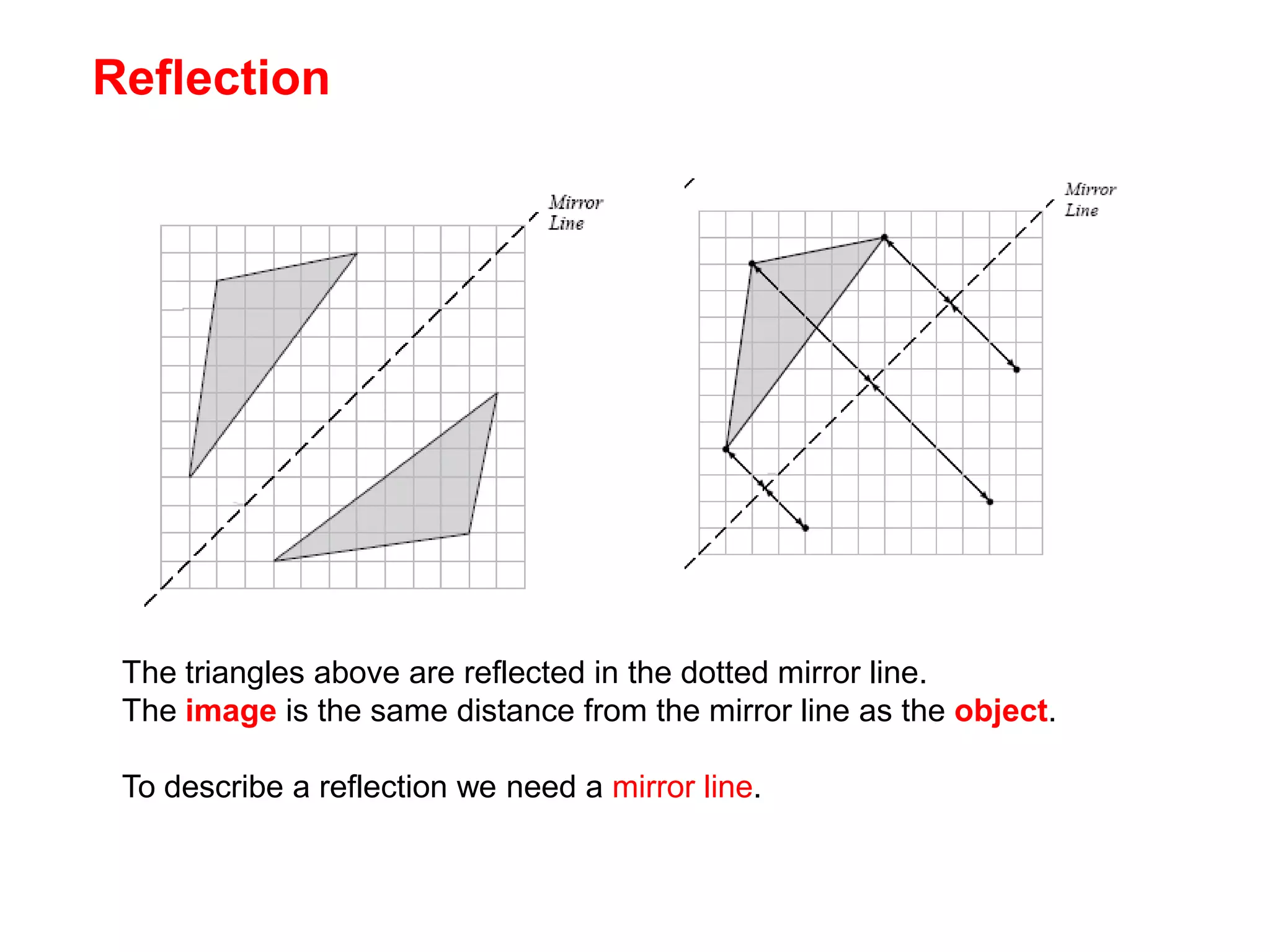
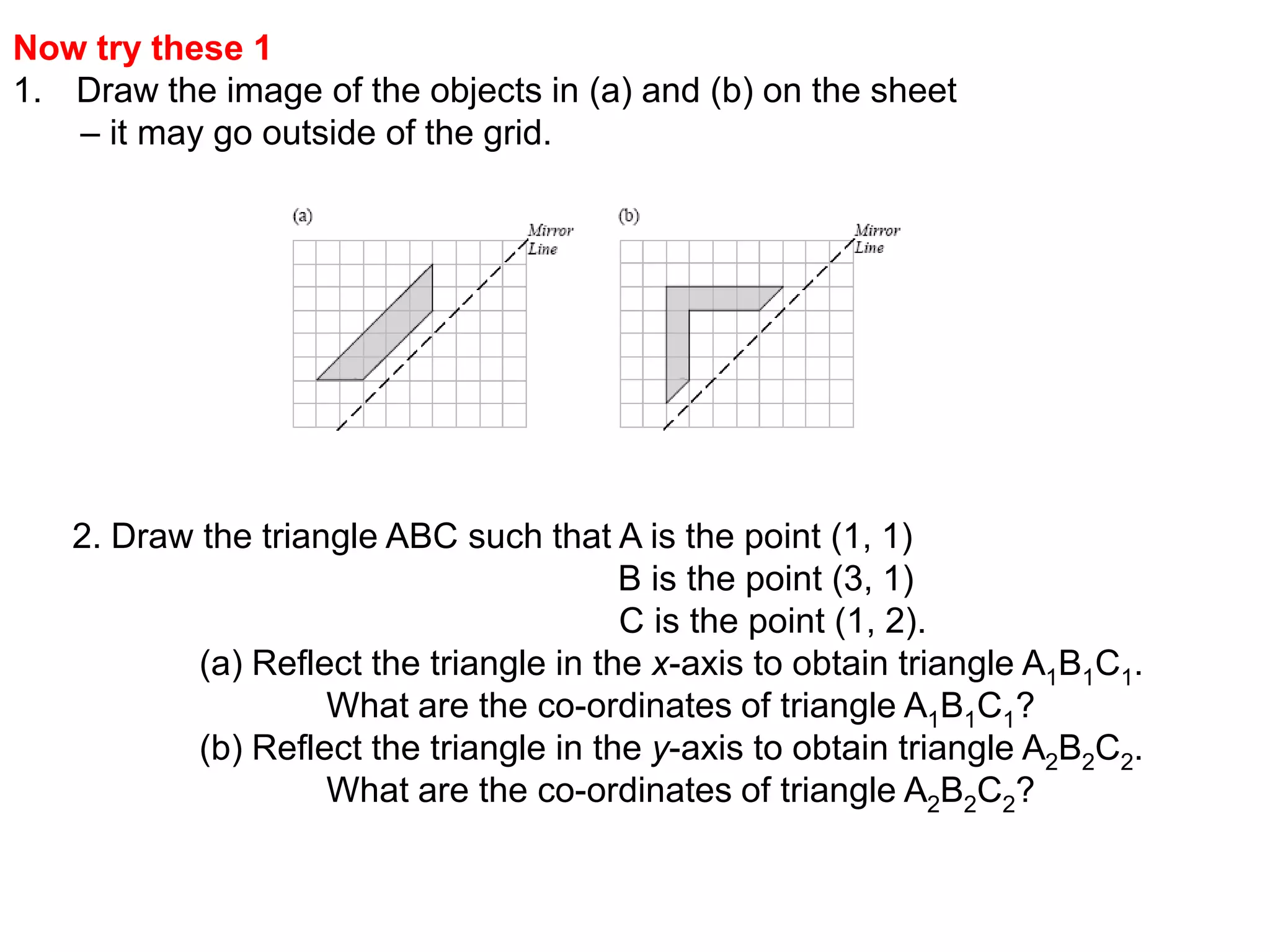
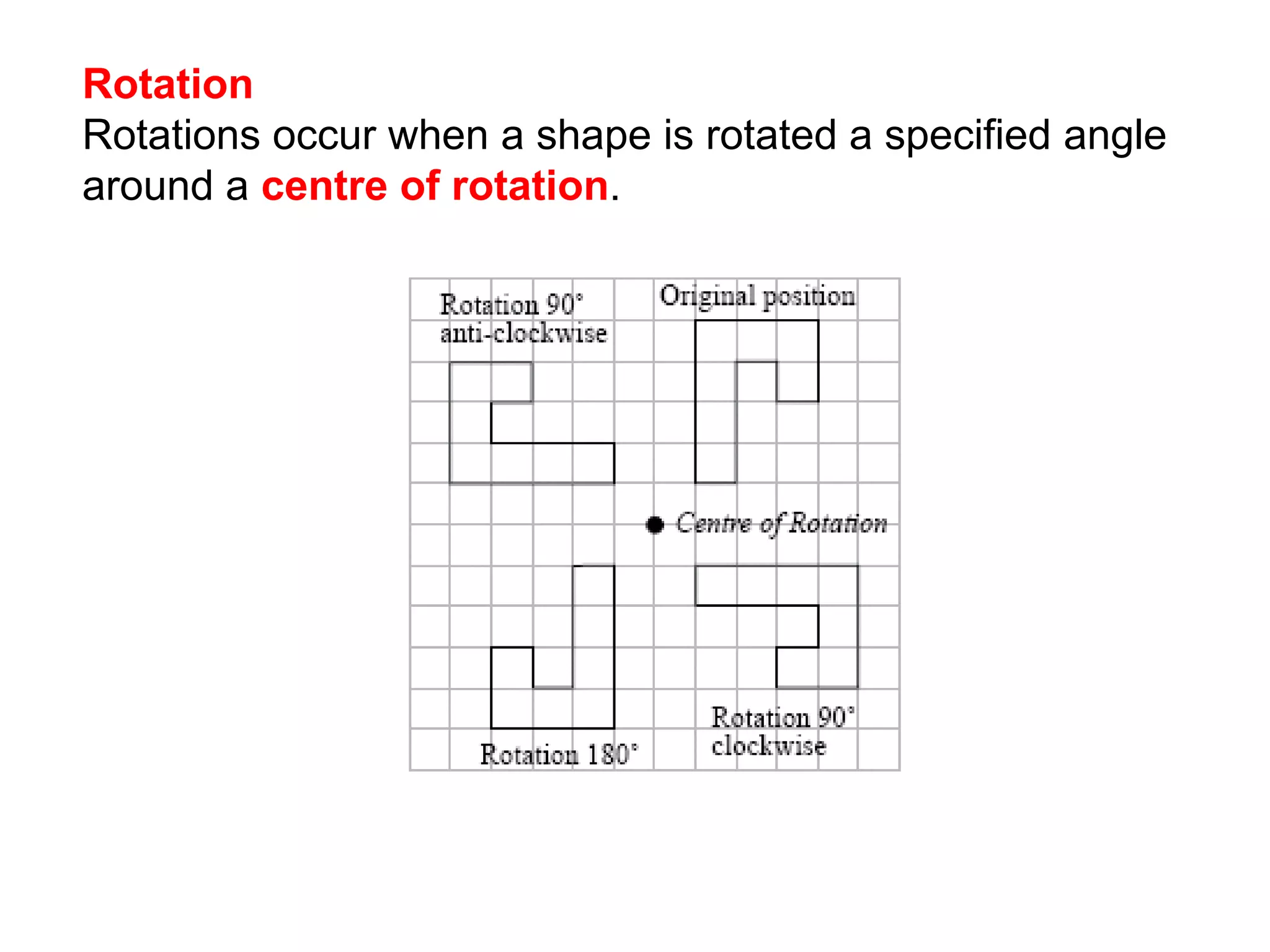
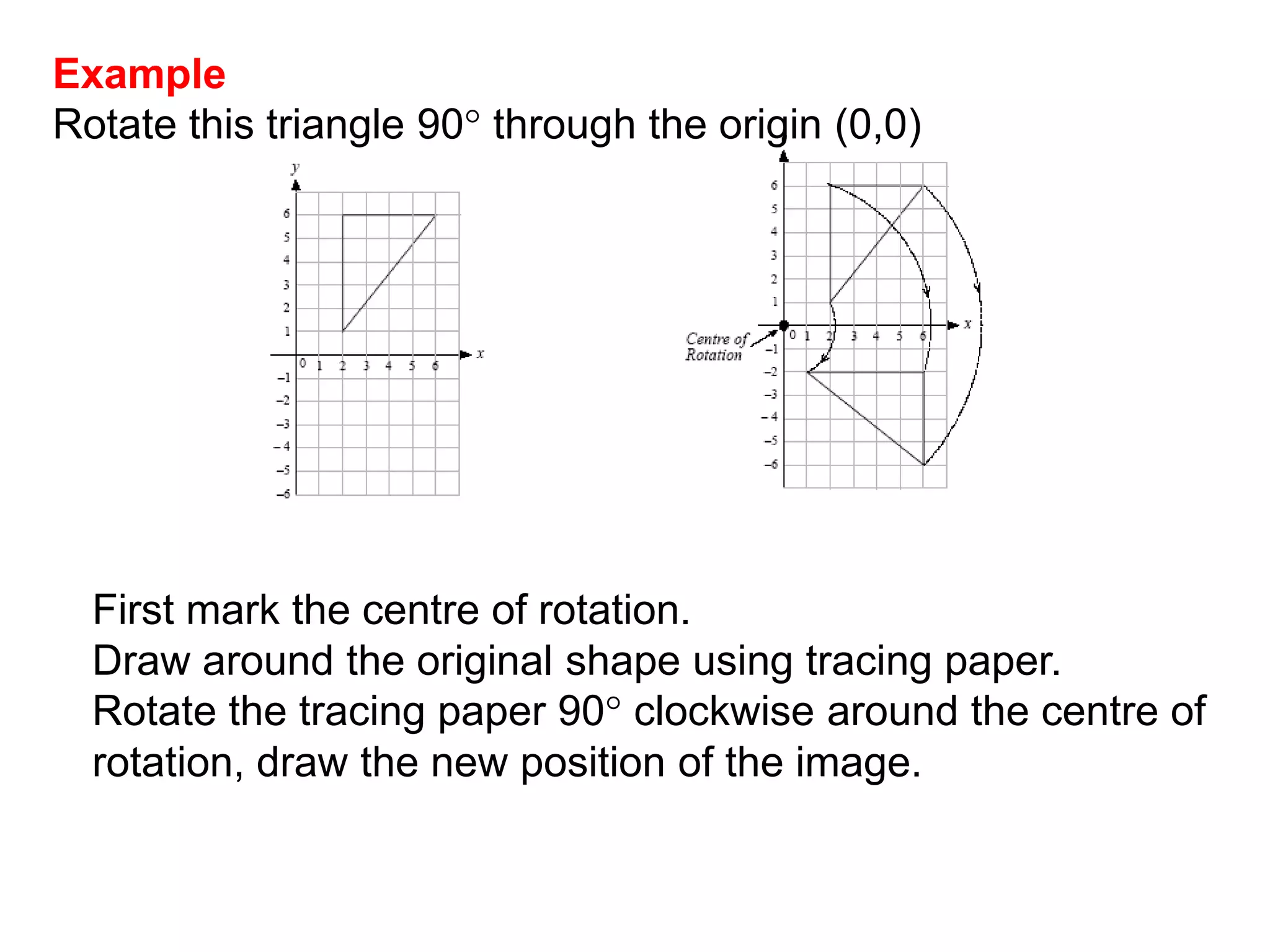
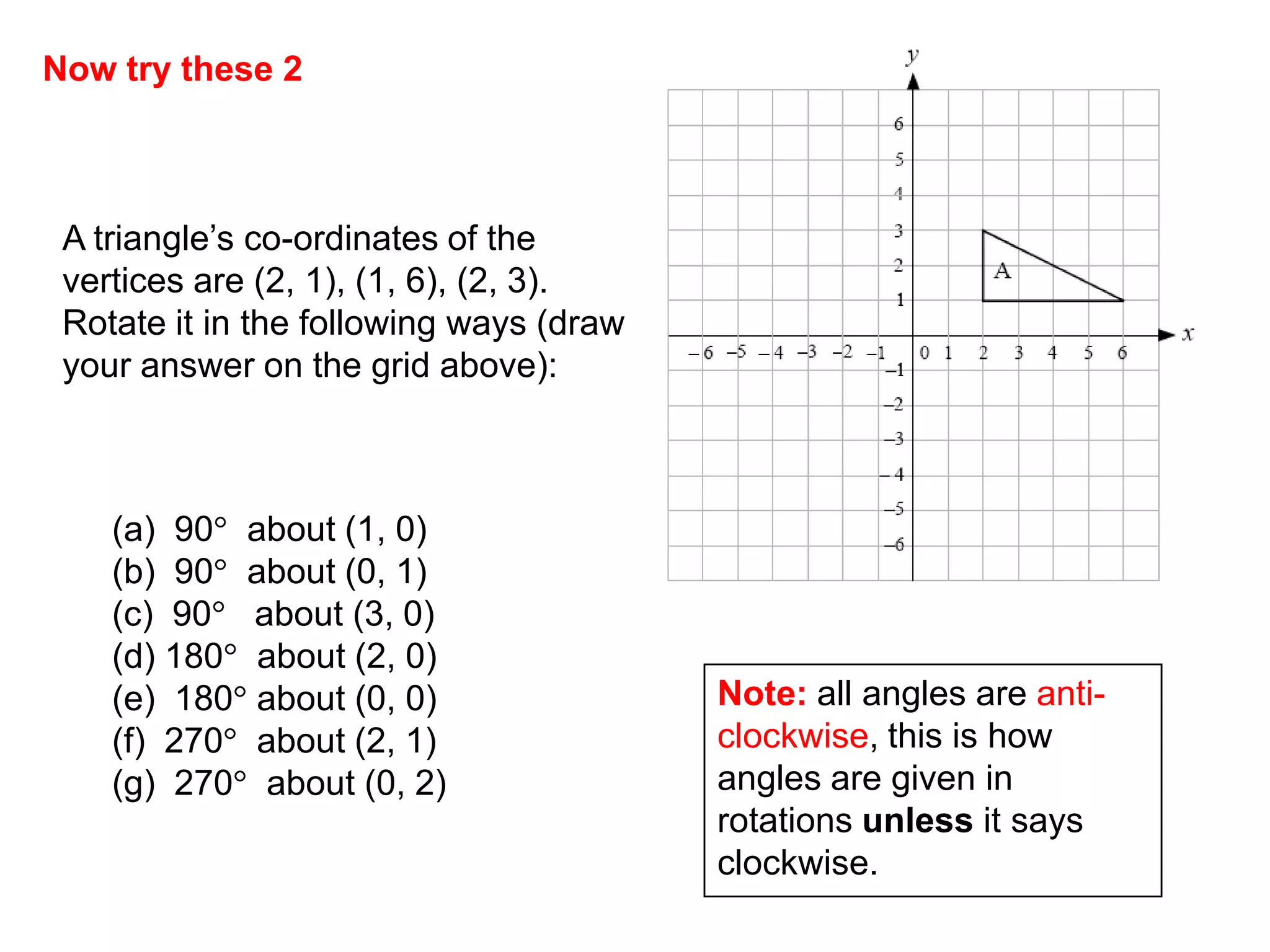
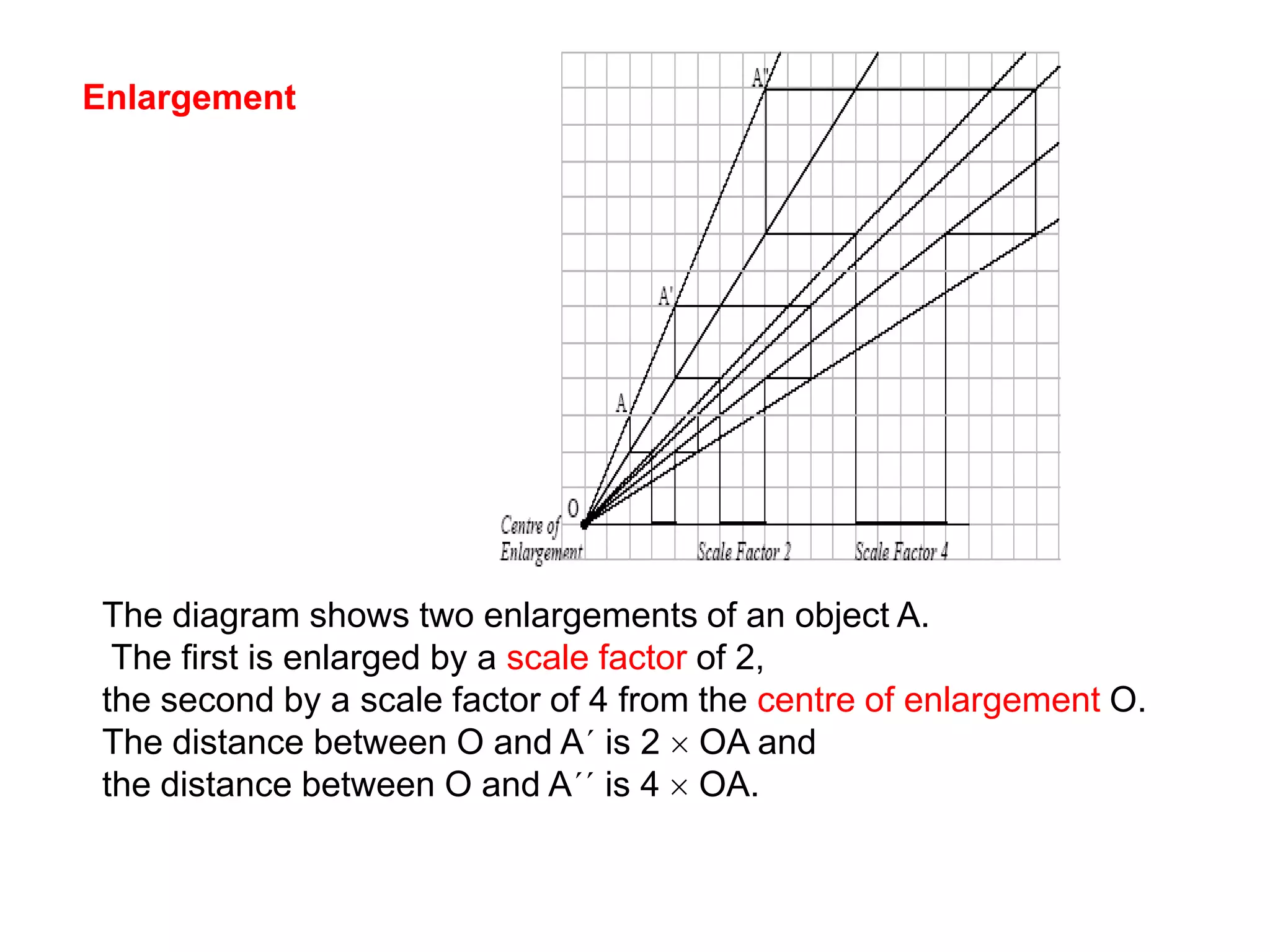
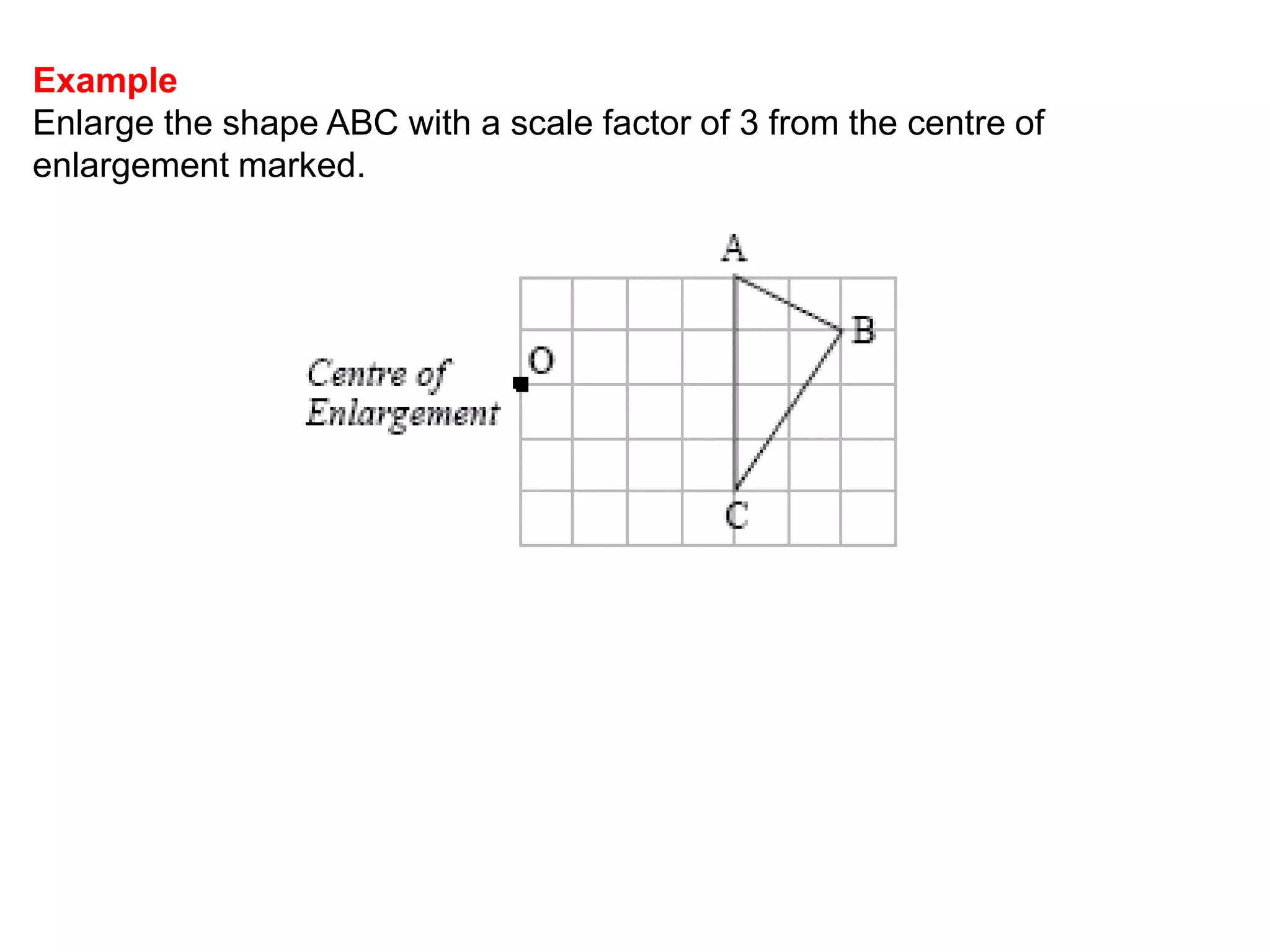
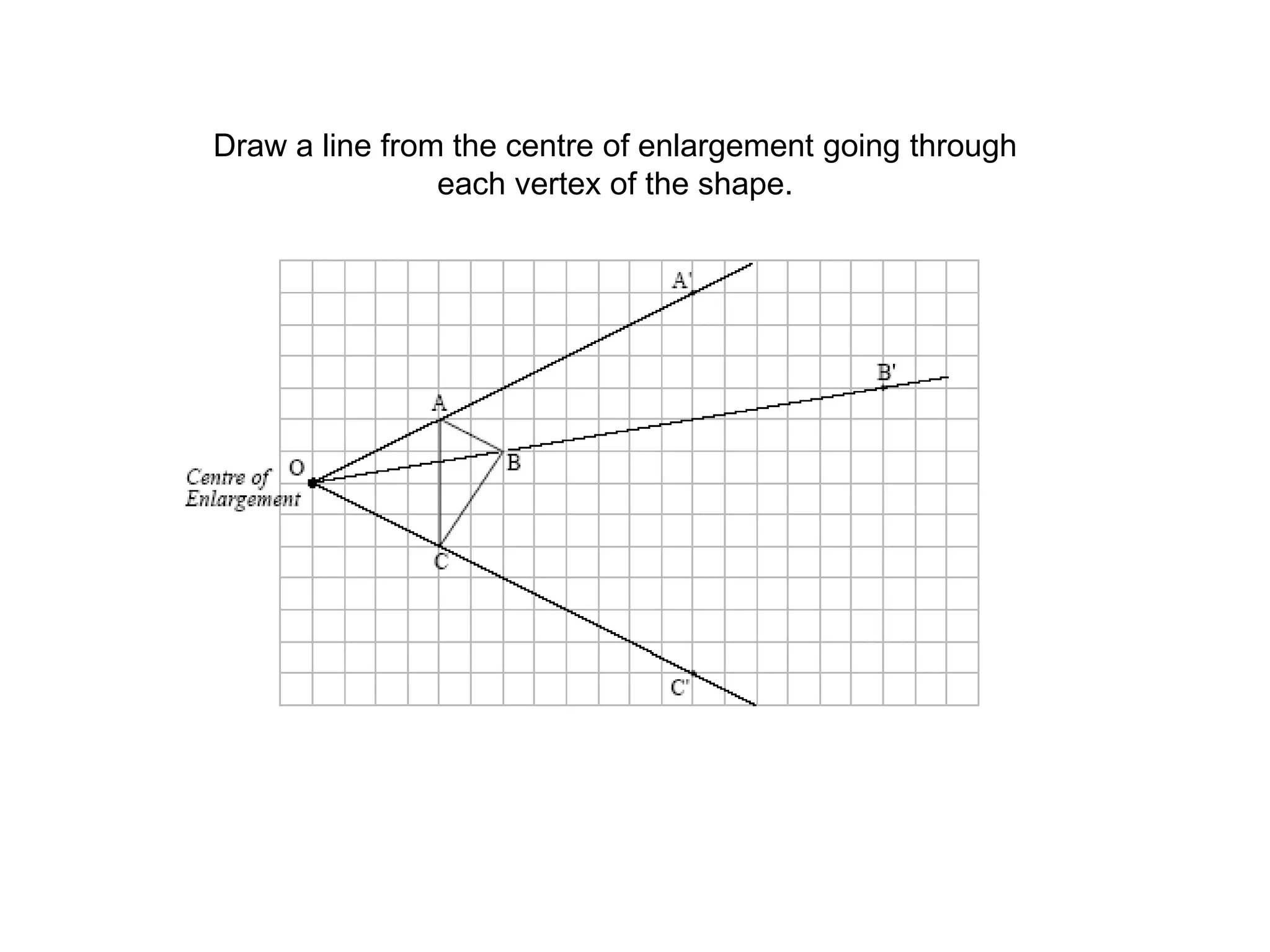
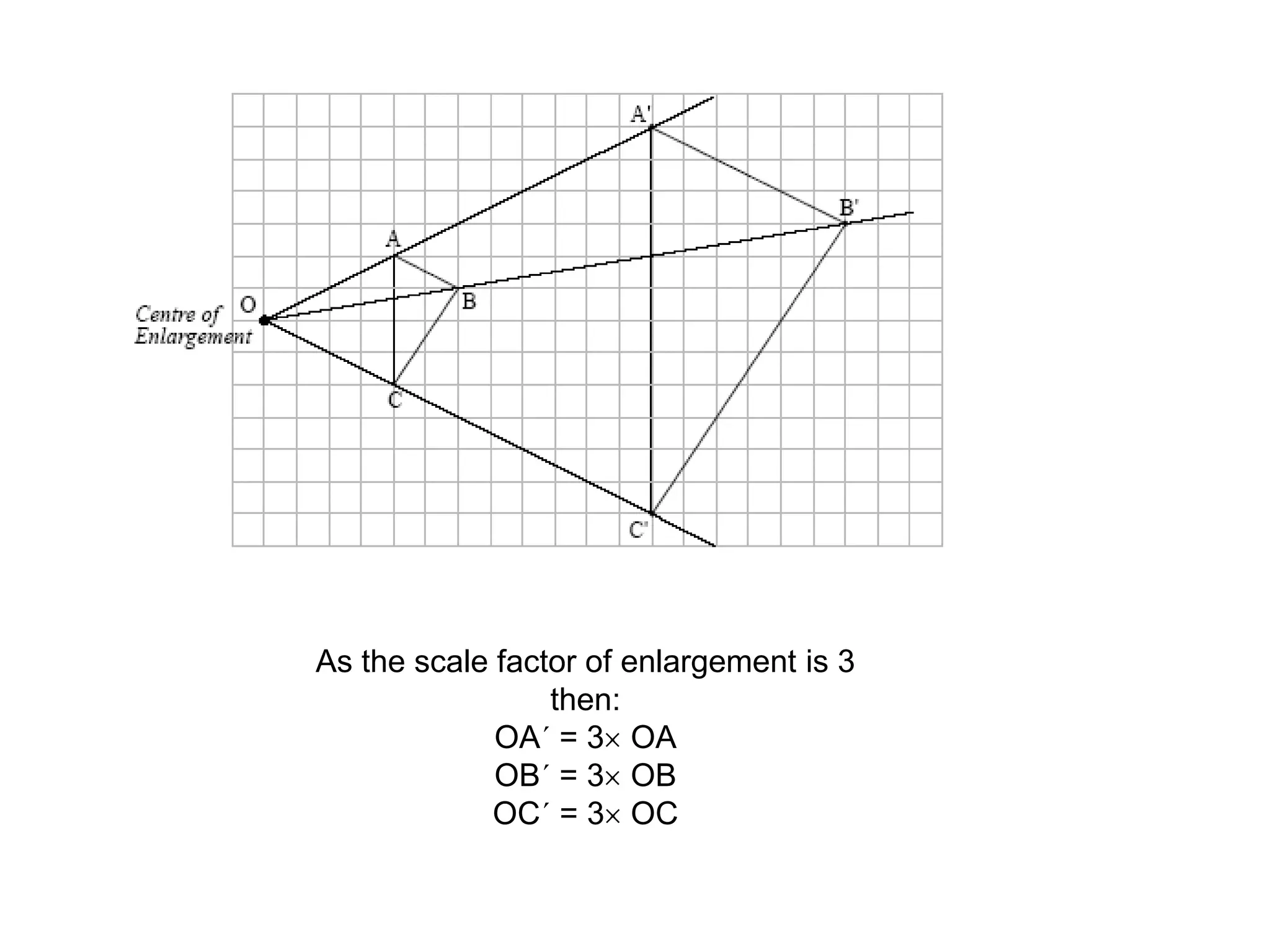
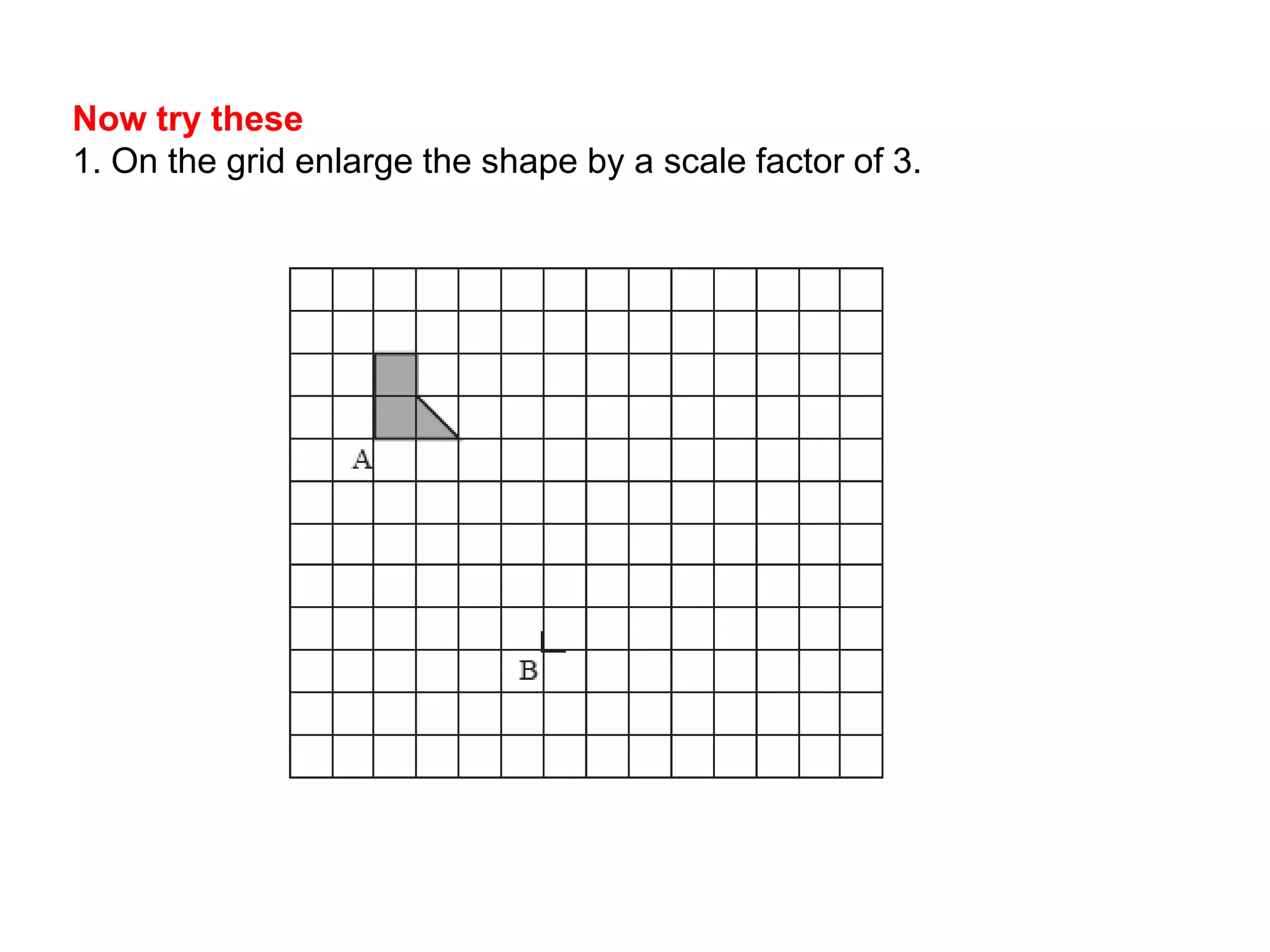
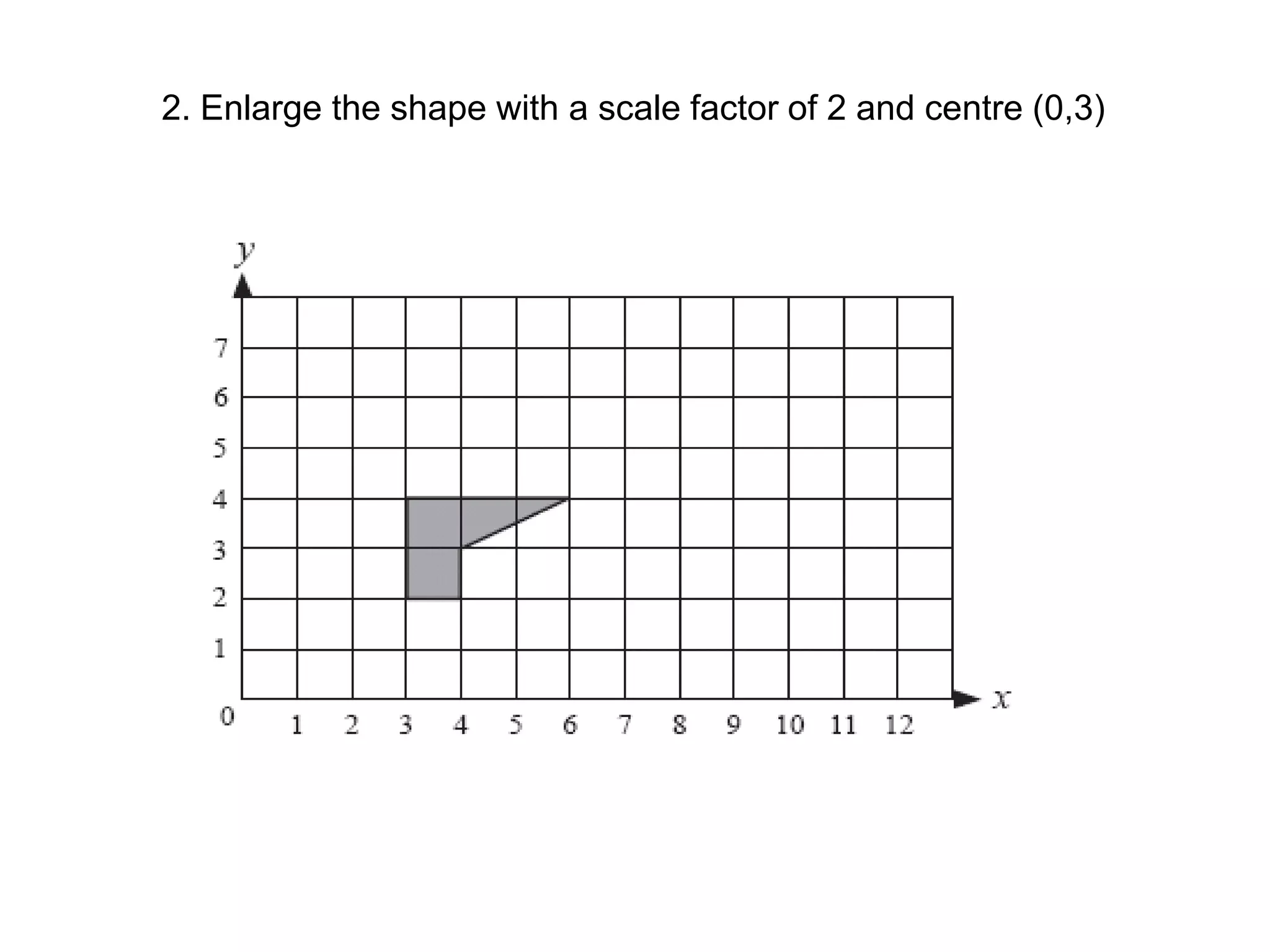
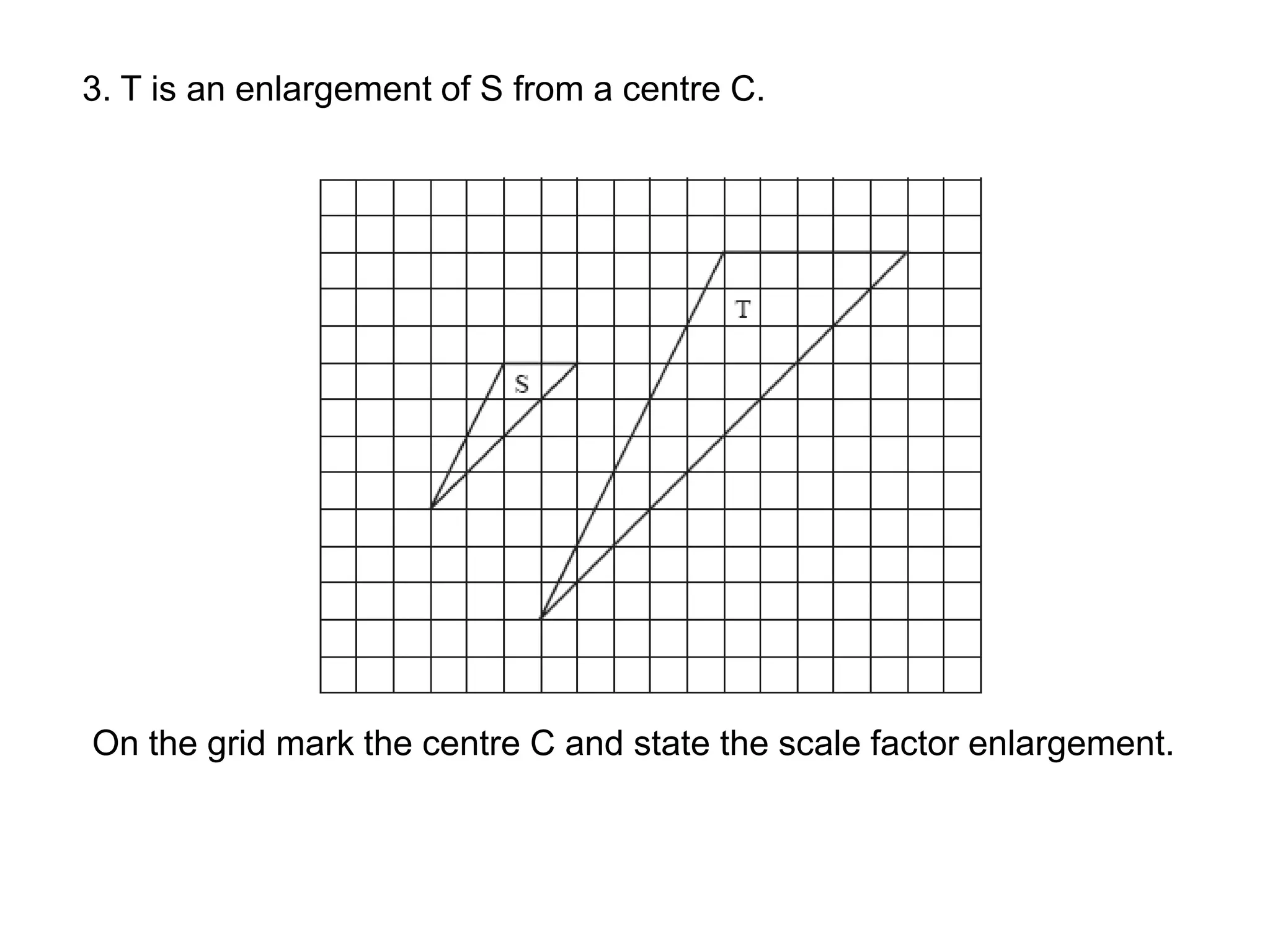
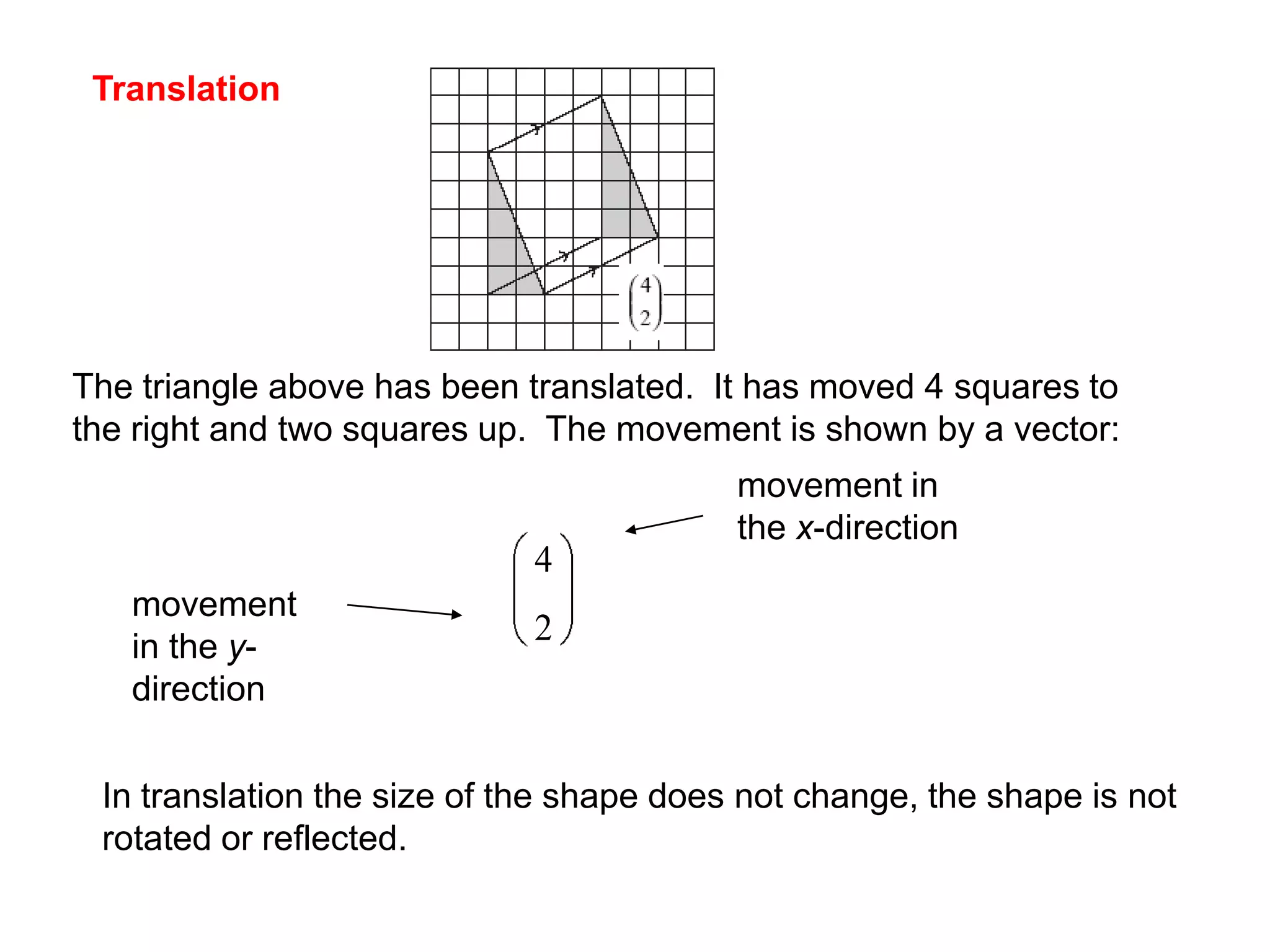
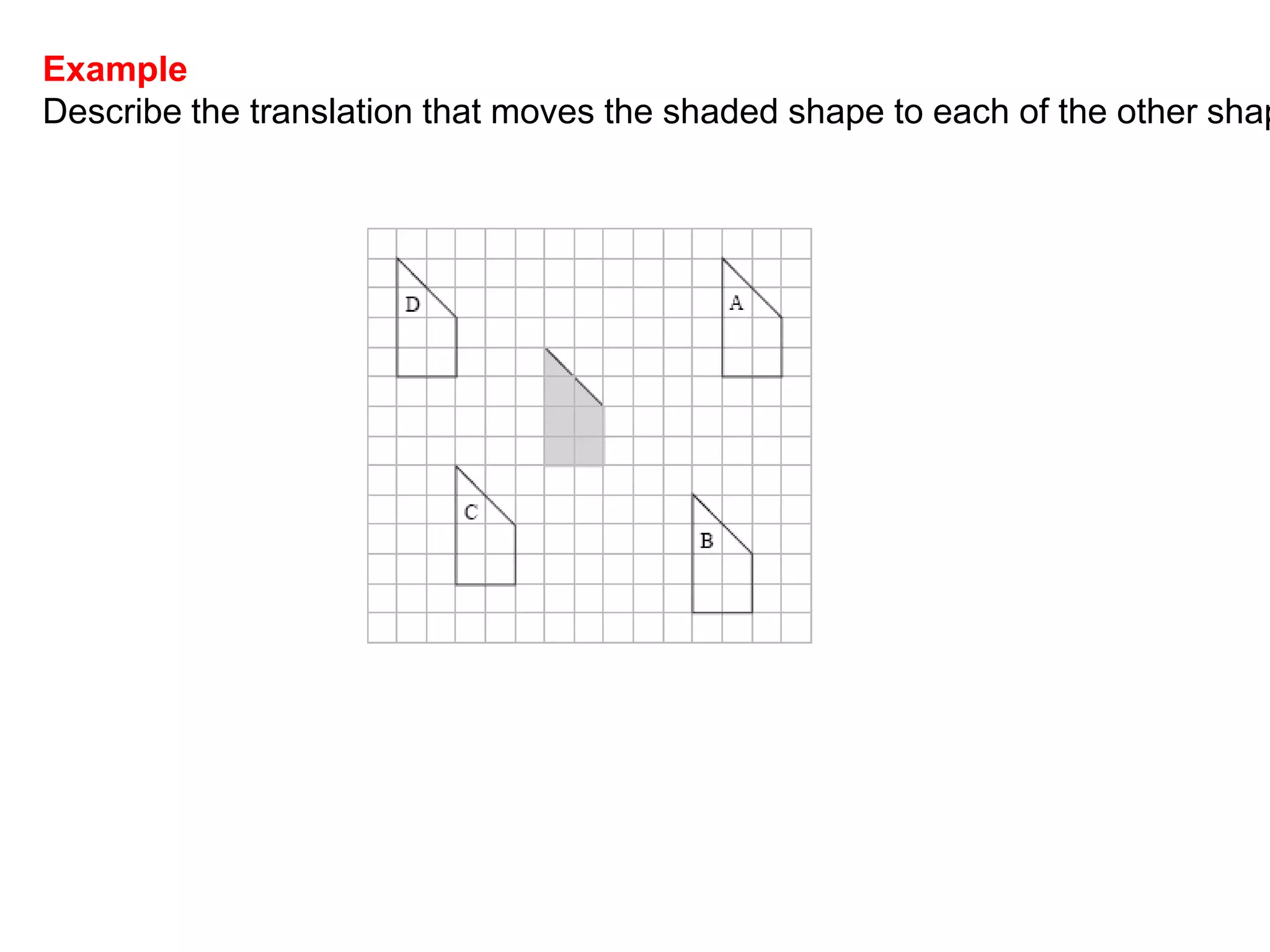
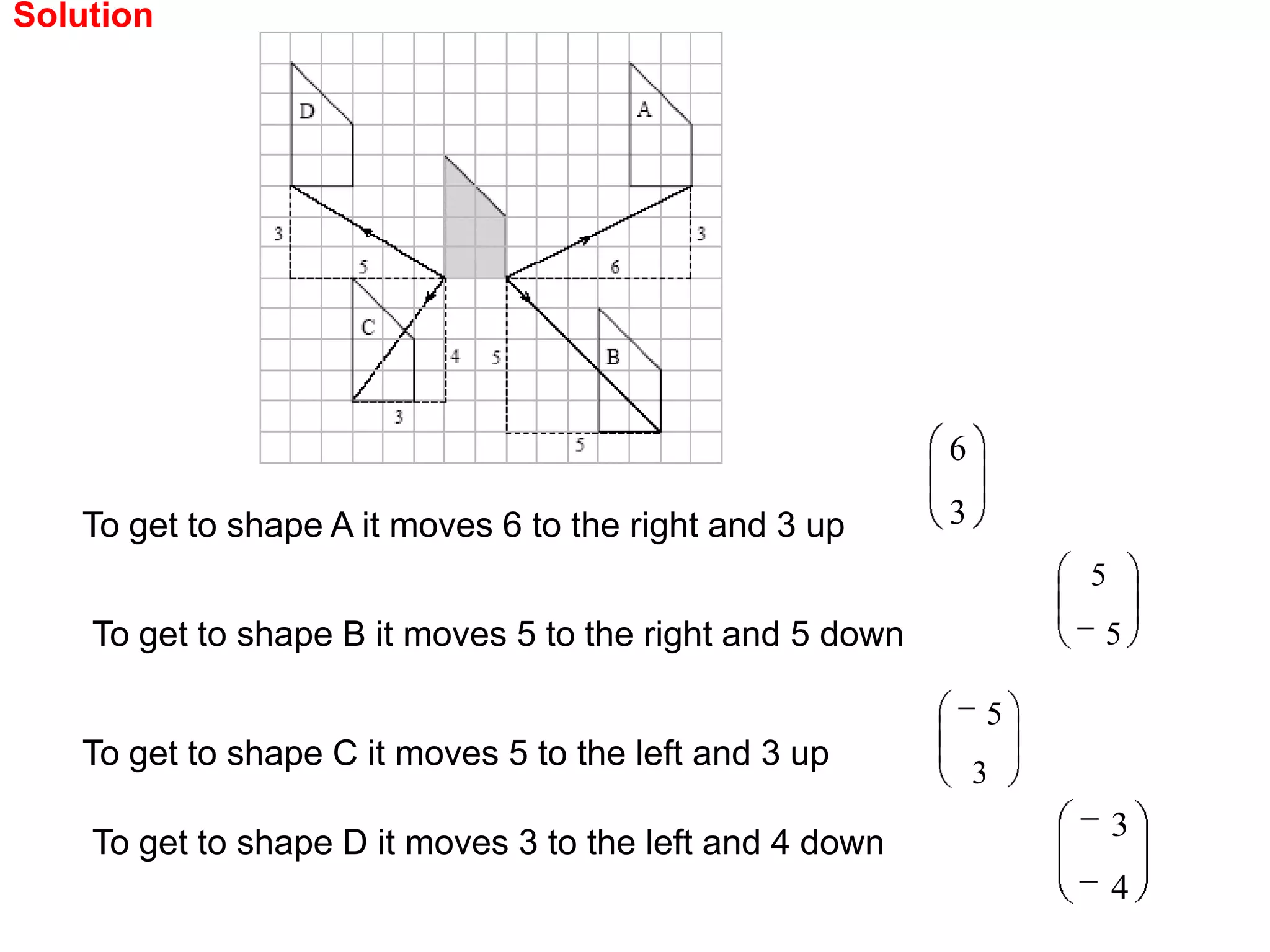
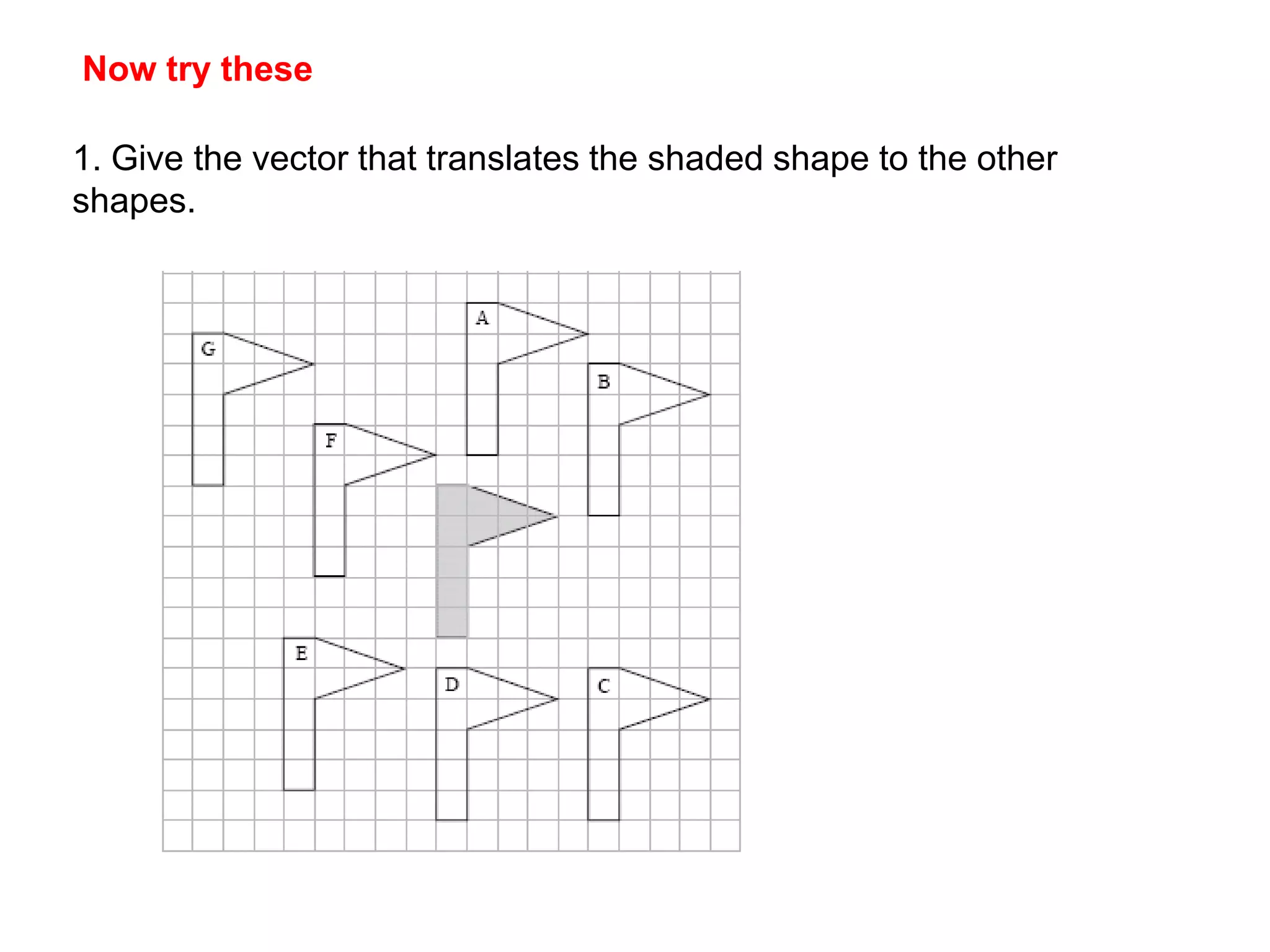
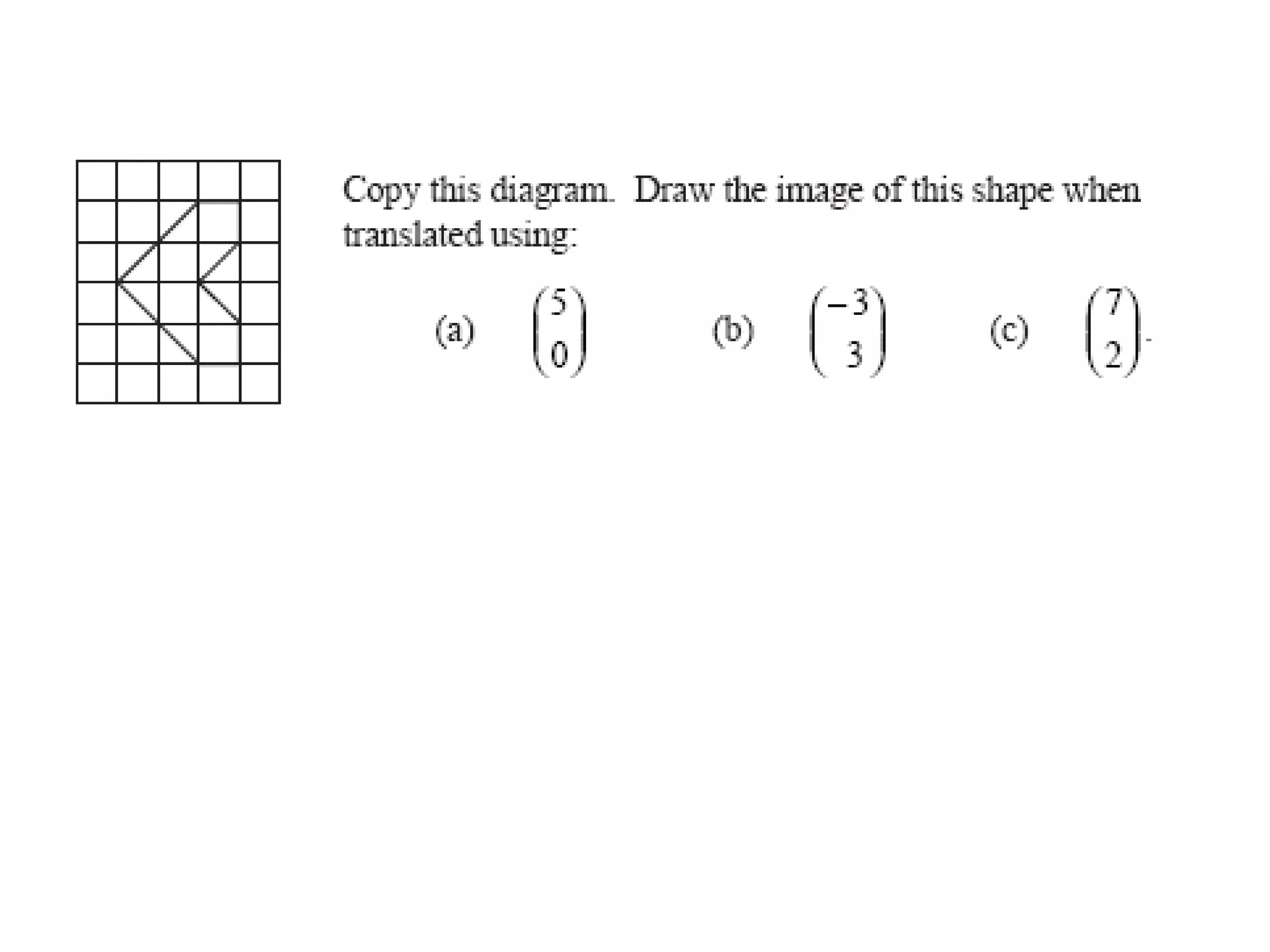
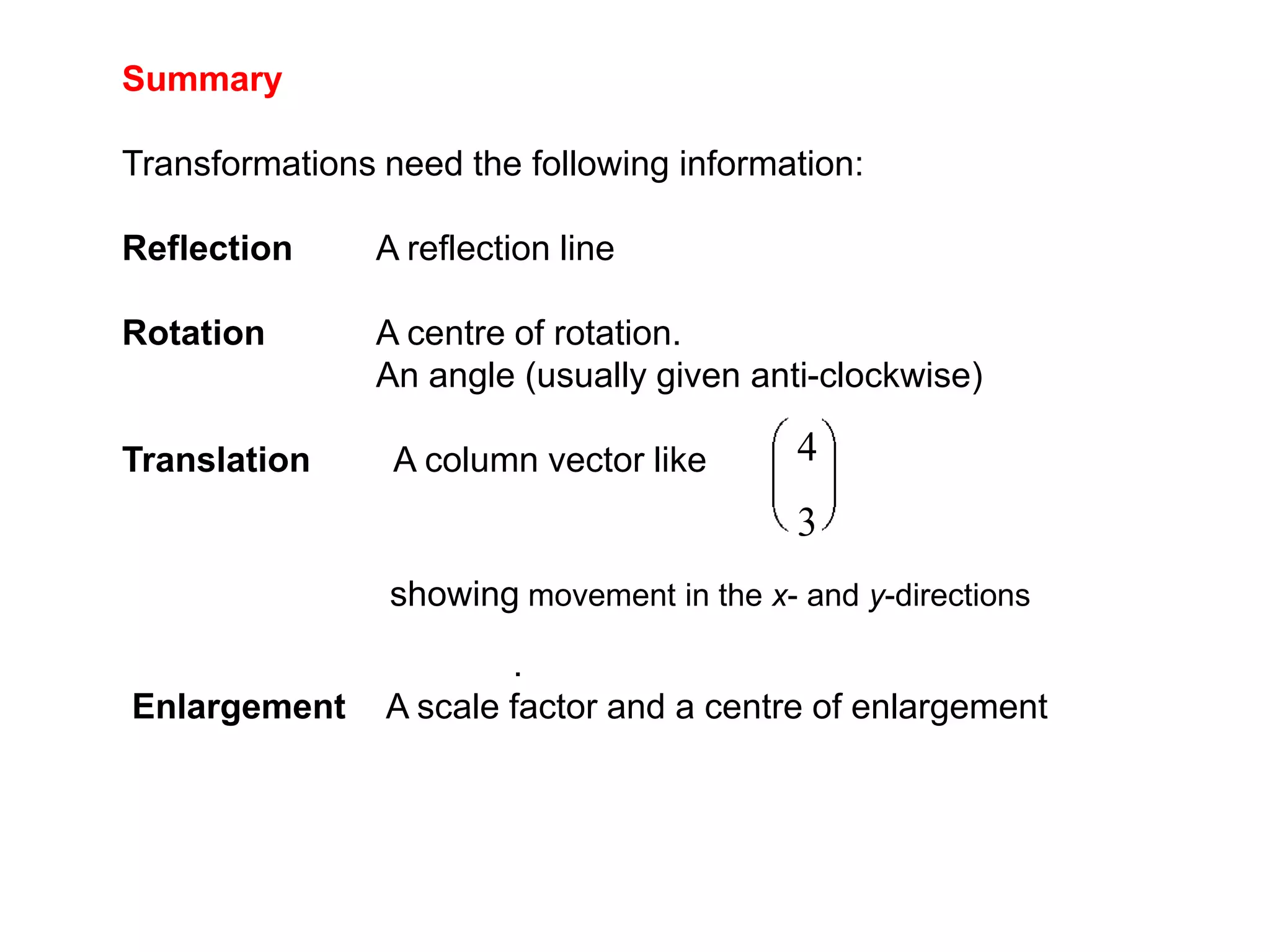
This document discusses different types of geometric transformations including reflections, rotations, translations, and enlargements. It provides examples and explanations of each type of transformation. Reflections require a mirror line and produce a image that is the same distance from the mirror line as the original shape. Rotations occur around a center of rotation when a shape is turned a specified angle. Translations move a shape without changing its size or orientation through a movement described by a vector. Enlargements produce similar shapes that are enlarged or reduced versions of the original through a scale factor from a center of enlargement.