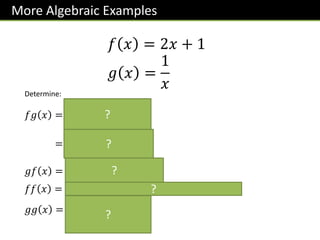
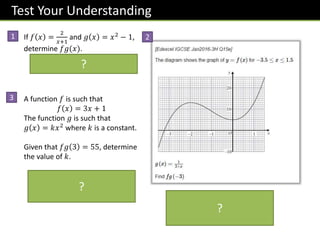
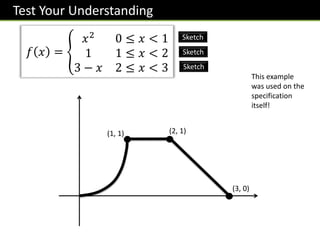
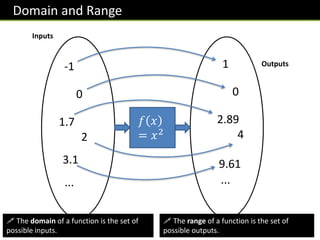
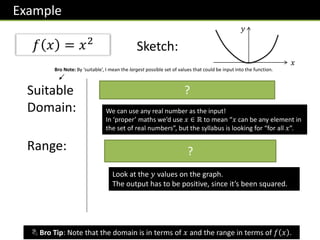
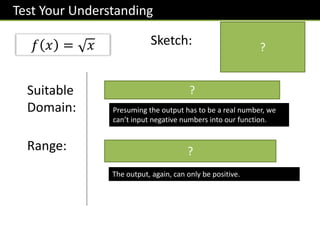
The document provides an overview of functions topics for GCSE/IGCSE mathematics, including understanding functions, inverse functions, composite functions, domain and range of functions, and piecewise functions. It contains examples of different types of functions and exercises for students to practice evaluating functions, finding inverse functions, and solving word problems involving functions. The document is intended to help students learn and teachers teach key concepts related to functions.






![Exercise 1
If 𝑓 𝑥 = 2𝑥 + 5, find:
a) 𝑓 3 = 𝟏𝟏
b) 𝑓 −1 = 𝟑
c) 𝑓
1
2
= 𝟔
If 𝑓 𝑥 = 𝑥2
+ 5, find
a) 𝑓 −1 = 𝟔
b) the possible values of 𝑎 such that
𝑓 𝑎 = 41 𝒂 = ±𝟔
c) The possible values of 𝑘 such that
𝑓 𝑘 = 5.25 𝒌 = ±
𝟏
𝟐
[AQA Worksheet] 𝑓 𝑥 = 2𝑥3
− 250.
Work out 𝑥 when 𝑓 𝑥 = 0
𝟐𝒙𝟑 − 𝟐𝟓𝟎 = 𝟎 → 𝒙 = 𝟓
1
2
(exercises on provided sheet)
[AQA Worksheet] 𝑓 𝑥 = 𝑥2 + 𝑎𝑥 − 8.
If 𝑓 −3 = 13, determine the value of 𝑎.
𝟗 − 𝟑𝒂 − 𝟖 = 𝟏𝟑
𝒂 = −𝟒
If 𝑓 𝑥 = 5𝑥 + 2, determine the
following, simplifying where possible.
a) 𝑓 𝑥 + 1 = 𝟓 𝒙 + 𝟏 + 𝟐 = 𝟓𝒙 + 𝟕
b) 𝑓 𝑥2
= 𝟓𝒙𝟐
+ 𝟐
[AQA IGCSEFM June 2012 Paper 2]
𝑓 𝑥 = 3𝑥 − 5 for all values of 𝑥. Solve
𝑓 𝑥2
= 43
𝟑𝒙𝟐
− 𝟓 = 𝟒𝟑
𝒙 = ±𝟒
3
4
5
6
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gcseandigcsefm-functions-240322124102-36e1ef76/85/Functions-ppt-Dr-Frost-Maths-Mixed-questions-9-320.jpg)
![[AQA Worksheet] 𝑓 𝑥 = 𝑥2 + 3𝑥 − 10
Show that 𝑓 𝑥 + 2 = 𝑥 𝑥 + 7
𝒇 𝒙 + 𝟐 = 𝒙 + 𝟐 𝟐
+ 𝟑 𝒙 + 𝟐 − 𝟏𝟎
= 𝒙𝟐
+ 𝟒𝒙 + 𝟒 + 𝟑𝒙 + 𝟔 − 𝟏𝟎
= 𝒙𝟐
+ 𝟕𝒙 = 𝒙 𝒙 + 𝟕
If 𝑓 𝑥 = 2𝑥 − 1 determine:
(a) 𝑓 2𝑥 = 𝟒𝒙 − 𝟏
(b) 𝑓 𝑥2 = 𝟐𝒙𝟐 − 𝟏
(c) 𝑓 2𝑥 − 1 = 𝟐 𝟐𝒙 − 𝟏 − 𝟏 = 𝟒𝒙 − 𝟑
(d) 𝑓 1 + 2𝑓 𝑥 − 1
= 𝒇 𝟒𝒙 − 𝟓 = 𝟖𝒙 − 𝟏𝟏
(e) Solve 𝑓 𝑥 + 1 + 𝑓 𝑥 − 1 = 0
𝟐 𝒙 + 𝟏 − 𝟏 + 𝟐 𝒙 − 𝟏 − 𝟏 = 𝟎
𝟒𝒙 − 𝟐 = 𝟎 → 𝒙 =
𝟏
𝟐
Exercise 1
7
8
9
N
(exercises on provided sheet)
[Edexcel Specimen Papers Set 1, Paper
2H Q18]
𝑓 𝑥 = 3𝑥2 − 2𝑥 − 8
Express 𝑓 𝑥 + 2 in the form 𝑎𝑥2
+ 𝑏𝑥
𝟑𝒙𝟐
+ 𝟏𝟎𝒙
[Senior Kangaroo 2011 Q20] The
polynomial 𝑓 𝑥 is such that
𝑓 𝑥2
+ 1 = 𝑥4
+ 4𝑥2
and
𝑓 𝑥2
− 1 = 𝑎𝑥4
+ 4𝑏𝑥2
+ 𝑐. What is
the value of 𝑎2
+ 𝑏2
+ 𝑐2
?
𝒇 𝒙𝟐 + 𝟏 = 𝒙𝟐(𝒙𝟐 + 𝟒)
By letting 𝒚 = 𝒙𝟐 + 𝟏:
𝒇 𝒚 = (𝒚 − 𝟏)(𝒚 + 𝟑)
Thus 𝒇 𝒙𝟐 − 𝟏 = 𝒇 𝒚 − 𝟐
= 𝒚 − 𝟑 𝒚 + 𝟏
= 𝒙𝟐 − 𝟐 𝒙𝟐 + 𝟐
= 𝒙𝟒 − 𝟒
𝒂 = 𝟏, 𝒃 = 𝟎, 𝒄 = −𝟒
𝒂𝟐
+ 𝒃𝟐
+ 𝒄𝟐
= 𝟏𝟕
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gcseandigcsefm-functions-240322124102-36e1ef76/85/Functions-ppt-Dr-Frost-Maths-Mixed-questions-10-320.jpg)


![Exercise 2
Find 𝑓−1
(𝑥) for the following functions.
𝑓 𝑥 = 5𝑥 𝒇−𝟏 𝒙 =
𝒙
𝟓
𝑓 𝑥 = 1 + 𝑥 𝒇−𝟏
𝒙 = 𝒙 − 𝟏
𝑓 𝑥 = 6𝑥 − 4 𝒇−𝟏
𝒙 =
𝒙+𝟒
𝟔
𝑓 𝑥 =
𝑥+7
3
𝒇−𝟏 𝒙 = 𝟑𝒙 − 𝟕
𝑓 𝑥 = 5 𝑥 + 1 𝒇−𝟏
𝒙 =
𝒙−𝟏
𝟓
𝟐
𝑓 𝑥 = 10 − 3𝑥 𝒇−𝟏
𝒙 =
𝟏𝟎−𝒙
𝟑
[Edexcel IGCSE Jan2016(R)-3H Q16c]
𝑓 𝑥 =
2𝑥
𝑥 − 1
Find 𝑓−1 𝑥
=
𝒙
𝒙 − 𝟐
Find 𝑓−1
(𝑥) for the following functions.
𝑓 𝑥 =
𝑥
𝑥 + 3
𝒇−𝟏
𝒙 =
𝟑𝒙
𝟏 − 𝒙
𝑓 𝑥 =
𝑥 − 2
𝑥
𝒇−𝟏
𝒙 =
𝟐
𝟏 − 𝒙
𝑓 𝑥 =
2𝑥 − 1
𝑥 − 1
𝒇−𝟏 𝒙 =
𝒙 − 𝟏
𝒙 − 𝟐
𝑓 𝑥 =
1 − 𝑥
3𝑥 + 1
𝒇−𝟏 𝒙 =
𝟏 − 𝒙
𝟑𝒙 + 𝟏
𝑓 𝑥 =
3𝑥
3 + 2𝑥
𝒇−𝟏
𝒙 =
𝟑𝒙
𝟑 − 𝟐𝒙
Find the value of 𝑎 for which 𝑓 𝑥 =
𝑥
𝑥+𝑎
is a self inverse function.
𝒇−𝟏
𝒙 =
𝒂𝒙
𝟏 − 𝒙
If self-inverse:
𝒙
𝒙+𝒂
≡
𝒂𝒙
𝟏−𝒙
𝒂𝒙𝟐 + 𝒂𝟐𝒙 ≡ 𝒙 − 𝒙𝟐
For 𝒙𝟐
and 𝒙 terms to match, 𝒂 = −𝟏.
1 3
N
a
b
c
d
e
f
a
b
c
d
e
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
2
(exercises on provided sheet)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gcseandigcsefm-functions-240322124102-36e1ef76/85/Functions-ppt-Dr-Frost-Maths-Mixed-questions-16-320.jpg)

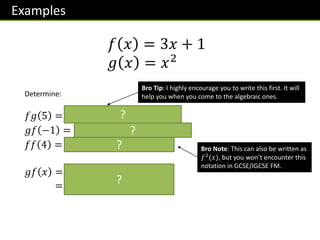
![Exercise 3
If 𝑓 𝑥 = 3𝑥 and 𝑔 𝑥 = 𝑥 + 1, determine:
𝑓𝑔 2 = 𝟗 𝑔𝑓 4 = 𝟏𝟑
𝑓𝑔 𝑥 = 𝟑𝒙 + 𝟑 𝑔𝑓 𝑥 = 𝟑𝒙 + 𝟏
𝑔𝑔 𝑥 = 𝒙 + 𝟐
If 𝑓 𝑥 = 2𝑥 + 1 and 𝑔 𝑥 = 3𝑥 + 1
determine:
𝑓𝑔 𝑥 = 𝟔𝒙 + 𝟑 𝑔𝑓 𝑥 = 𝟔𝒙 + 𝟒
𝑓𝑓 𝑥 = 𝟒𝒙 + 𝟑
If 𝑓 𝑥 = 𝑥2
− 2𝑥 and 𝑔 𝑥 = 𝑥 + 1, find
𝑓𝑔(𝑥), simplifying your expression.
𝒇 𝒙 + 𝟏 = 𝒙 + 𝟏 𝟐
− 𝟐 𝒙 + 𝟏
= 𝒙𝟐
+ 𝟐𝒙 + 𝟏 − 𝟐𝒙 − 𝟐
= 𝒙𝟐
− 𝟏
If 𝑓 𝑥 = 𝑥 + 𝑘 and 𝑔 𝑥 = 𝑥2
and
𝑔𝑓 3 = 16, find the possible values of 𝑘.
𝒈𝒇 𝟑 = 𝒈 𝟑 + 𝒌 = 𝟑 + 𝒌 𝟐
= 𝟏𝟔
𝒌 = 𝟏, −𝟕
If 𝑓 𝑥 = 2(𝑥 + 𝑘) and 𝑔 𝑥 = 𝑥2
− 𝑥 and
𝑓𝑔 3 = 30, find 𝑘.
𝒇 𝒈 𝟑 = 𝒇 𝟔 = 𝟐 𝟔 + 𝒌 = 𝟑𝟎
𝒌 = 𝟗
Let 𝑓 𝑥 = 𝑥 + 1 and 𝑔 𝑥 = 𝑥2
+ 1.
If 𝑔𝑓 𝑥 = 17, determine the possible values of 𝑥.
𝒈𝒇 𝒙 = 𝒙 + 𝟏 𝟐
+ 𝟏 = 𝟏𝟕
𝒙𝟐
+ 𝟐𝒙 + 𝟐 = 𝟏𝟕
𝒙𝟐
+ 𝟐𝒙 − 𝟏𝟓 = 𝟎
𝒙 + 𝟓 𝒙 − 𝟑 = 𝟎
𝒙 = −𝟓 𝒐𝒓 𝒙 = 𝟑
Let 𝑓 𝑥 = 𝑥2
+ 3𝑥 and 𝑔 𝑥 = 𝑥 − 2.
If 𝑓𝑔 𝑥 = 0, determine the possible values of 𝑥.
𝒙 = −𝟏 𝒐𝒓 𝒙 = 𝟐
[Based on MAT question]
𝑓 𝑥 = 𝑥 + 1 and 𝑔 𝑥 = 2𝑥
Let 𝑓𝑛
(𝑥) means that you apply the function 𝑓 𝑛
times.
a) Find 𝑓𝑛
(𝑥) in terms of 𝑥 and 𝑛.
= 𝒙 + 𝒏
b) Note that 𝑔𝑓2
𝑔 𝑥 = 4𝑥 + 4. Find all other
ways of combining 𝑓 and 𝑔 that result in the
function 4𝑥 + 4.
𝒈𝟐
𝒇, 𝒇𝟐
𝒈𝒇𝒈, 𝒇𝟒
𝒈𝟐
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
N
?
(exercises on provided sheet)
?
? ?
?
? ?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gcseandigcsefm-functions-240322124102-36e1ef76/85/Functions-ppt-Dr-Frost-Maths-Mixed-questions-21-320.jpg)

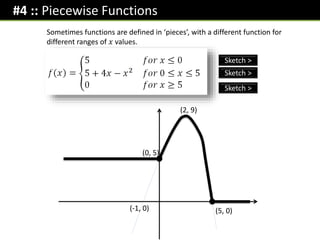
![Exercise 4 (Exercises on provided sheet)
[Jan 2013 Paper 2] A function 𝑓(𝑥) is defined as:
𝑓 𝑥 =
4 𝑥 < −2
𝑥2
−2 ≤ 𝑥 ≤ 2
12 − 4𝑥 𝑥 > 2
(a) Draw the graph of 𝑦 = 𝑓(𝑥) for
−4 ≤ 𝑥 ≤ 4
(b) Use your graph to write down how many
solutions there are to 𝑓 𝑥 = 3 3 sols
(c) Solve 𝑓 𝑥 = −10 𝟏𝟐 − 𝟒𝒙 = −𝟏𝟎 → 𝒙 =
𝟏𝟏
𝟐
[June 2013 Paper 2] A function 𝑓(𝑥) is
defined as:
𝑓 𝑥 =
𝑥 + 3 −3 ≤ 𝑥 < 0
3 0 ≤ 𝑥 < 1
5 − 2𝑥 1 ≤ 𝑥 ≤ 2
Draw the graph of 𝑦 = 𝑓(𝑥) for
−3 ≤ 𝑥 < 2
a ?
b ?
c ?
1 2
?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gcseandigcsefm-functions-240322124102-36e1ef76/85/Functions-ppt-Dr-Frost-Maths-Mixed-questions-25-320.jpg)
![[Set 1 Paper 1] A function 𝑓(𝑥) is defined as:
𝑓 𝑥 =
3 0 ≤ 𝑥 < 2
𝑥 + 1 2 ≤ 𝑥 < 4
9 − 𝑥 4 ≤ 𝑥 ≤ 9
Draw the graph of 𝑦 = 𝑓(𝑥) for 0 ≤ 𝑥 ≤ 9.
Exercise 4 (Exercises on provided sheet)
[Specimen 1 Q4] A function 𝑓(𝑥) is
defined as:
𝑓 𝑥 =
3𝑥 0 ≤ 𝑥 < 1
3 1 ≤ 𝑥 < 3
12 − 3𝑥 3 ≤ 𝑥 ≤ 4
Calculate the area enclosed by the
graph of 𝑦 = 𝑓 𝑥 and the 𝑥 −axis.
3 4
Area = 𝟗
? Sketch ?
?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gcseandigcsefm-functions-240322124102-36e1ef76/85/Functions-ppt-Dr-Frost-Maths-Mixed-questions-26-320.jpg)
![Exercise 4 (Exercises on provided sheet)
[AQA Worksheet Q9]
𝑓 𝑥 =
−𝑥2
0 ≤ 𝑥 < 2
−4 2 ≤ 𝑥 < 3
2𝑥 − 10 3 ≤ 𝑥 ≤ 5
Draw the graph of 𝑓(𝑥) from 0 ≤ 𝑥 ≤ 5.
[AQA Worksheet Q10]
𝑓 𝑥 =
2𝑥 0 ≤ 𝑥 < 1
3 − 𝑥 1 ≤ 𝑥 < 4
𝑥 − 7
3
4 ≤ 𝑥 ≤ 7
Show that 𝑎𝑟𝑒𝑎 𝑜𝑓 𝐴: 𝑎𝑟𝑒𝑎 𝑜𝑓 𝐵 =
3: 2
Area of 𝑨 =
𝟏
𝟐
× 𝟑 × 𝟐 = 𝟑
Area of 𝑩 =
𝟏
𝟐
× 𝟒 × 𝟏 = 𝟐
5 6
-1
-2
-3
-4
1 2 3 4 5 3
2
-1
7
?
?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gcseandigcsefm-functions-240322124102-36e1ef76/85/Functions-ppt-Dr-Frost-Maths-Mixed-questions-27-320.jpg)

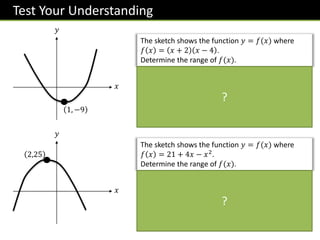

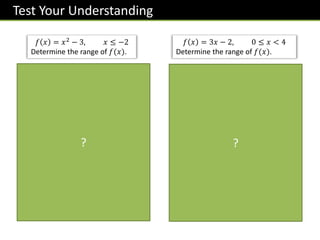
![Exercise 5
Work out the range for each of these
functions.
(a) 𝑓 𝑥 = 𝑥2
+ 6 for all 𝑥
𝒇 𝒙 ≥ 𝟔
(b) 𝑓 𝑥 = 3𝑥 − 5, −2 ≤ 𝑥 ≤ 6
−𝟏𝟏 ≤ 𝒇 𝒙 ≤ 𝟏𝟑
(c) 𝑓 𝑥 = 3𝑥4, 𝑥 < −2
𝒇 𝒙 > 𝟒𝟖
(a) 𝑓 𝑥 =
𝑥+2
𝑥−3
Give a reason why 𝑥 > 0 is not a suitable
domain for 𝑓(𝑥).
It would include 3, for which 𝒇(𝒙) is
undefined.
(b) Give a possible domain for
𝑓 𝑥 = 𝑥 − 5 𝒙 ≥ 𝟓
𝑓 𝑥 = 3 − 2𝑥, 𝑎 < 𝑥 < 𝑏
The range of 𝑓(𝑥) is −5 < 𝑓 𝑥 < 5
Work out 𝑎 and 𝑏.
𝒂 = −𝟏, 𝒃 = 𝟒
[Set 1 Paper 2] (a) The function 𝑓(𝑥) is
defined as:
𝑓 𝑥 = 22 − 7𝑥, −2 ≤ 𝑥 ≤ 𝑝
The range of 𝑓(𝑥) is −13 ≤ 𝑓 𝑥 ≤ 36
Work out the value of 𝑝.
𝒑 = 𝟓
(b) The function 𝑔(𝑥) is defined as
𝑔 𝑥 = 𝑥2
− 4𝑥 + 5 for all 𝑥.
(i) Express 𝑔(𝑥) in the form 𝑥 − 𝑎 2
+ 𝑏
𝒈 𝒙 = 𝒙 − 𝟐 𝟐
+ 𝟏
(ii) Hence write down the range of 𝑔(𝑥).
𝒈 𝒙 ≥ 𝟏
[June 2012 Paper 1] 𝑓 𝑥 = 2𝑥2 + 7 for
all values of 𝑥.
(a) What is the value of 𝑓 −1 ?
𝒇 −𝟏 = 𝟗
(b) What is the range of 𝑓(𝑥)?
𝒇 𝒙 ≥ 𝟕
1
2
3
4
5
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
(exercises on provided sheet)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gcseandigcsefm-functions-240322124102-36e1ef76/85/Functions-ppt-Dr-Frost-Maths-Mixed-questions-39-320.jpg)
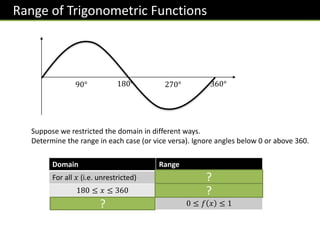
![Exercise 5
[Jan 2013 Paper 2]
𝑓 𝑥 = sin 𝑥 180° ≤ 𝑥 ≤ 360°
𝑔 𝑥 = cos 𝑥 0° ≤ 𝑥 ≤ 𝜃
(a) What is the range of 𝑓(𝑥)?
−𝟏 ≤ 𝒇 𝒙 ≤ 𝟎
(b) You are given that 0 ≤ 𝑔 𝑥 ≤ 1.
Work out the value of 𝜃.
𝜽 = 𝟗𝟎°
By completing the square or otherwise,
determine the range of the following
functions:
(a) 𝑓 𝑥 = 𝑥2
− 2𝑥 + 5, for all 𝑥
= 𝒙 − 𝟏 𝟐
+ 𝟒
Range: 𝒇 𝒙 ≥ 𝟒
(b) 𝑓 𝑥 = 𝑥2
+ 6𝑥 − 2, for all 𝑥
= 𝒙 + 𝟑 𝟐 − 𝟏𝟏
Range: 𝒇 𝒙 ≥ −𝟏𝟏
6
7
8
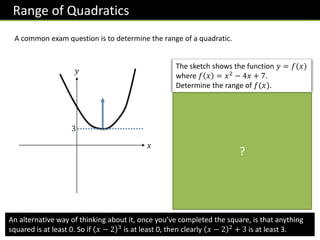
Here is a sketch of
𝑓 𝑥 = 𝑥2 + 6𝑥 + 𝑎 for all 𝑥,
where 𝑎 is a constant. The range
of 𝑓(𝑥) is 𝑓 𝑥 ≥ 11. Work out
the value of 𝑎.
𝒇 𝒙 = 𝒙 + 𝟑 𝟐 − 𝟗 + 𝒂
−𝟗 + 𝒂 = 𝟏𝟏
𝒂 = 𝟐𝟎
?
?
?
?
?
(exercises on provided sheet)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gcseandigcsefm-functions-240322124102-36e1ef76/85/Functions-ppt-Dr-Frost-Maths-Mixed-questions-40-320.jpg)
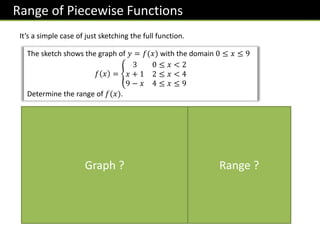
![Exercise 5
The function 𝑓(𝑥) is defined as:
𝑓 𝑥 = 𝑥2
− 4 0 ≤ 𝑥 < 3
14 − 3𝑥 3 ≤ 𝑥 ≤ 5
Work out the range of 𝑓 𝑥 .
𝒇(𝒙) ≤ 𝟓
The function 𝑓(𝑥) has the domain
−3 ≤ 𝑥 ≤ 3 and is defined as:
𝑓 𝑥 = 𝑥2
+ 3𝑥 + 2 −3 ≤ 𝑥 < 0
2 + 𝑥 0 ≤ 𝑥 ≤ 3
Work out the range of 𝑓 𝑥 .
−
𝟏
𝟒
≤ 𝒇 𝒙 ≤ 𝟓
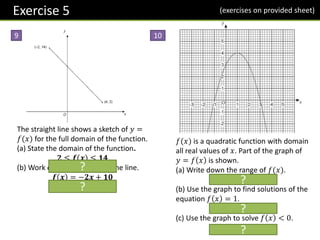
[June 2012 Paper 2] A sketch of 𝑦 =
𝑔(𝑥) for domain 0 ≤ 𝑥 ≤ 8 is shown.
The graph is symmetrical about 𝑥 = 4.
The range of 𝑔(𝑥) is 0 ≤ 𝑔 𝑥 ≤ 12.
Work out the function 𝑔(𝑥).
𝑔 𝑥 =
? 0 ≤ 𝑥 ≤ 4
? 4 < 𝑥 ≤ 8
𝒈 𝒙 =
𝟑𝒙 𝟎 ≤ 𝒙 ≤ 𝟒
𝟐𝟒 − 𝟑𝒙 𝟒 < 𝒙 ≤ 𝟖
11 13
12
?
?
?
(exercises on provided sheet)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gcseandigcsefm-functions-240322124102-36e1ef76/85/Functions-ppt-Dr-Frost-Maths-Mixed-questions-42-320.jpg)