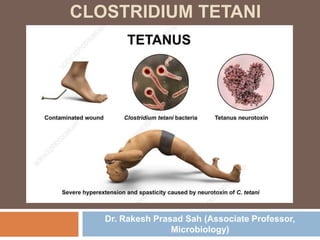
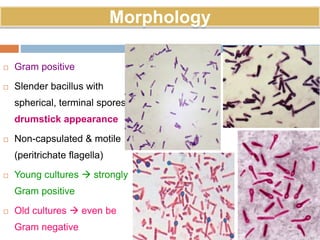
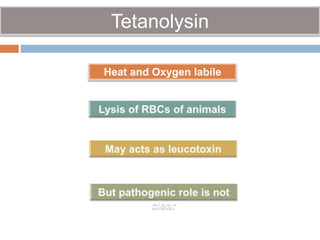
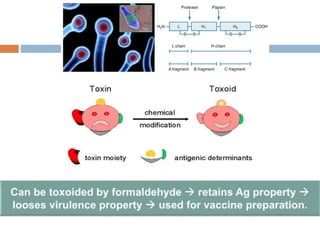
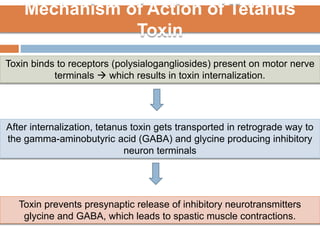
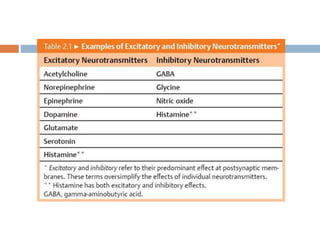
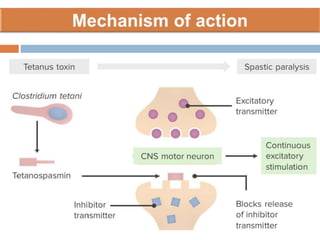
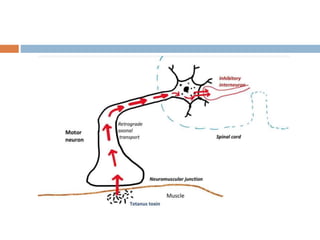
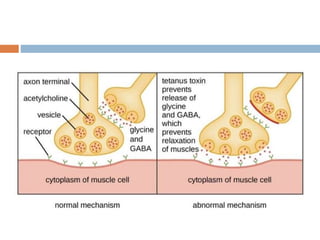
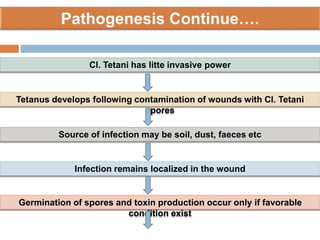
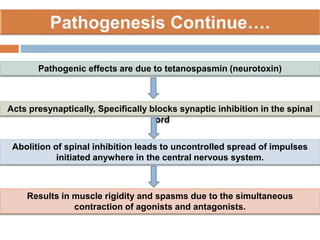
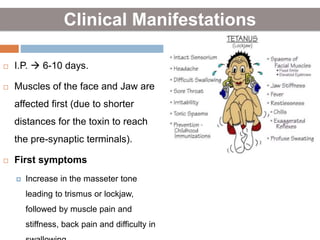
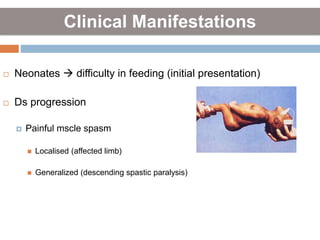
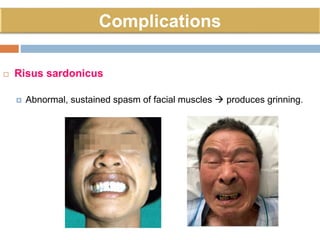
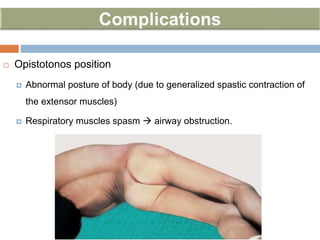
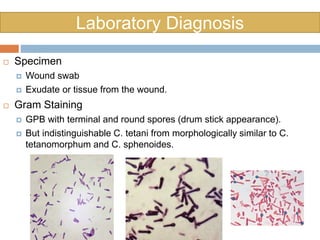
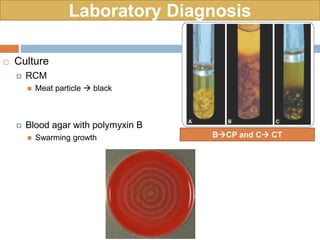
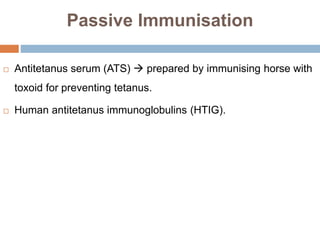
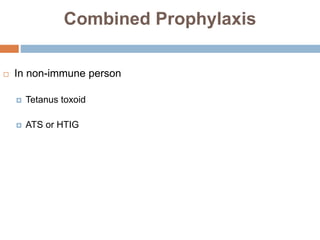
Clostridium tetani is the causative agent of tetanus, an acute disease characterized by skeletal muscle spasms and autonomic nervous system disturbances. C. tetani is a gram-positive, spore-forming bacillus found widely in soil and the intestines of humans and animals. It produces two toxins - tetanolysin and tetanospasmin, the powerful neurotoxin responsible for the clinical symptoms of tetanus. Tetanospasmin prevents the release of inhibitory neurotransmitters in the spinal cord, resulting in uncontrolled muscle contractions and spasms. Prophylaxis includes wound cleaning, antibiotics, active immunization with tetanus toxoid vaccines, and passive immun