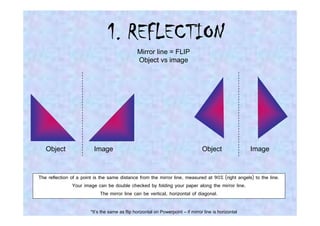
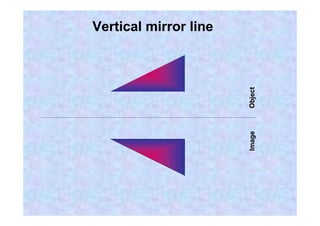
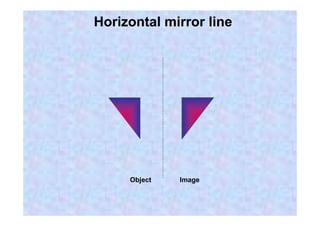
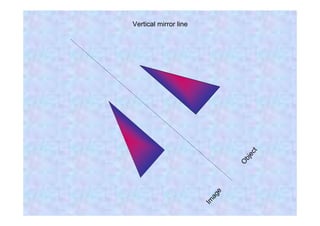
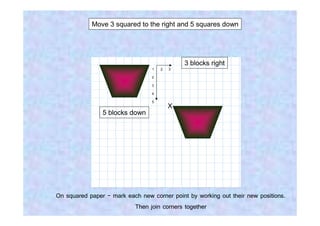
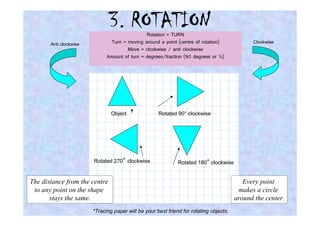
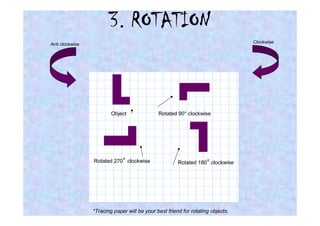
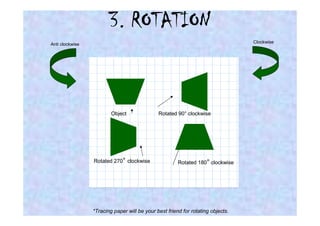
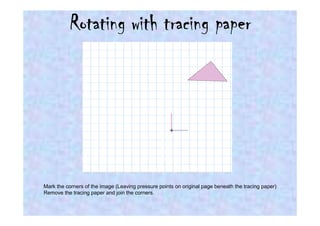
This document discusses different types of transformations in geometry: reflections, translations, and rotations. Reflections involve flipping a shape across a mirror line. Translations involve sliding a shape without turning or flipping. Rotations involve turning a shape around a central point by degrees or fractions of a full turn. All of these transformations produce a new position for the shape while keeping its size, angles, and measurements the same. Tracing paper is recommended for helping to rotate shapes accurately.