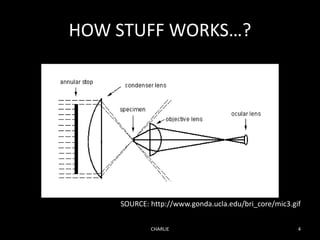
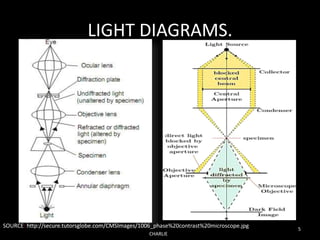
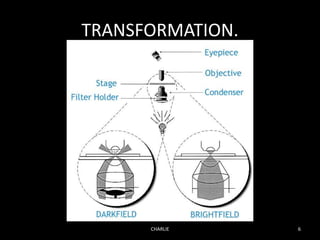
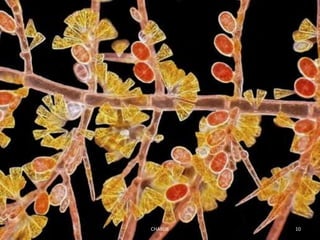
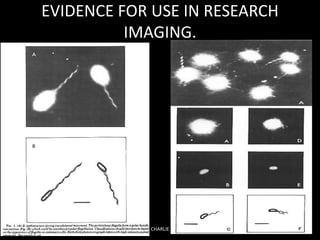
Dark field microscopy is a technique that allows samples to appear brightly lit against a dark background. It works by blocking the transmitted light and only allowing oblique rays to illuminate the specimen. This allows largely transparent and unstained samples to be visible. The document discusses how dark field microscopy works, some inexpensive alternatives to expensive equipment, applications like viewing bacteria and minerals, and advantages like being able to see unstained samples clearly. However, it also has disadvantages like being prone to distortions and requiring careful sample preparation. Evidence is presented for its use in research to image things like functionalized gold nanoparticles targeting cancer cells.