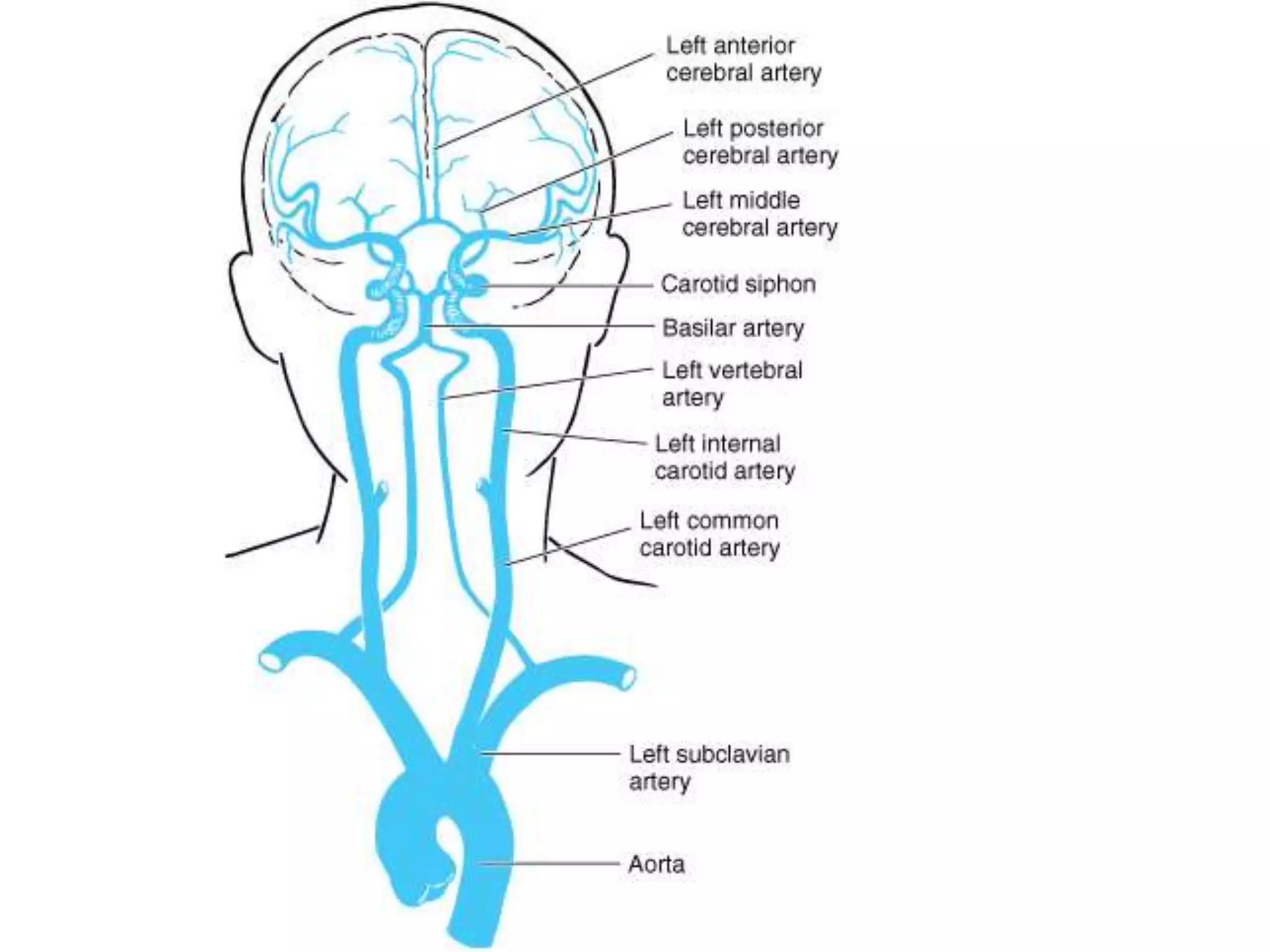
The brain receives a high blood supply to meet its metabolic demands. Arterial blood reaches the brain through the internal carotid and vertebral arteries, forming the circle of Willis at the base of the brain before branching into smaller vessels. Venous blood drains from the brain into internal jugular veins. Disruption of blood flow to the brain through cerebrovascular accidents like stroke can cause rapid loss of consciousness or permanent brain damage. Cerebrospinal fluid produced by choroid plexuses circulates within ventricles and around the brain and spinal cord, carrying nutrients and waste products.