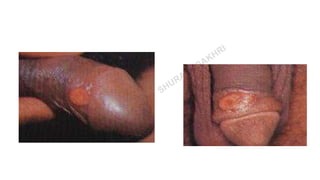
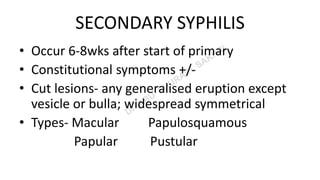
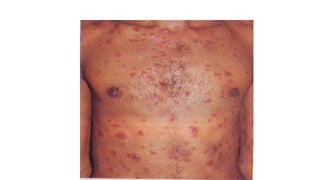
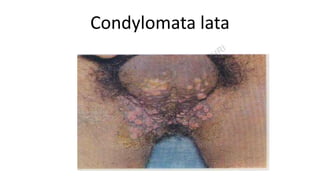
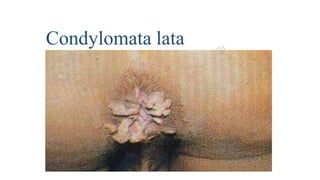
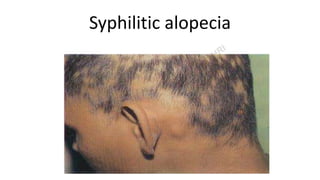
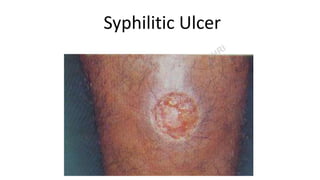
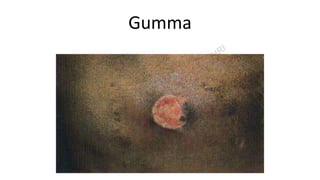
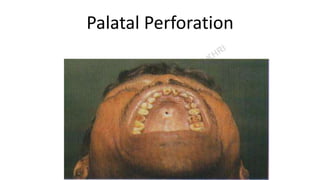
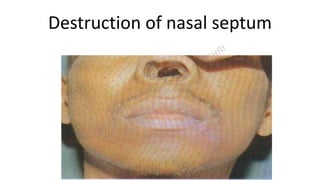
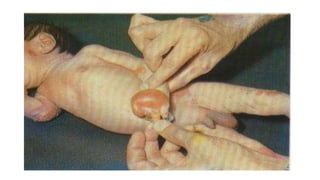
This document provides information about syphilis, caused by the spiral bacteria Treponema pallidum. It can affect all organs and cause a variety of manifestations. Syphilis is classified as either acquired or congenital. Acquired syphilis progresses through primary, secondary, early latent, and late stages. Primary syphilis causes painless ulcers. Secondary syphilis presents with rashes and mucous membrane lesions. Tertiary syphilis can cause gummas or damage to internal organs. Neurosyphilis can also occur. Congenital syphilis is transmitted from mother to child and can cause early symptoms or late complications if untreated. Diagnosis involves blood and CSF tests. Treatment depends on the