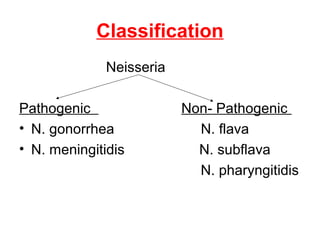
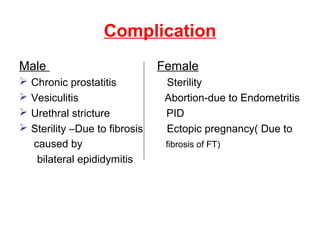
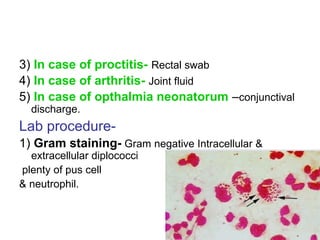
Neisseria gonorrhoeae and N. meningitidis are pathogenic Neisseria species. N. gonorrhoeae causes gonorrhea, transmitted sexually or from mother to child. It infects the urethra, cervix, and other sites. Without treatment, it can spread and cause complications like pelvic inflammatory disease. N. meningitidis causes meningitis, transmitted through airborne droplets. It infects the nasopharynx and can spread to the blood and CNS. Laboratory diagnosis involves gram stain, culture on selective media, and rapid carbohydrate utilization tests. Gonorrhea pathology in females includes salpingitis, tubo-ovarian abscess,