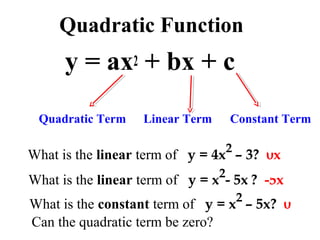
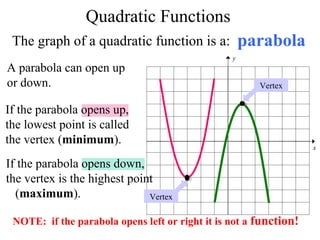
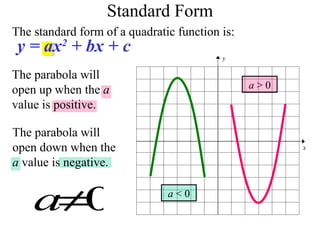
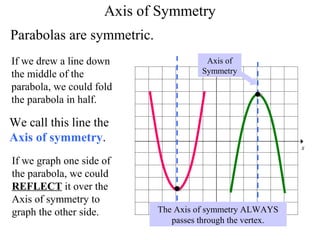
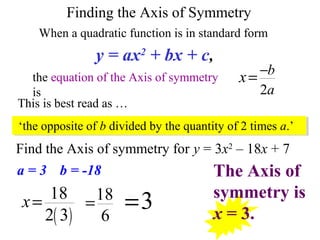
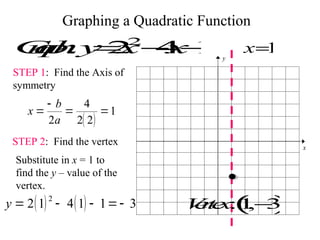
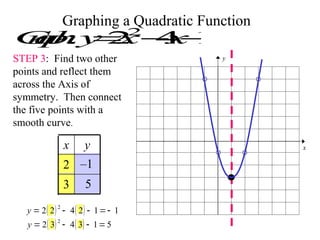
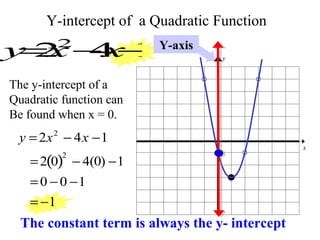
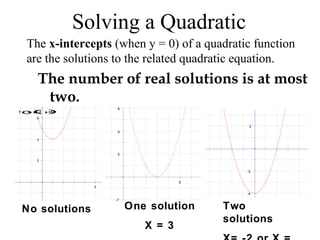
This document provides information about graphing quadratic functions. It defines the standard form of a quadratic function as y = ax^2 + bx + c and explains that the sign of a determines if the parabola opens up or down. It describes how to find the axis of symmetry, vertex, domain and range. The steps to graph a quadratic function are given as finding the axis of symmetry, the vertex, and then two other points to reflect across the axis and connect with a smooth curve. Methods for finding the axis of symmetry, vertex, y-intercept and solutions are demonstrated through examples.