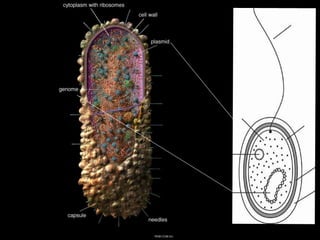
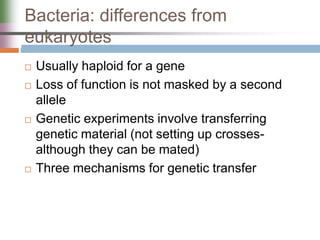
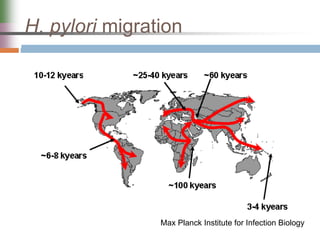
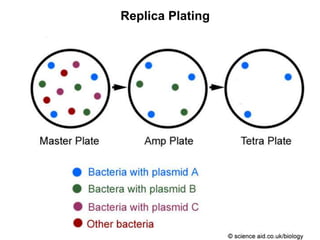
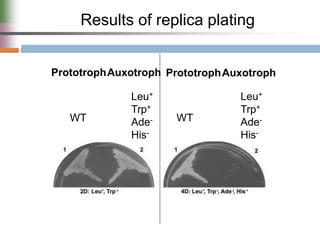
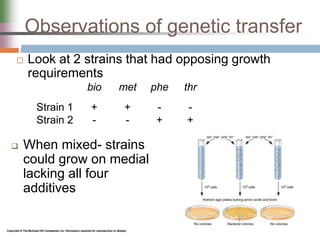
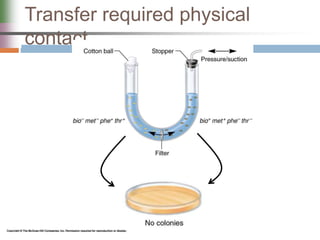
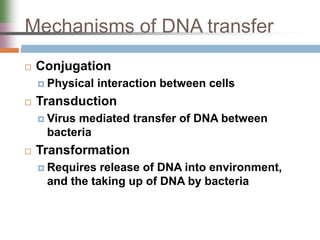
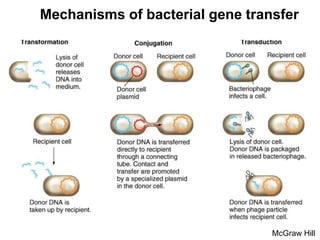
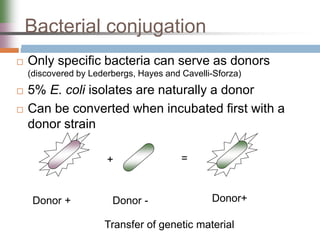
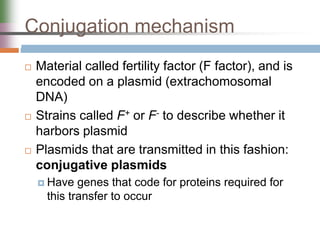
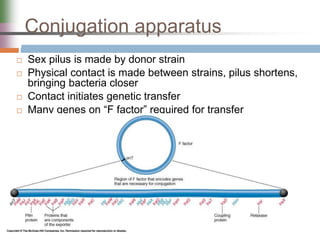
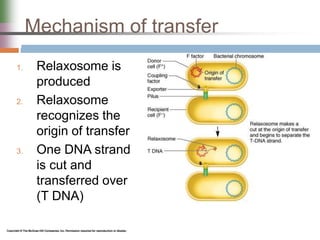
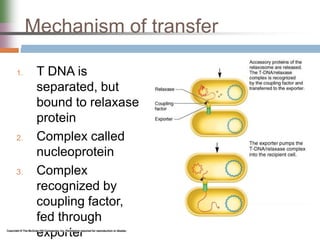
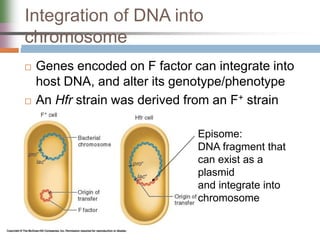
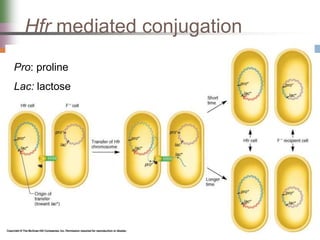
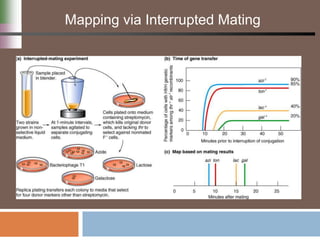
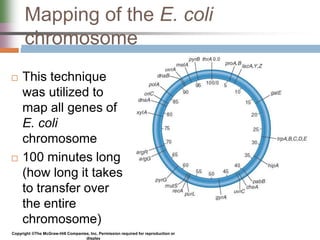
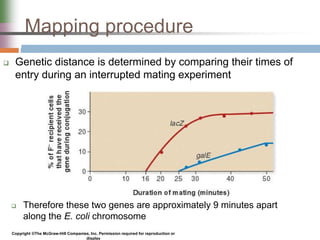
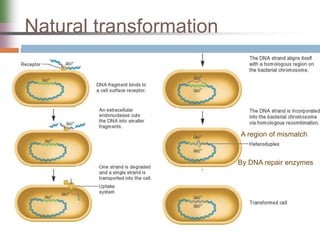
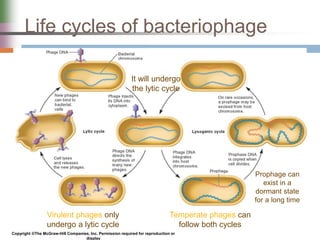
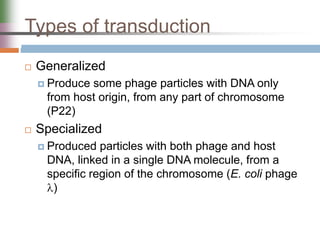
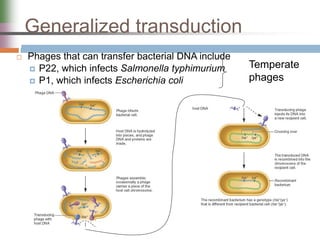
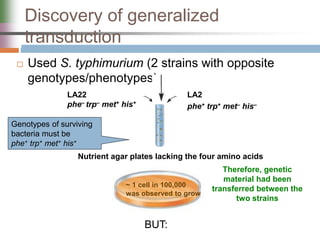
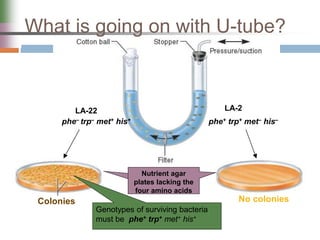
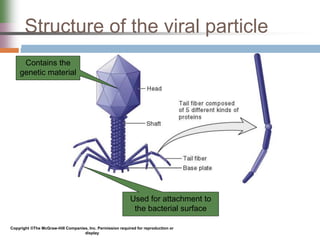
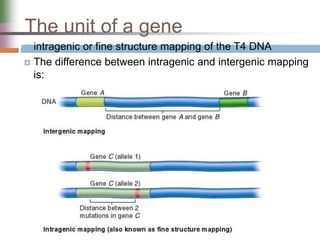
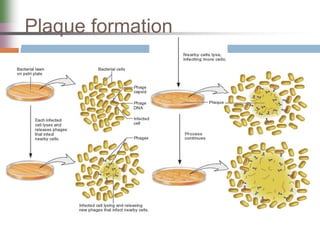
This document discusses various mechanisms of genetic transfer in bacteria, including conjugation, transduction, and transformation. Conjugation involves the physical transfer of genetic material between bacteria via cell-to-cell contact and an apparatus called a sex pilus. Transduction is virus-mediated and occurs when bacteriophages inadvertently package and transfer bacterial DNA. Transformation involves the natural uptake and incorporation of extracellular DNA into bacterial cells. These mechanisms allow for horizontal gene transfer and were important for mapping the bacterial chromosome and determining gene order.