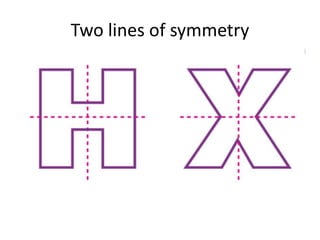
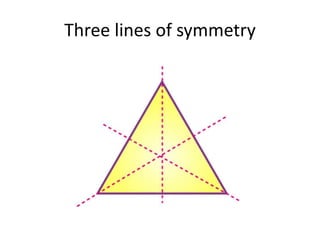
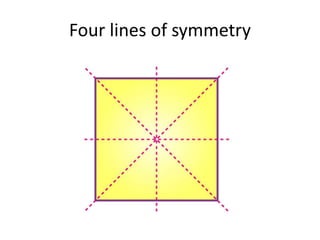
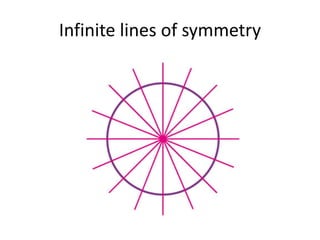
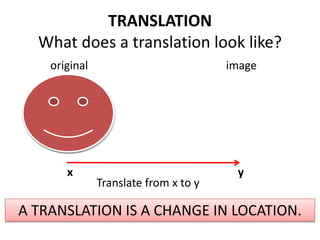
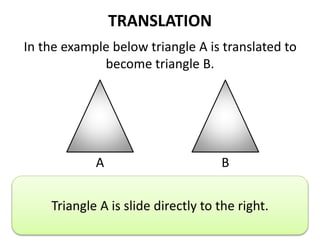
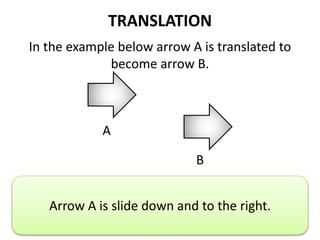
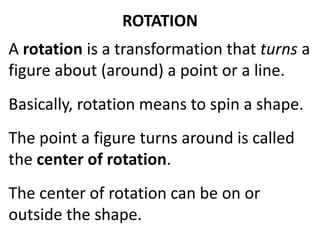
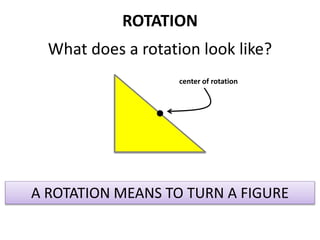
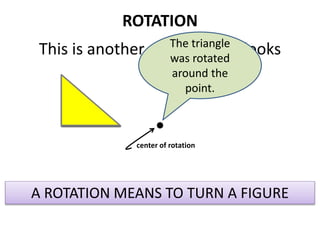
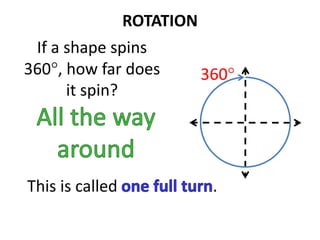
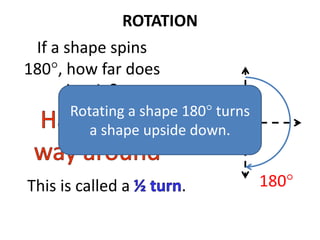
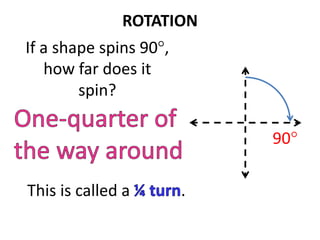
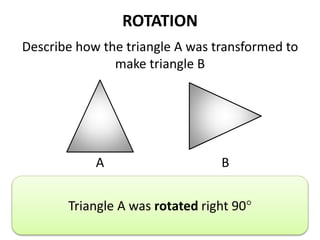
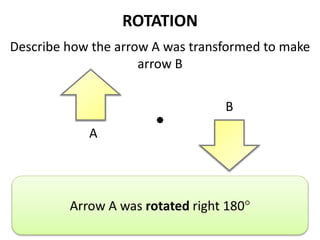
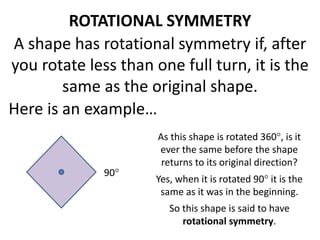
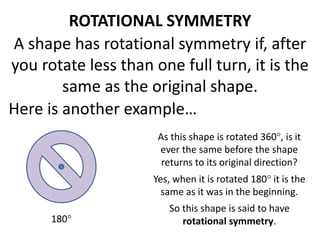
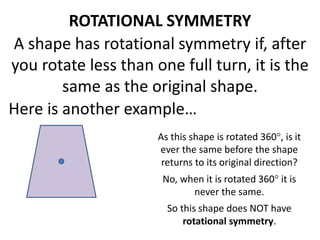
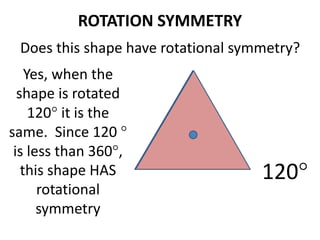
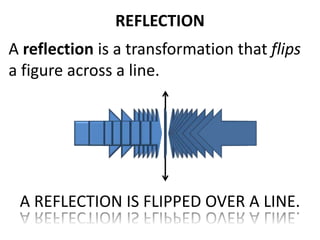
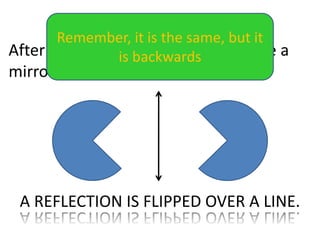
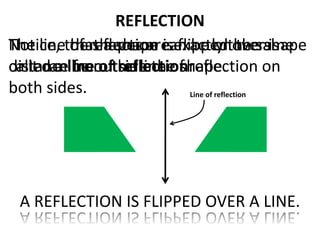
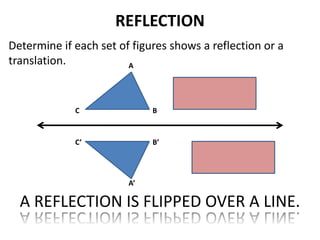
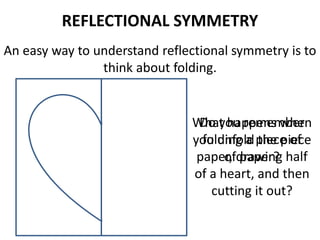
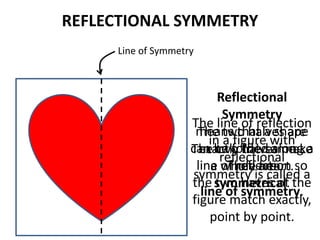
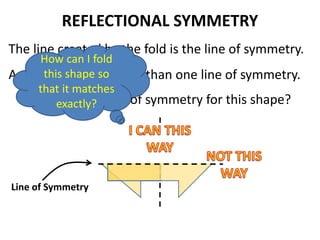
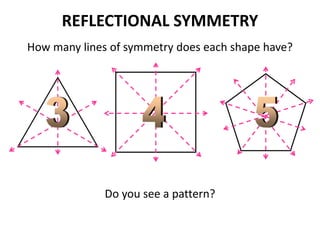
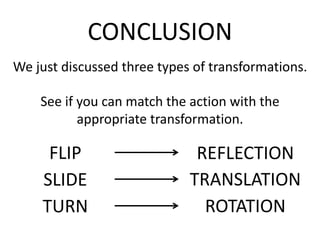
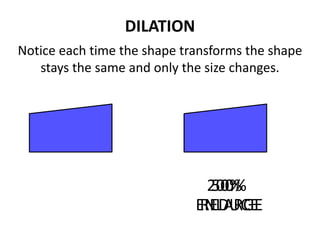
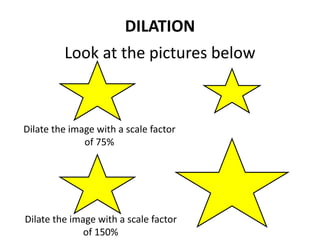
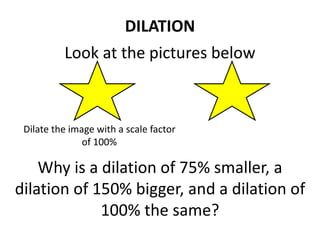
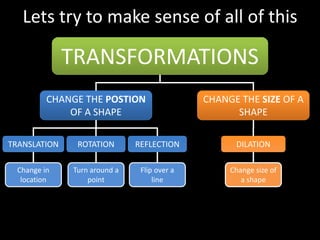
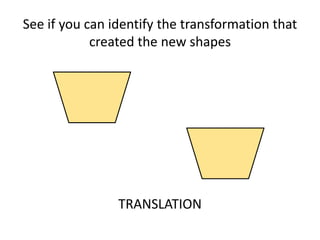
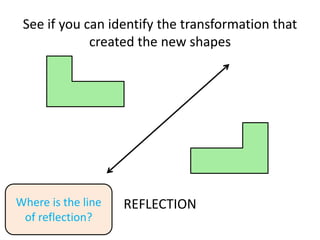
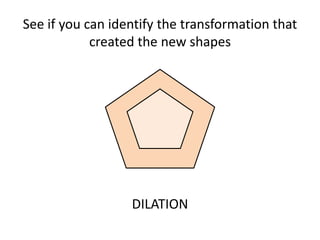
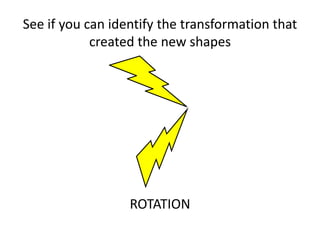
The document discusses different types of geometric transformations including translations, rotations, reflections, and dilations. A translation slides a figure across a plane without changing its size or shape. A rotation turns a figure around a central point. A reflection flips a figure over a line. A dilation enlarges or reduces the size of a figure proportionally without altering its shape. These transformations can create symmetries in shapes where halves are identical after being moved, flipped, or rotated.