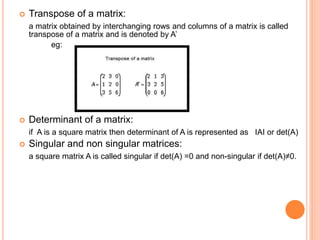
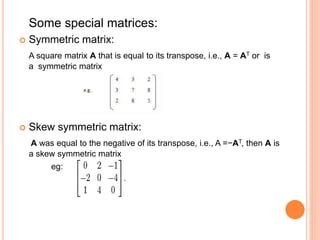
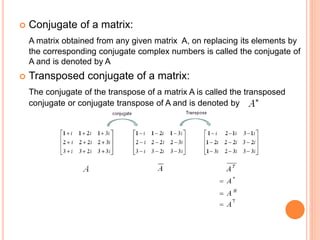
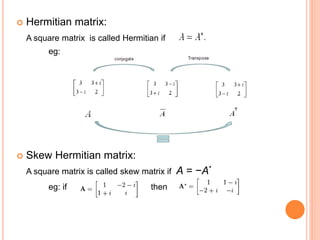
The document presents an overview of matrices, defining various types such as row matrices, column matrices, zero matrices, diagonal matrices, and others, alongside their applications in fields like graph theory and computer graphics. It elaborates on key concepts including the trace, transpose, determinant, singularity, and special types of matrices like symmetric, skew-symmetric, and hermitian matrices. Additionally, it introduces crucial properties of these matrices, such as the conditions for unitary and orthogonal matrices.