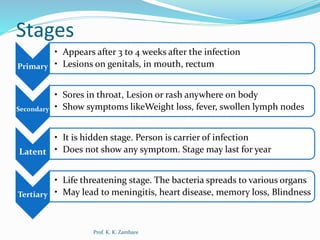
Syphilis is a sexually transmitted disease caused by the bacterium Treponema pallidum, transmitted through direct contact with an infected person, sexually, vertically from mother to fetus, or via blood transfusion. It progresses through four stages: primary with genital lesions, secondary with body rashes and flu-like symptoms, latent where the carrier shows no symptoms, and tertiary which can be life-threatening affecting various organs. Diagnosis involves physical examinations, microscopic tests, and serological tests, with complications including dementia, cardiovascular issues, and pregnancy problems.