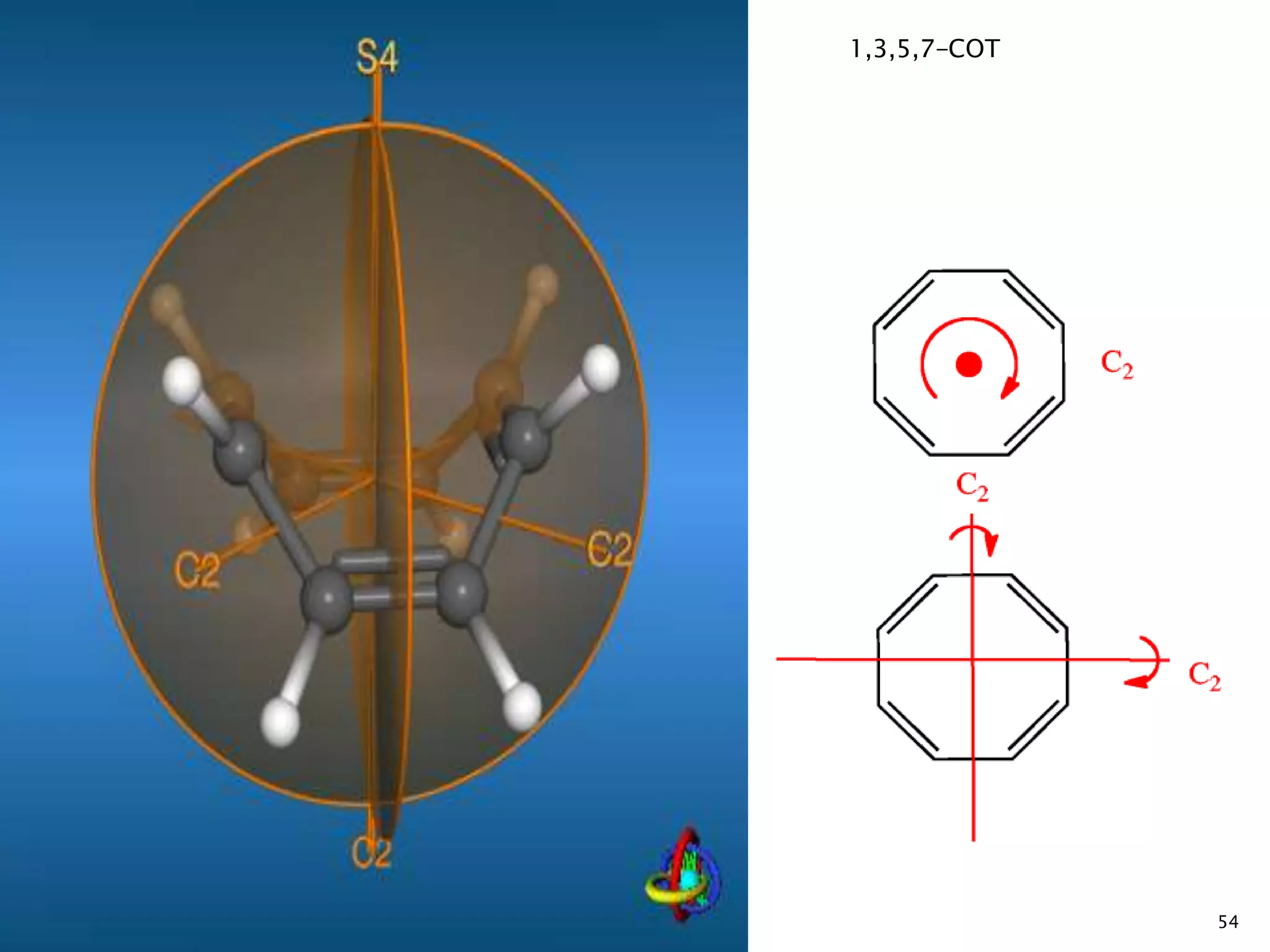
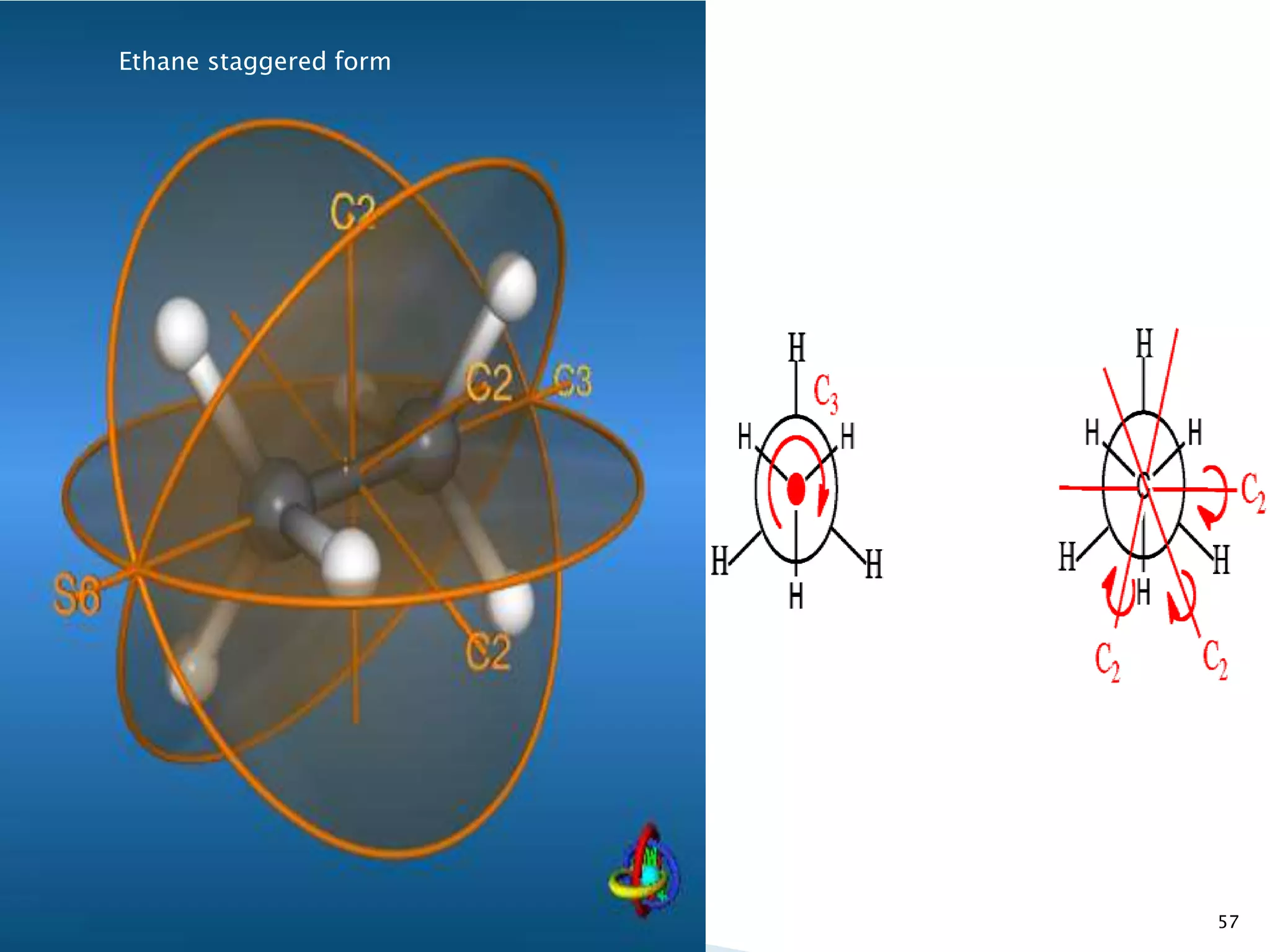
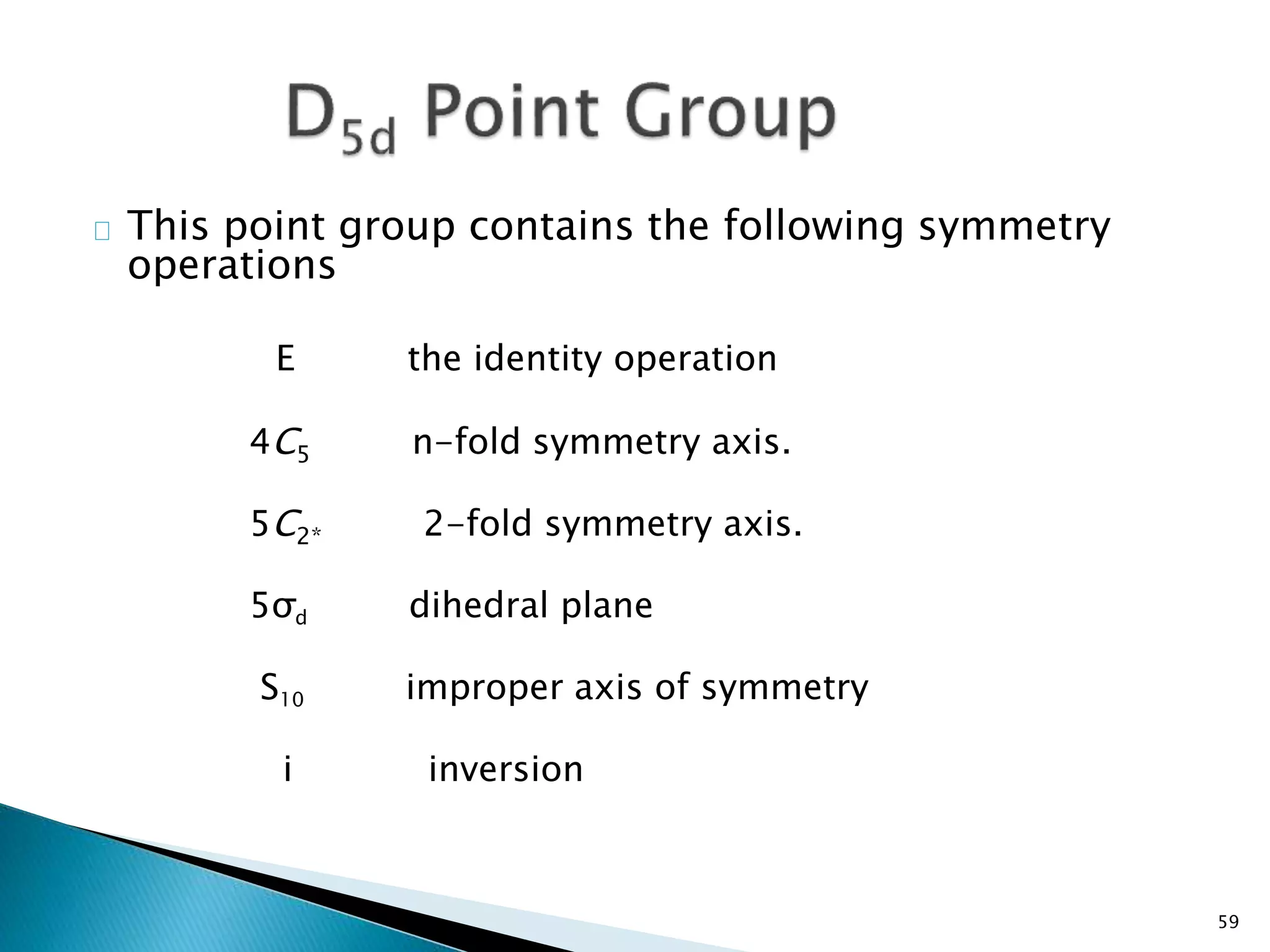
The document discusses symmetry operations and point groups in molecules. It defines five basic symmetry operations: identity, n-fold rotation, reflection, inversion, and improper n-fold rotation. Point groups describe the symmetry elements and operations in a molecule. There are 32 possible point groups that molecules can belong to depending on their specific symmetry properties. The document provides examples of molecules and their corresponding point groups.




















![26
9b H-Phenalene 3,7,11-trimethyl cyclo dodeca 1,5,9-triene
2,6,7-trimethyl-1-aza-bicyclo
[2.2.2]octane](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/symelem-141006082600-conversion-gate02/75/GROUP-THEORY-SYMMETRY-26-2048.jpg)





![36
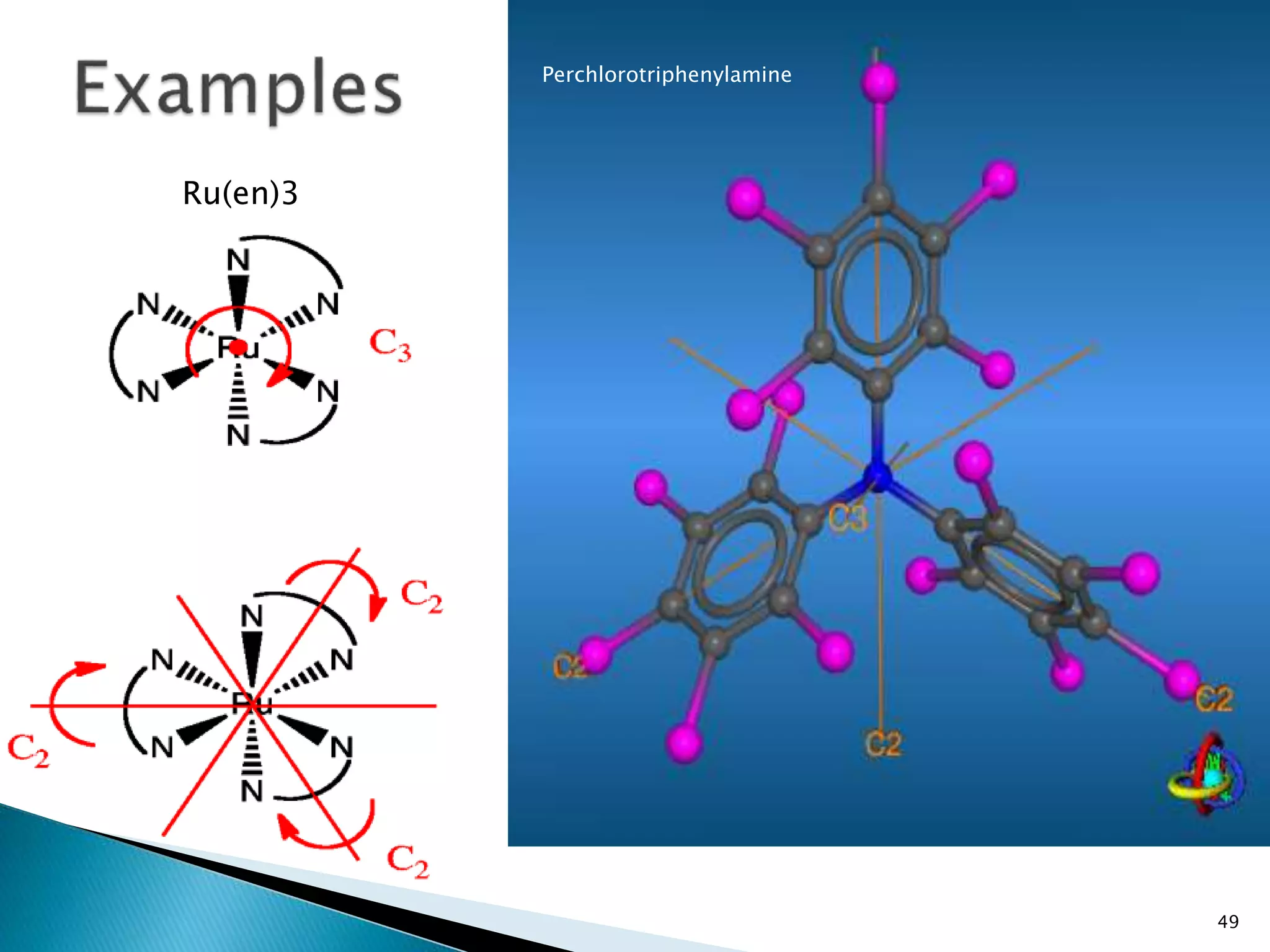
EXAMPLES
Xenon oxytetrafluoride
Sulfur chloride pentafluoride
Bromine pentafluoride
Fluorine pentafluoride
Calix[4]arene](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/symelem-141006082600-conversion-gate02/75/GROUP-THEORY-SYMMETRY-36-2048.jpg)




















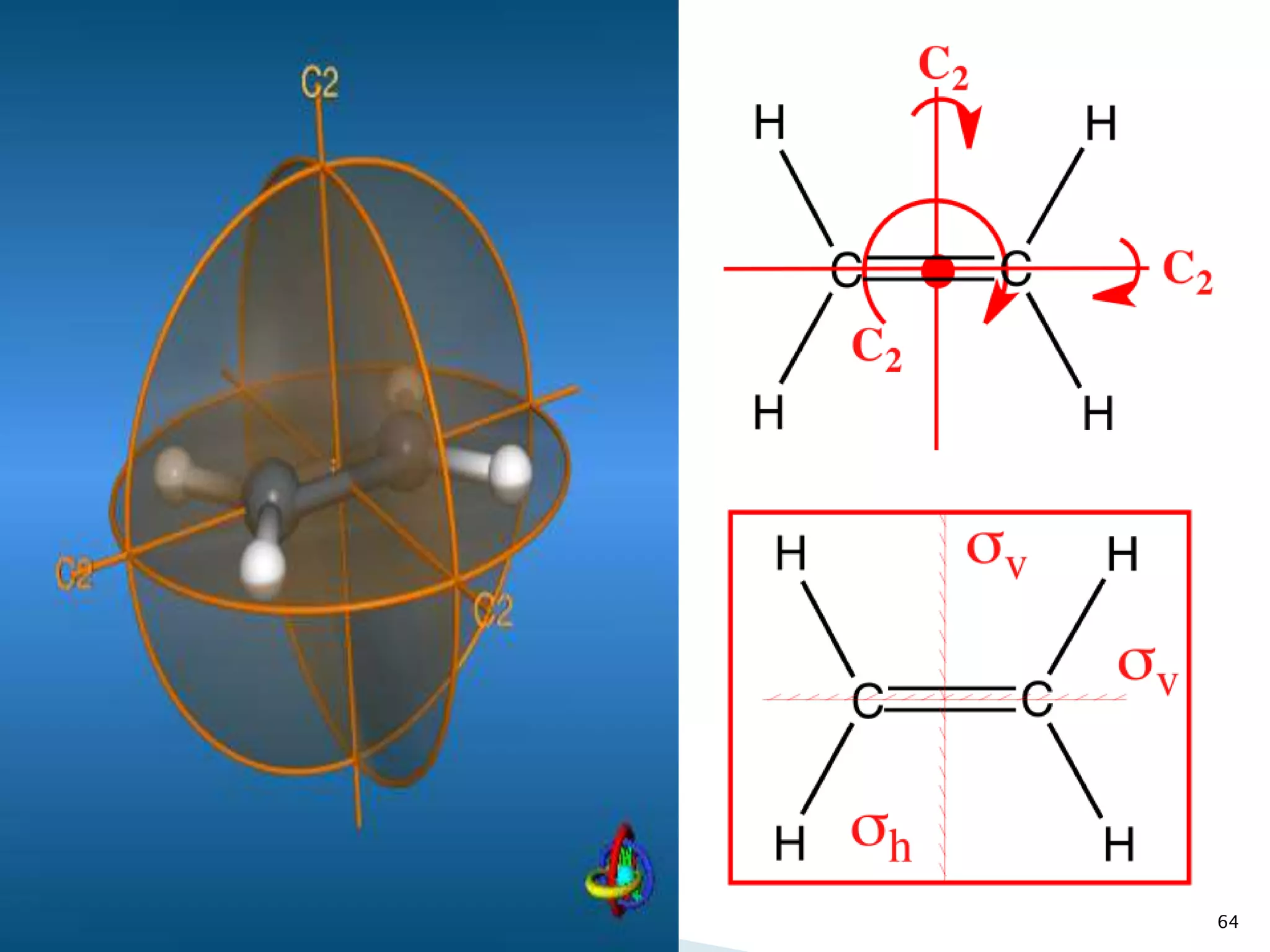
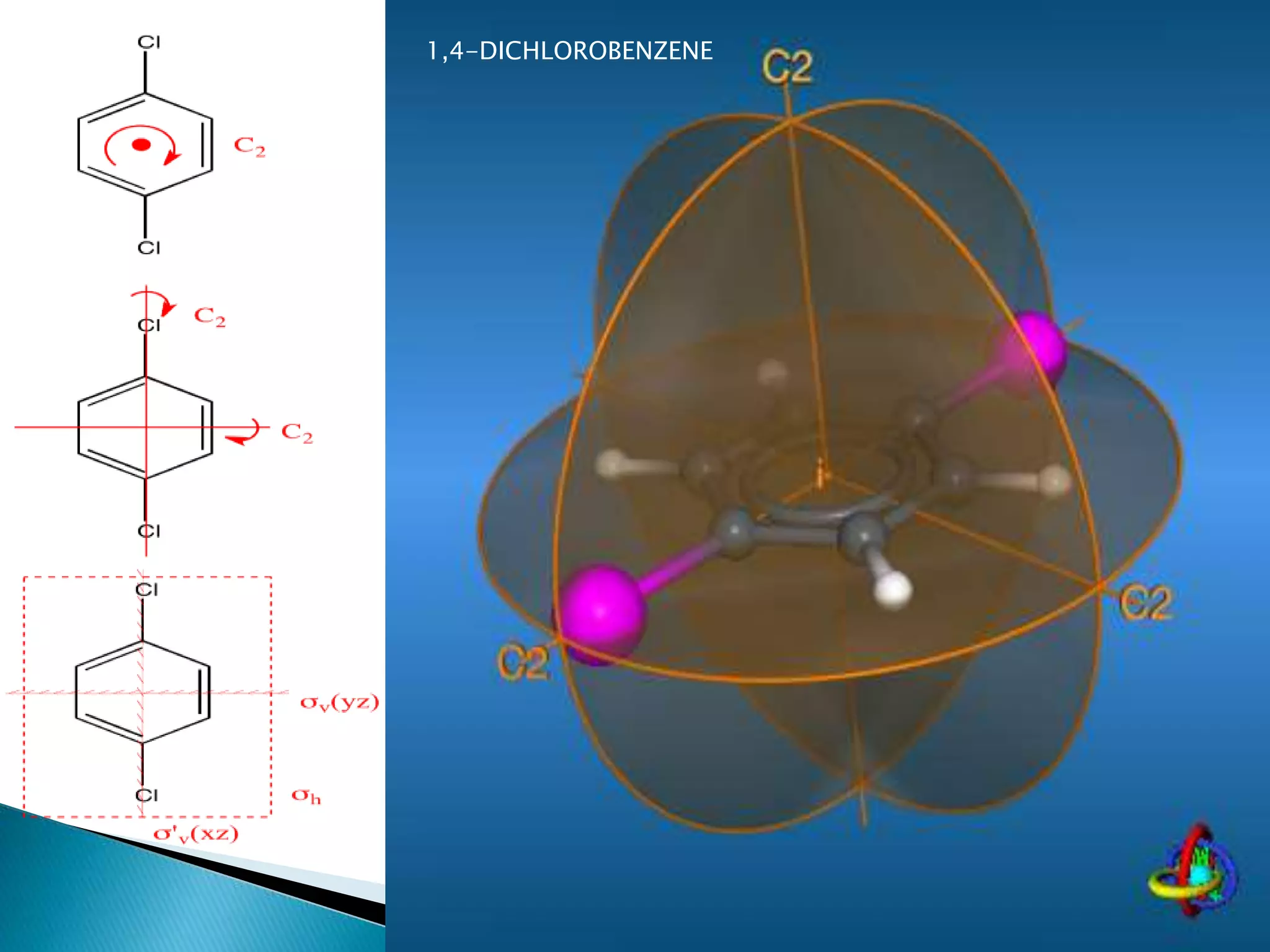
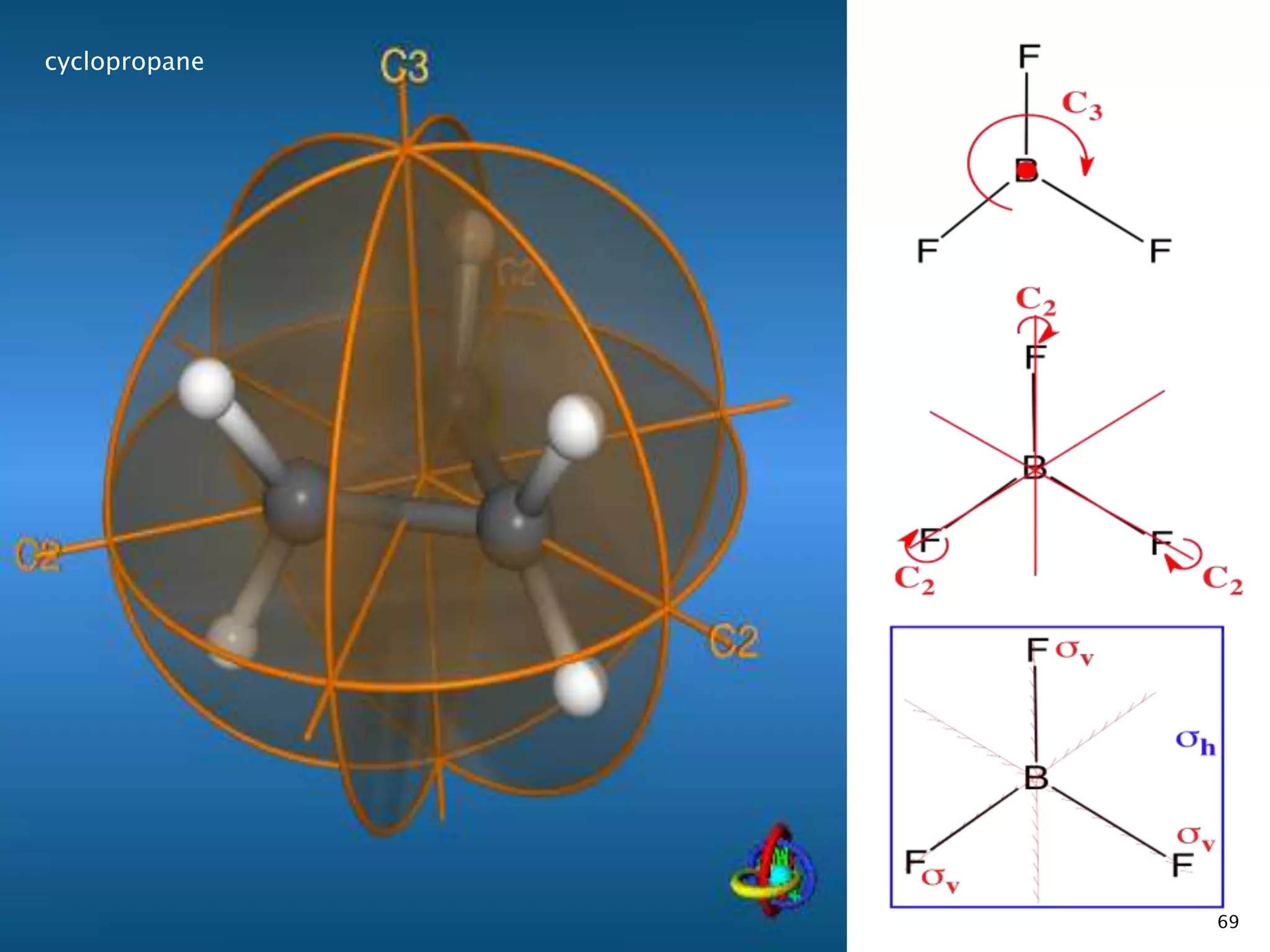
![66
[2,2] PARACYCLOPHANE](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/symelem-141006082600-conversion-gate02/75/GROUP-THEORY-SYMMETRY-66-2048.jpg)



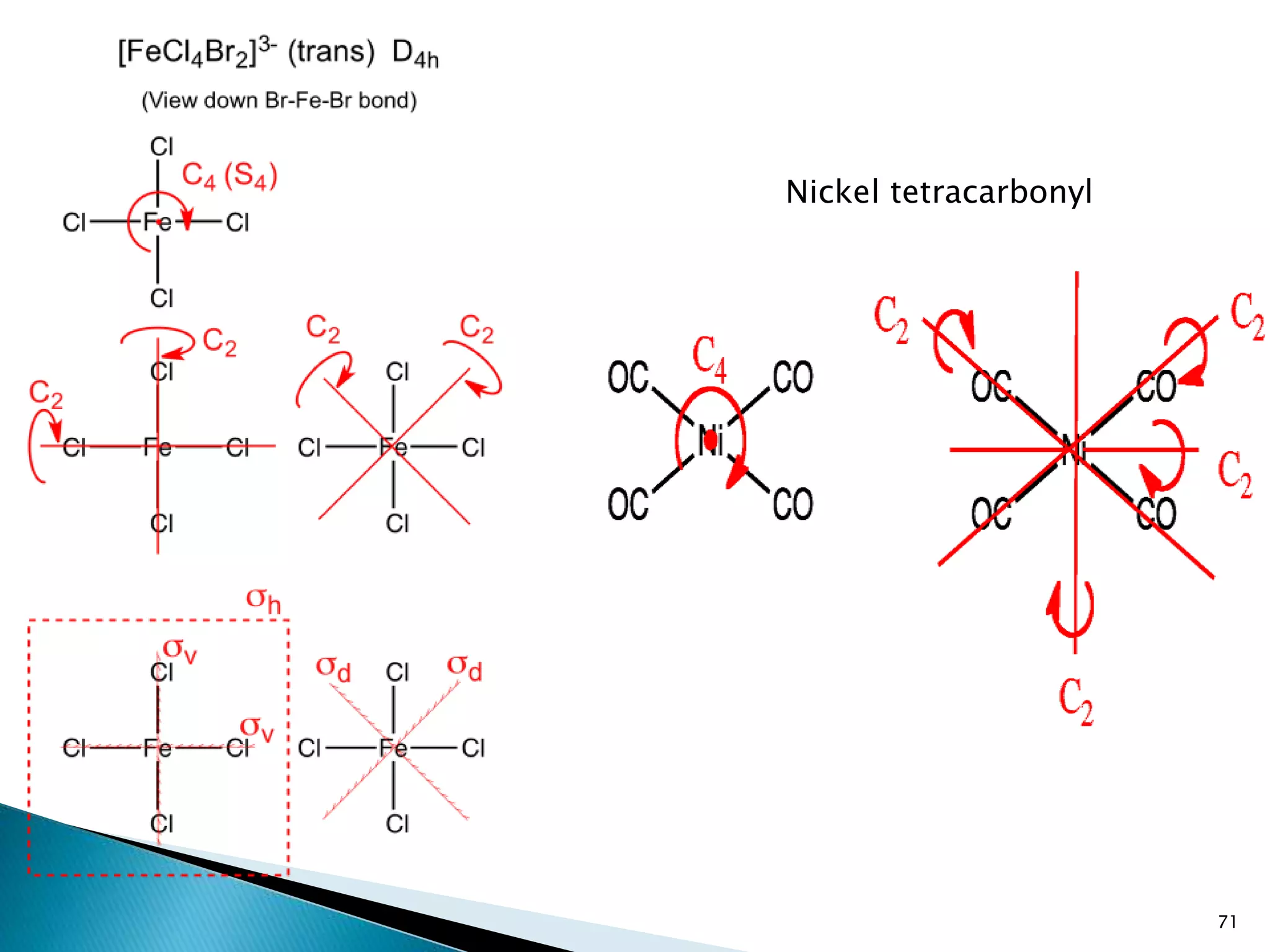
![72
[AlCl₄]− Xenon tetrafluoride](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/symelem-141006082600-conversion-gate02/75/GROUP-THEORY-SYMMETRY-72-2048.jpg)



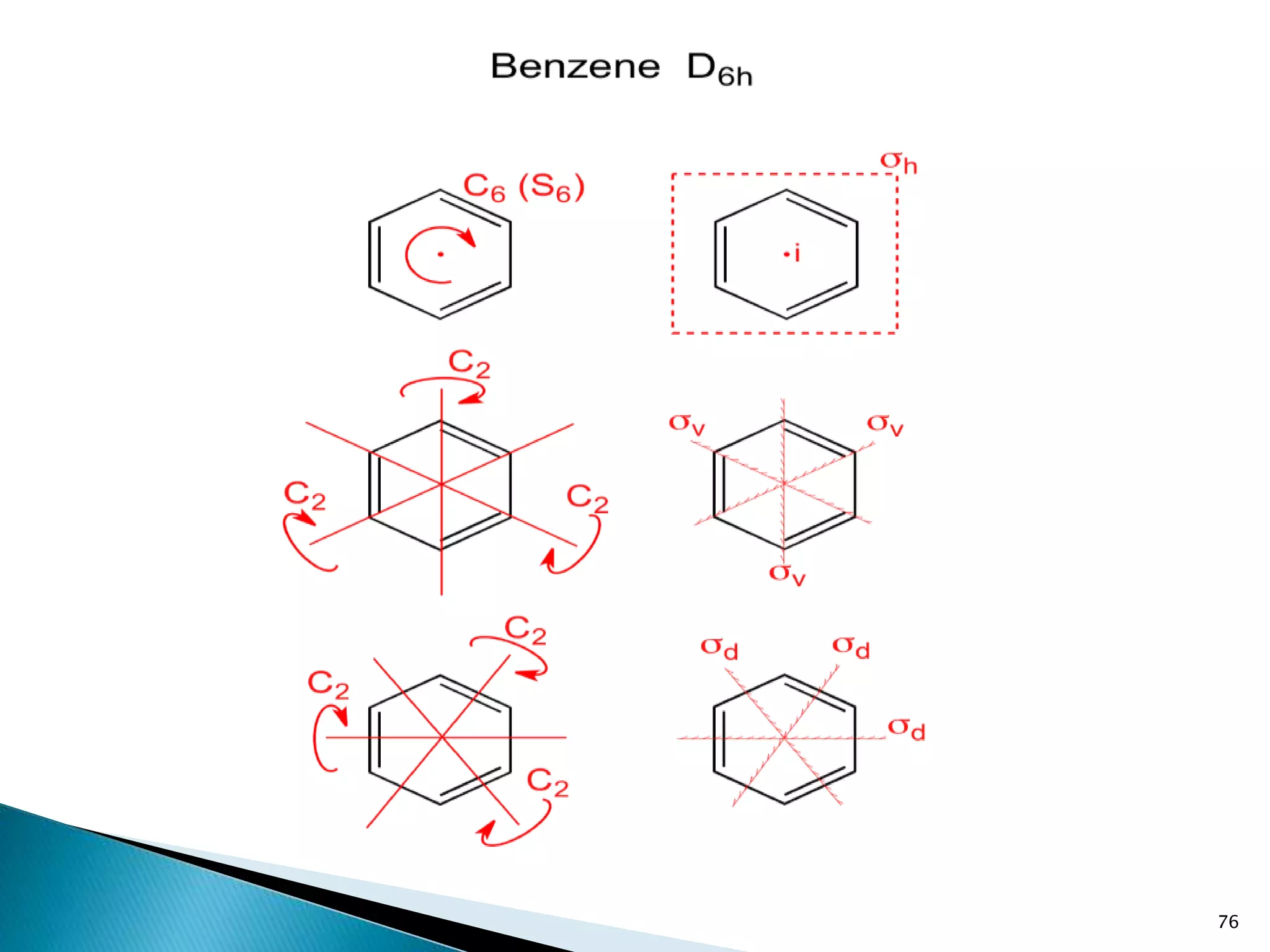
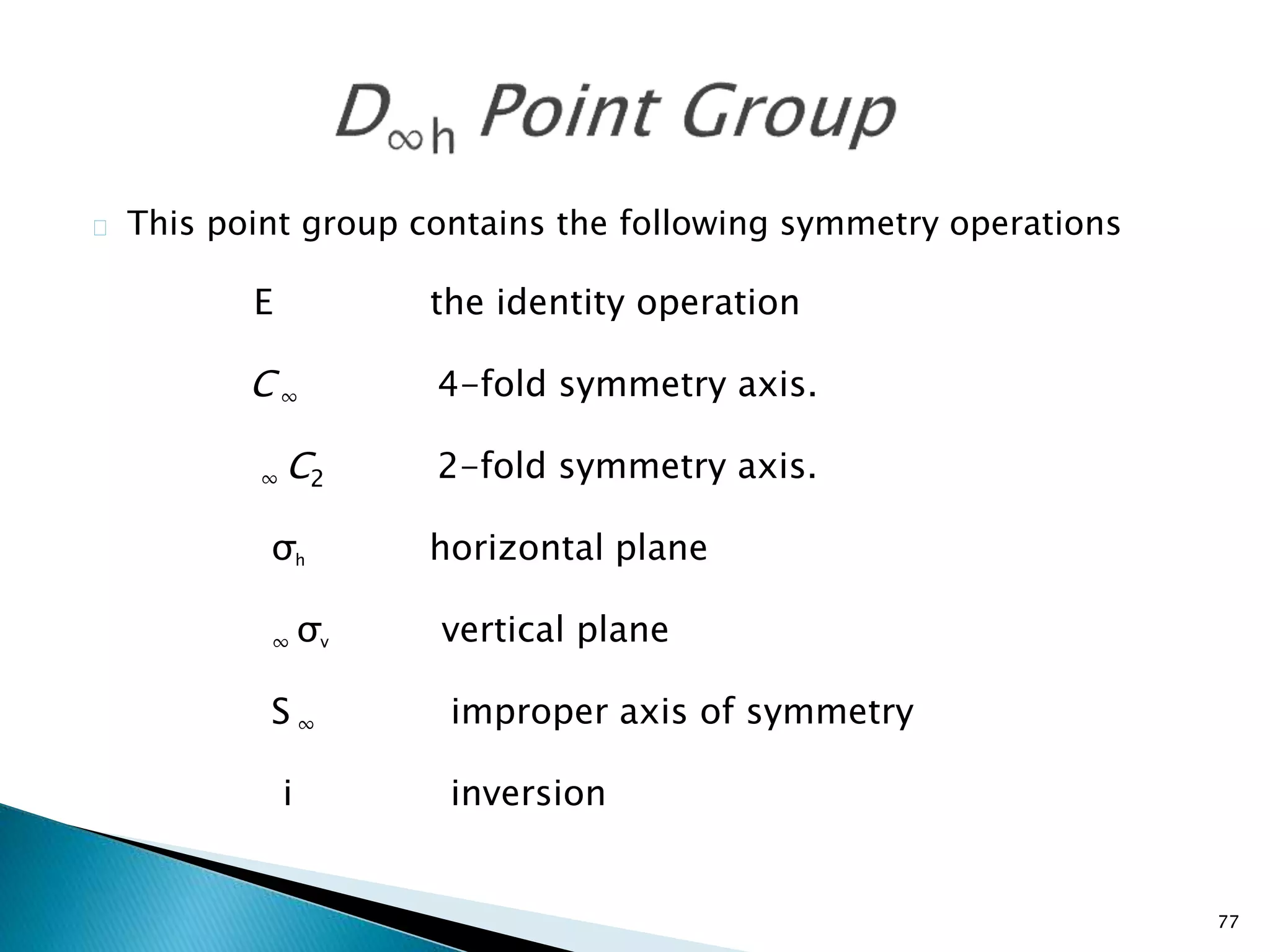


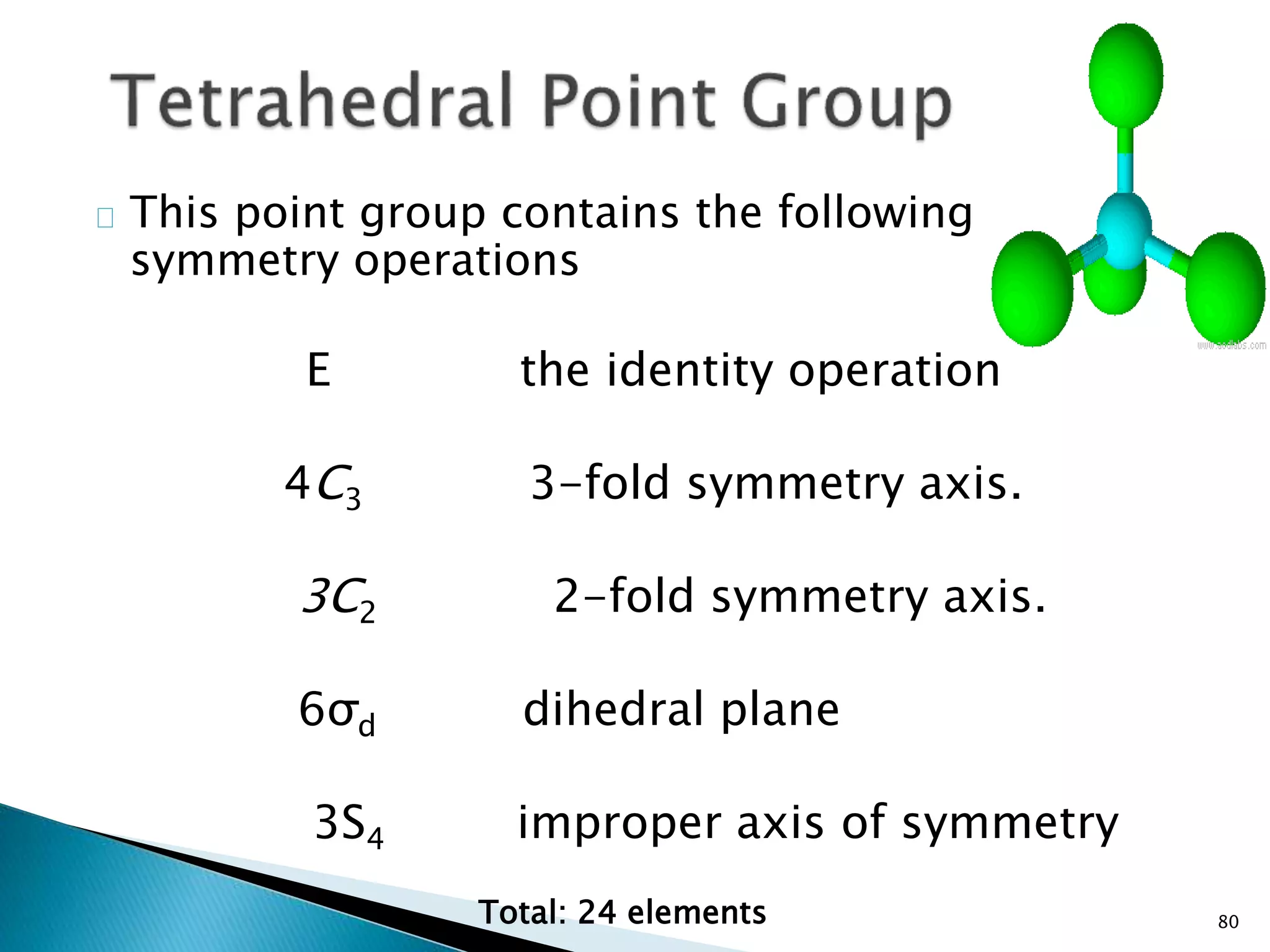

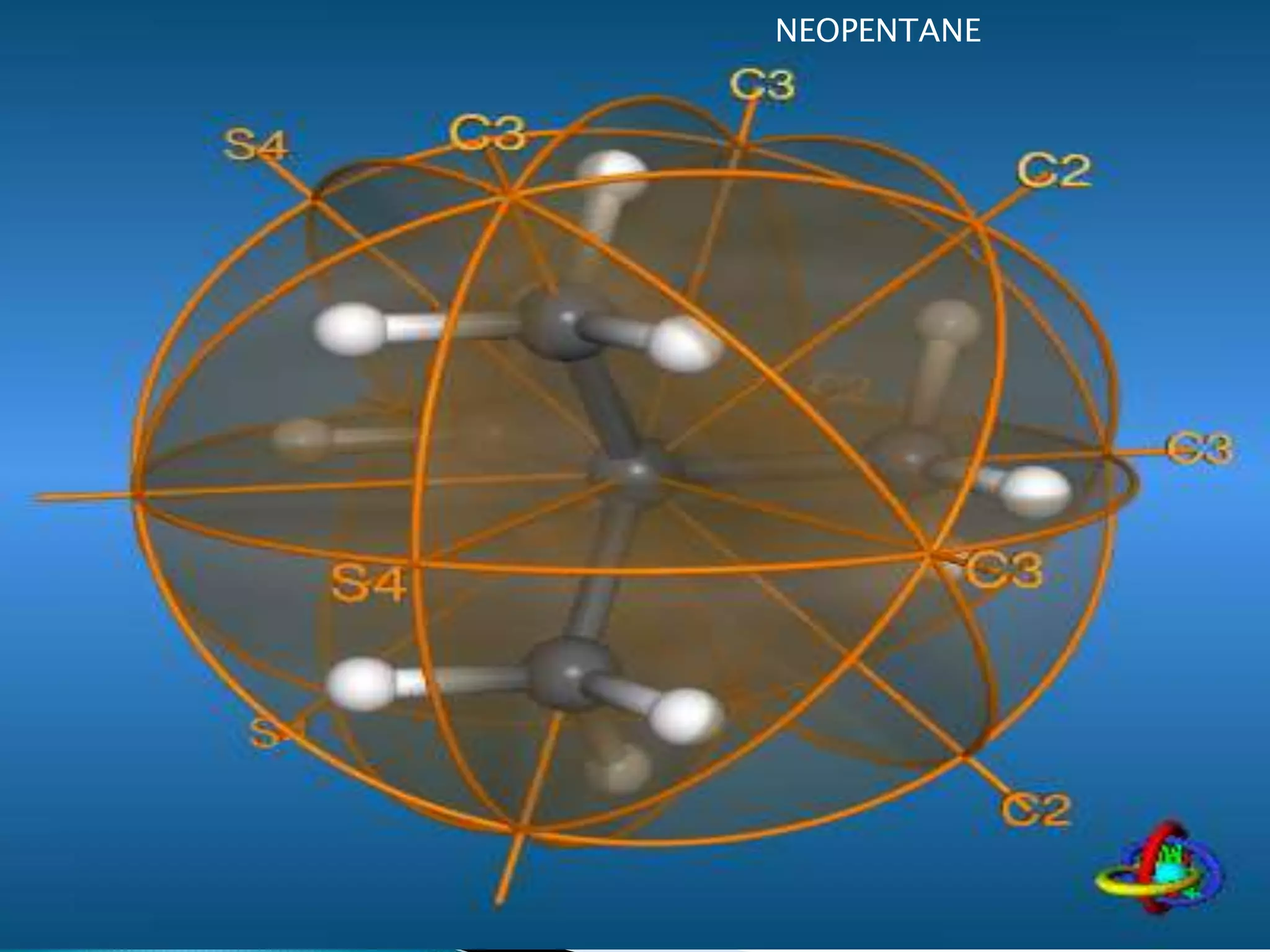

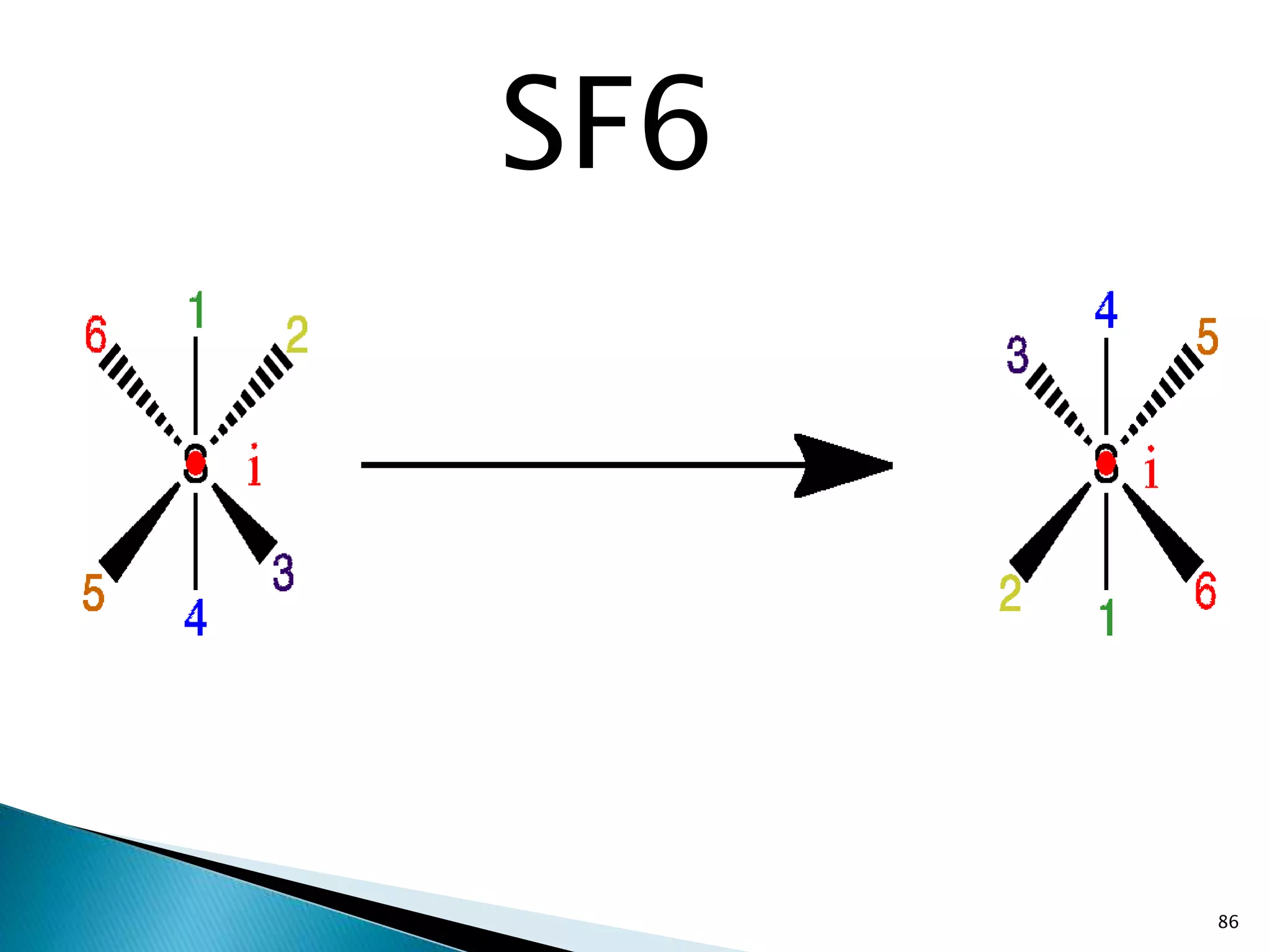
![84
Cr(CO)6
[PtCl6]2-](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/symelem-141006082600-conversion-gate02/75/GROUP-THEORY-SYMMETRY-84-2048.jpg)