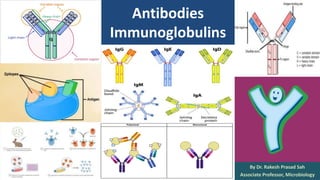
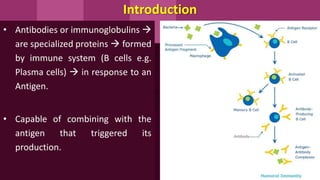
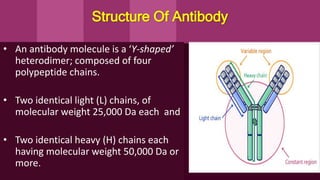
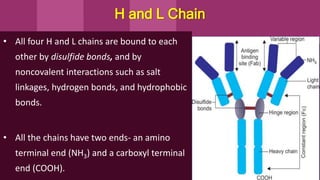
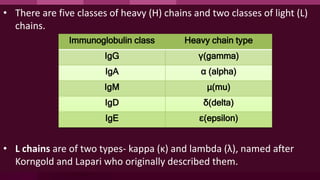
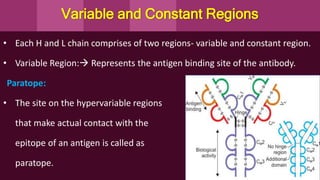
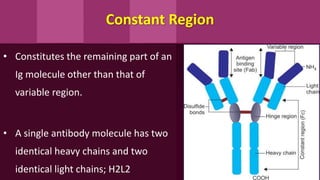
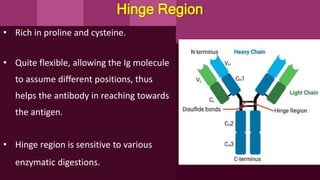
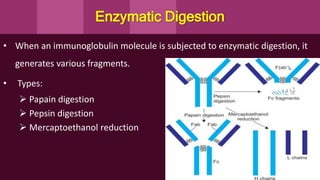
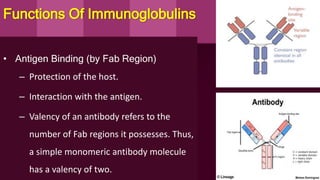
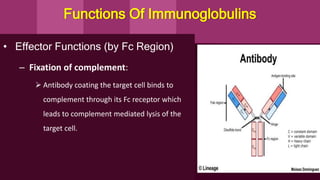
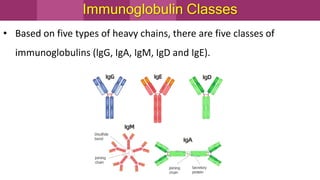
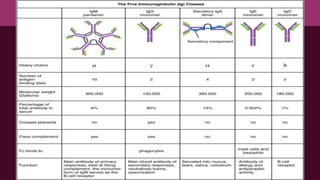
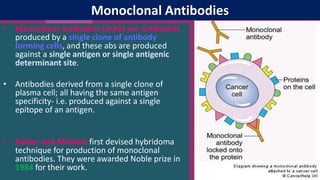
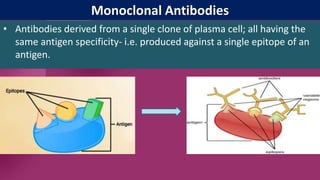
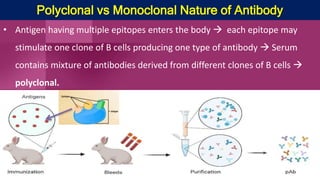
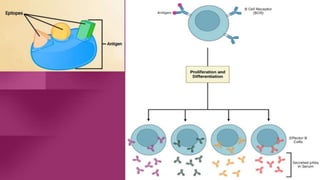
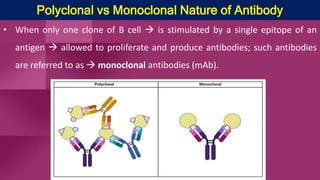
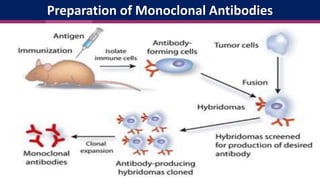
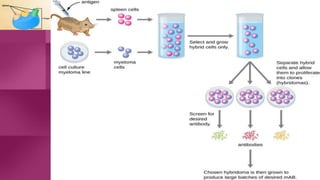
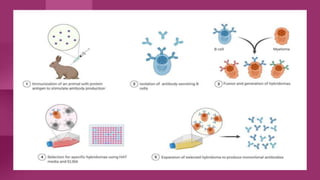
Antibodies, also known as immunoglobulins, are Y-shaped proteins produced by plasma cells in response to antigens. There are five classes of antibodies - IgG, IgA, IgM, IgD, and IgE - which have different structures and functions. Each antibody molecule consists of two heavy chains and two light chains that give it regions for antigen binding and effector functions. Monoclonal antibodies are derived from a single clone and bind to a single epitope, whereas polyclonal antibodies bind to multiple epitopes from different antibody clones. Monoclonal antibodies have many diagnostic and therapeutic uses. Abnormal immunoglobulins lacking antibody function can also be produced in certain diseases.