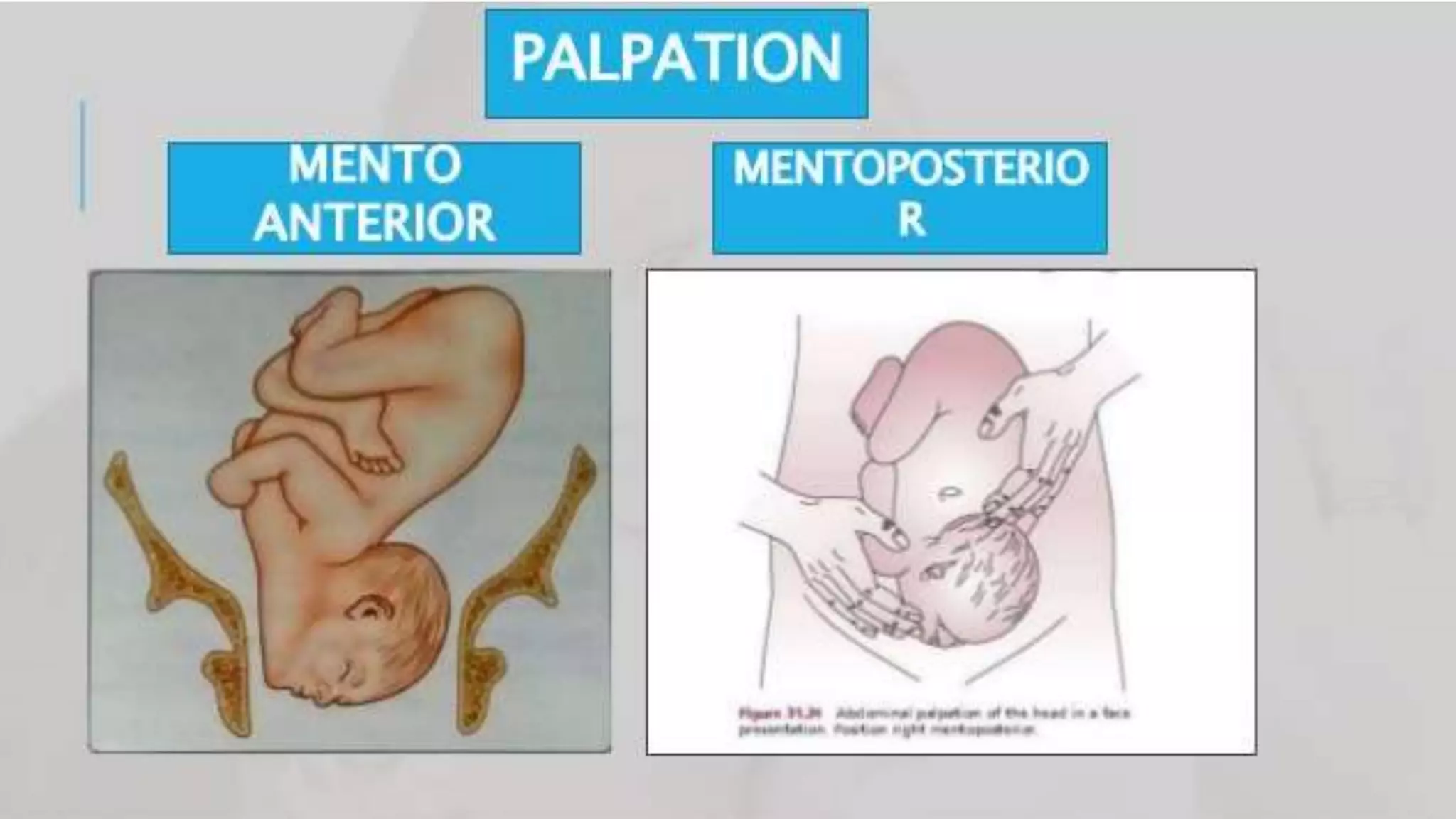
This document provides information on face presentation during childbirth. It defines face presentation as a cephalic presentation with the fetus in a complete extended attitude and the presenting part being the face. The two types of face presentation are primary (presenting before labor) and secondary (caused by extension during labor). The main positions are left and right mentoanterior and mentoposterior. Face presentation has a higher risk of complications compared to vertex presentation such as prolonged labor and increased need for operative delivery. The management involves allowing labor to progress for mentoanterior positions but cesarean section is usually needed for persistent mentoposterior.











![POSITIONS
• Left mentoanterior[LMA]
• Right mentoanterior[RMA]
• Right mentoposterior[RMP]
• Left mentoposterior[LMP]
• Mentoanterior-70%
• Mentoposterior-30%](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/facepresentation-220109091235/75/Face-Presentation-13-2048.jpg)