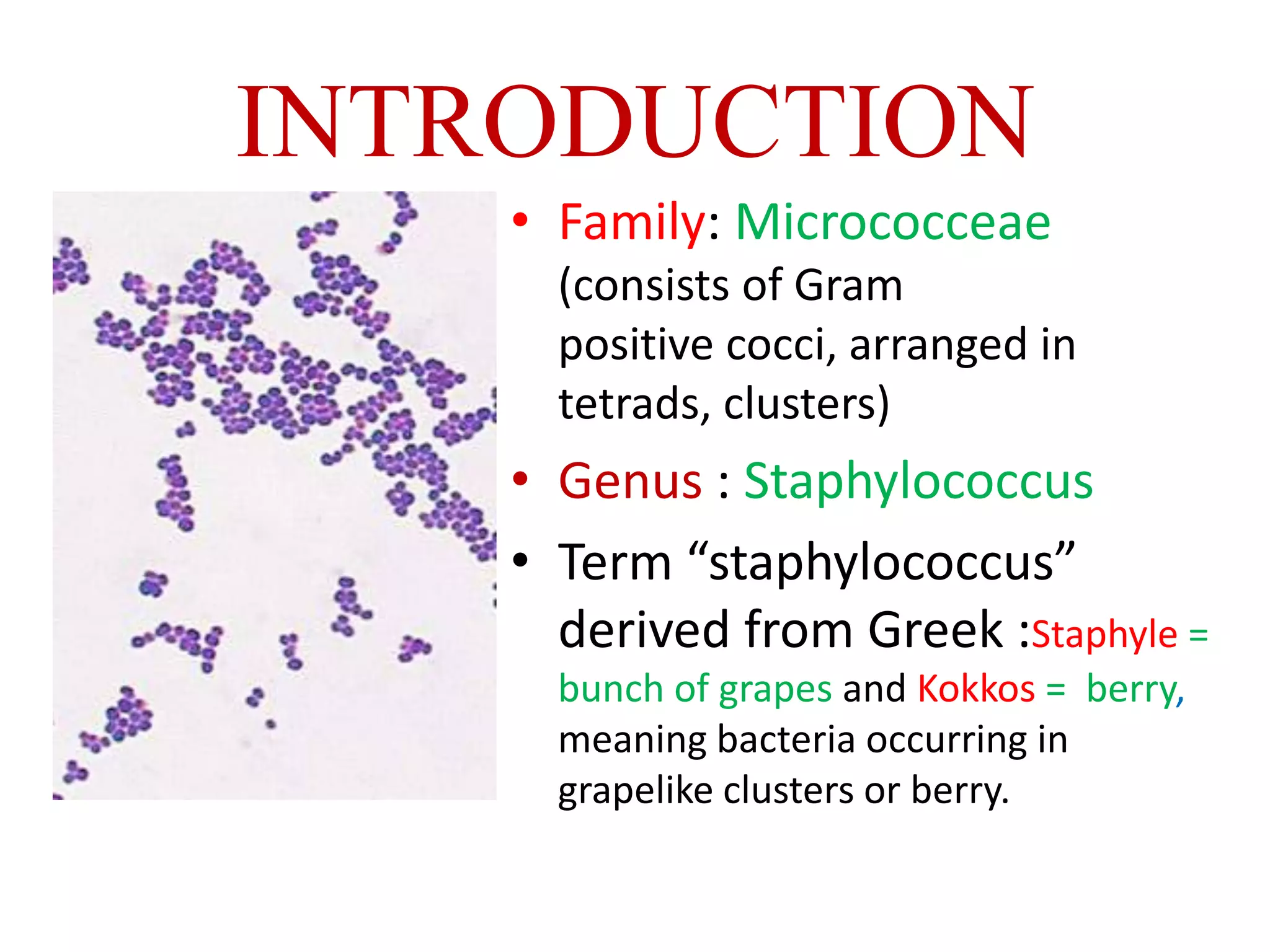
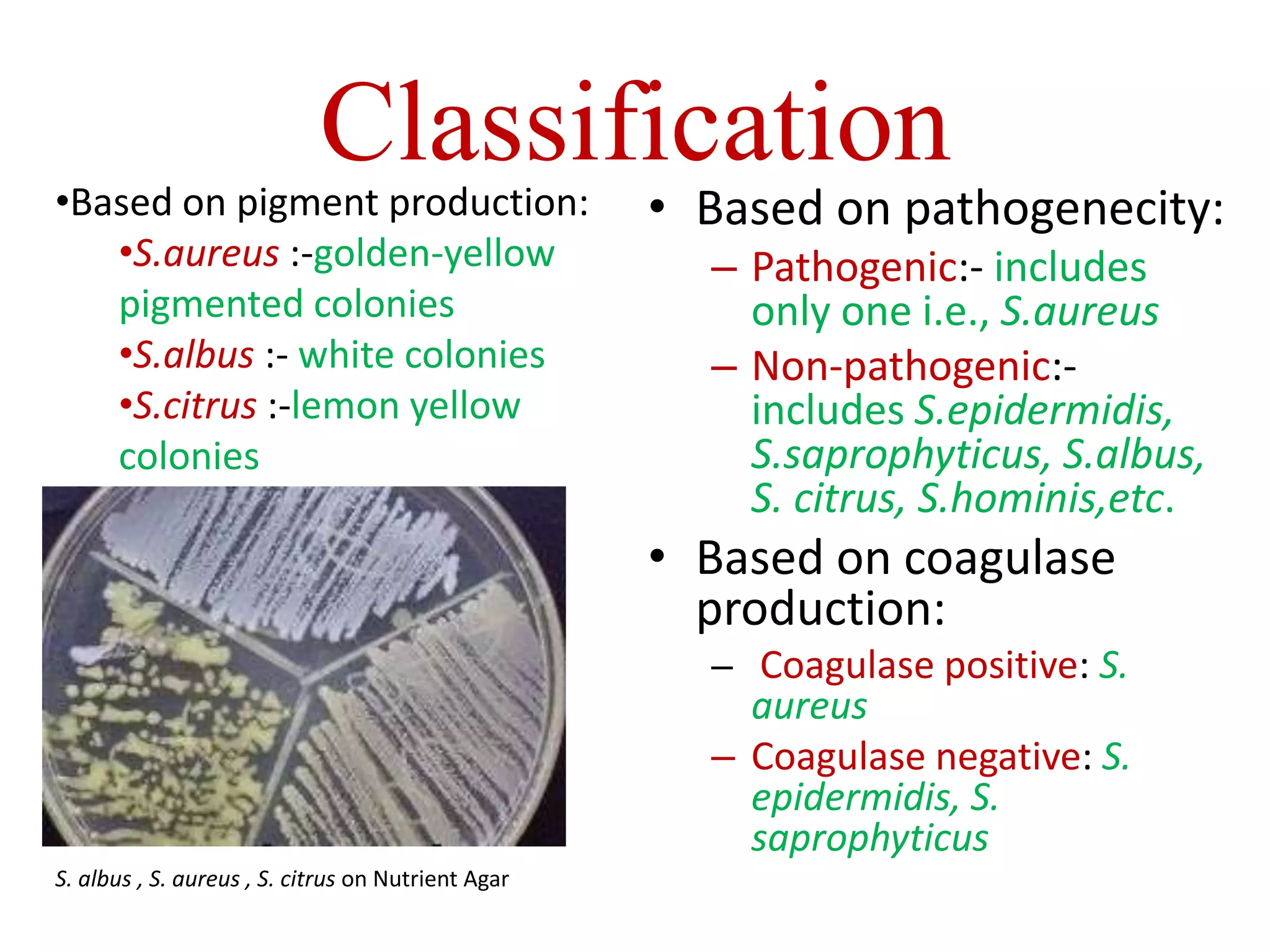
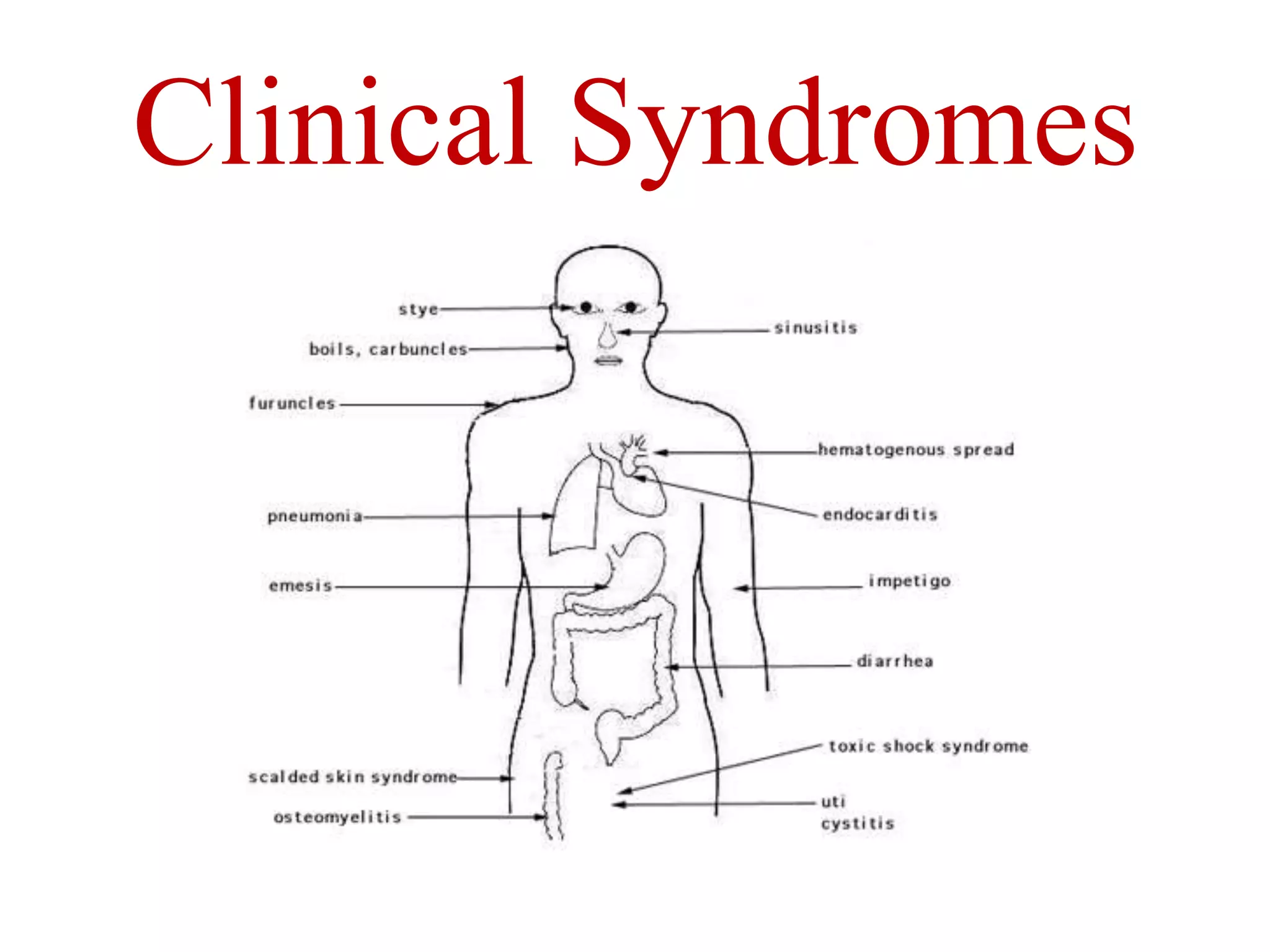
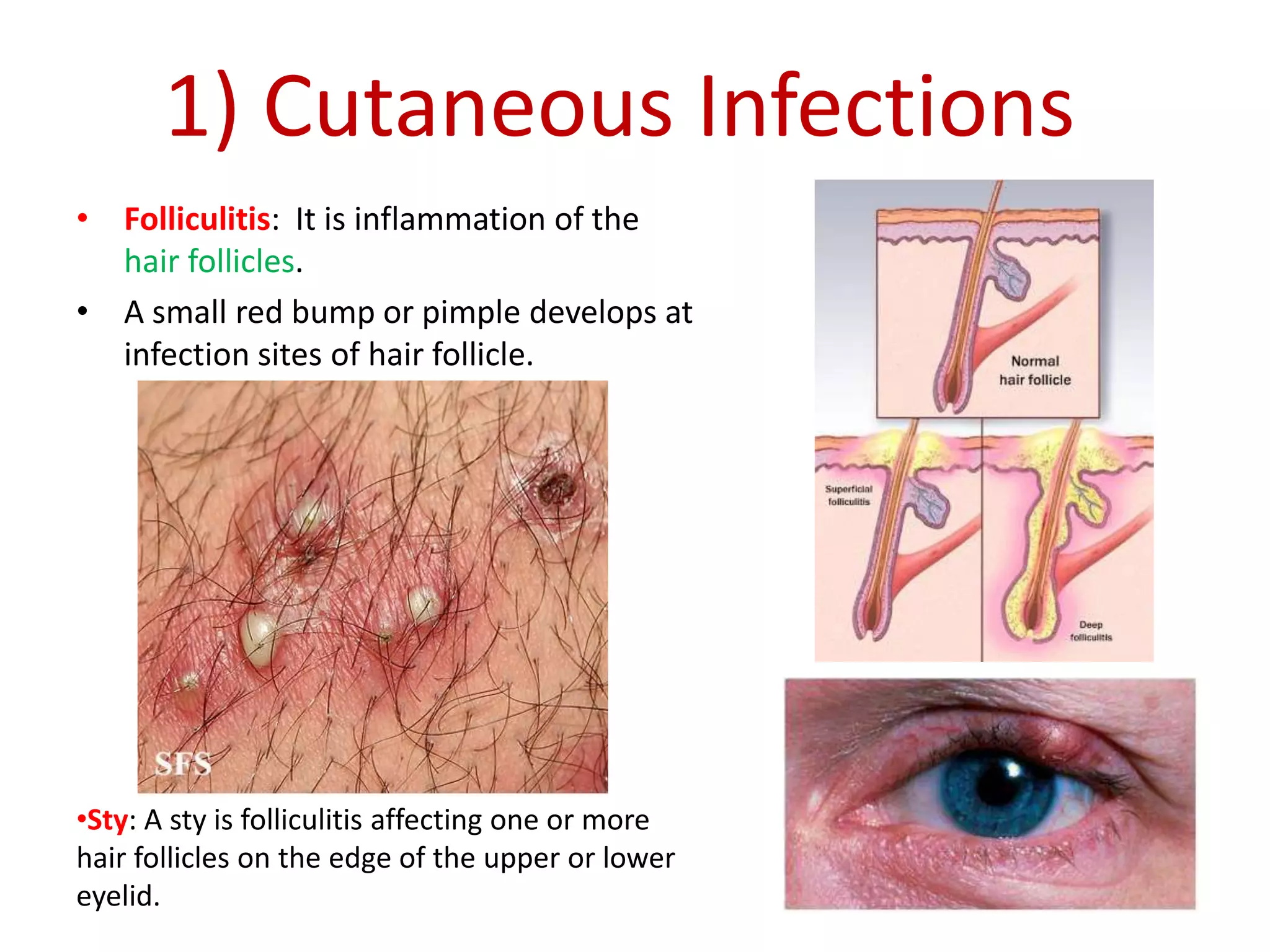
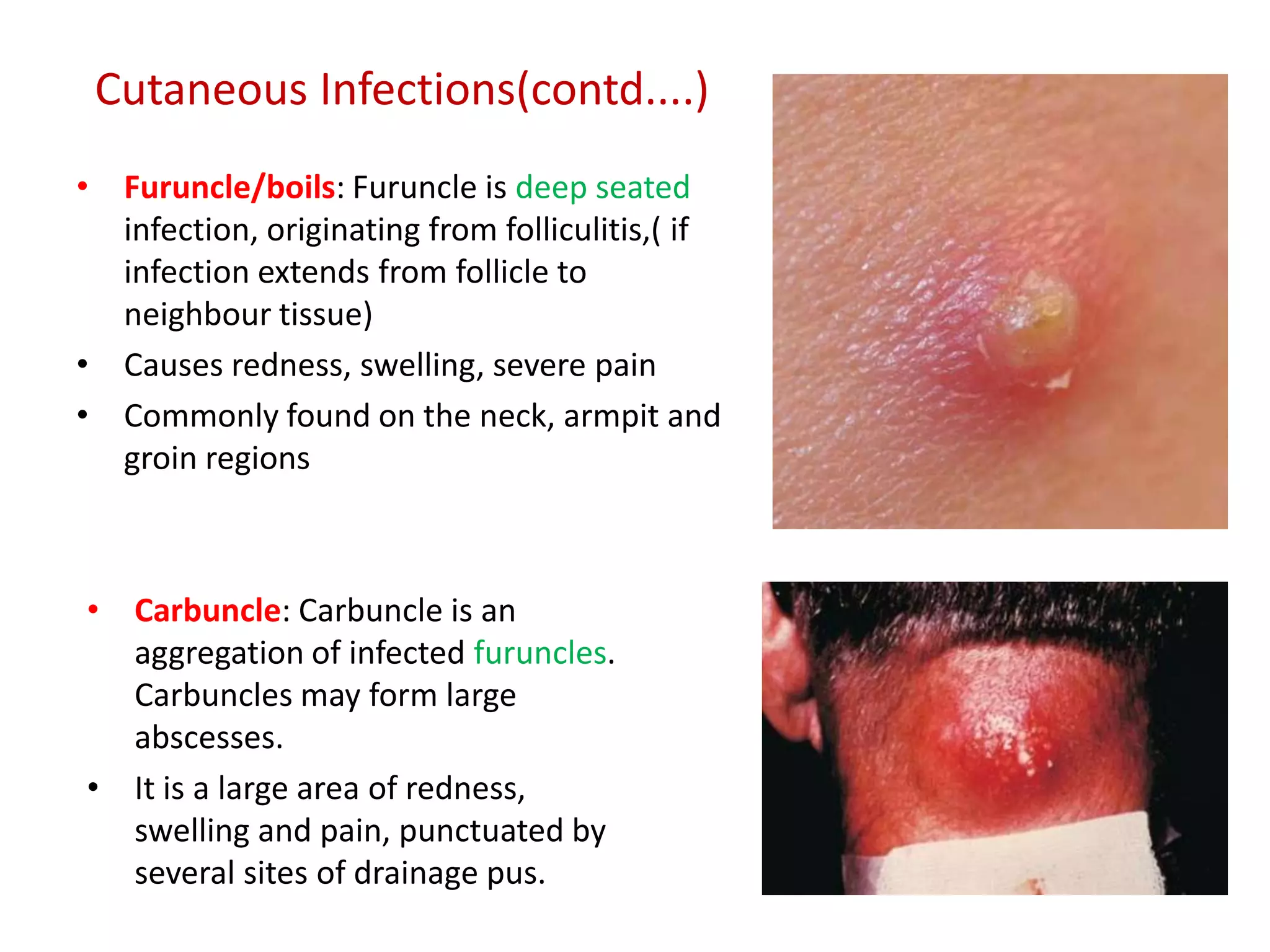
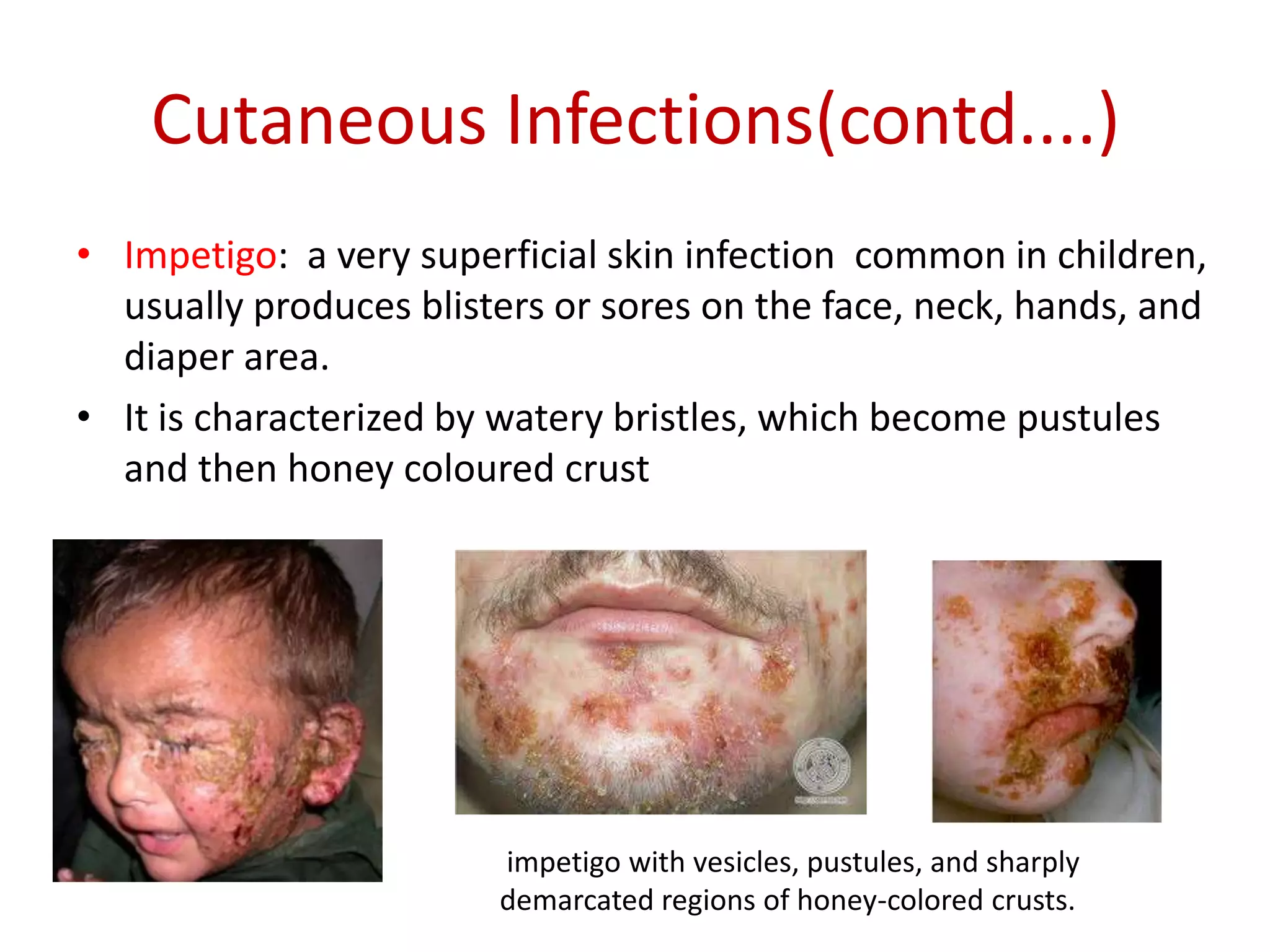
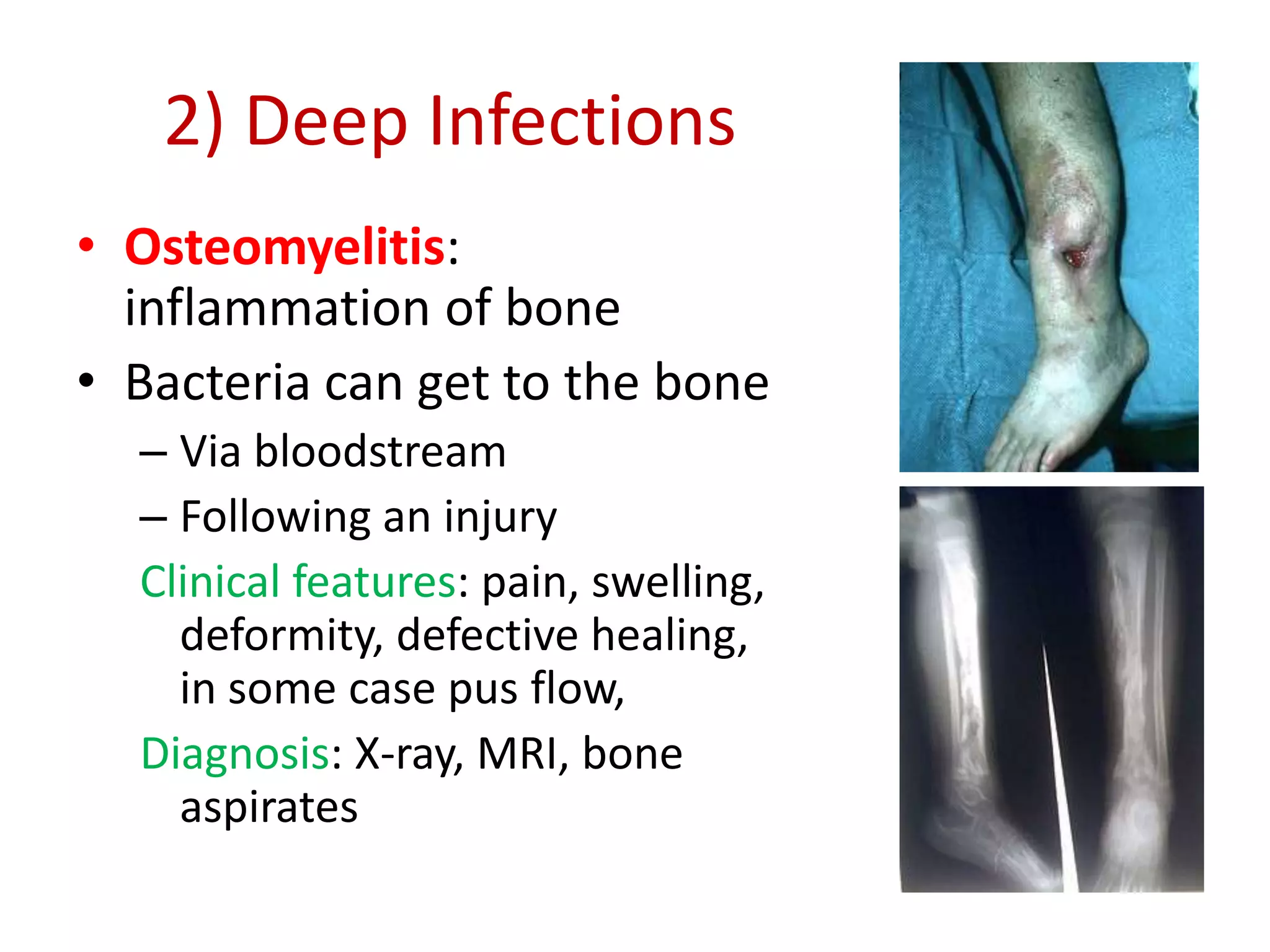
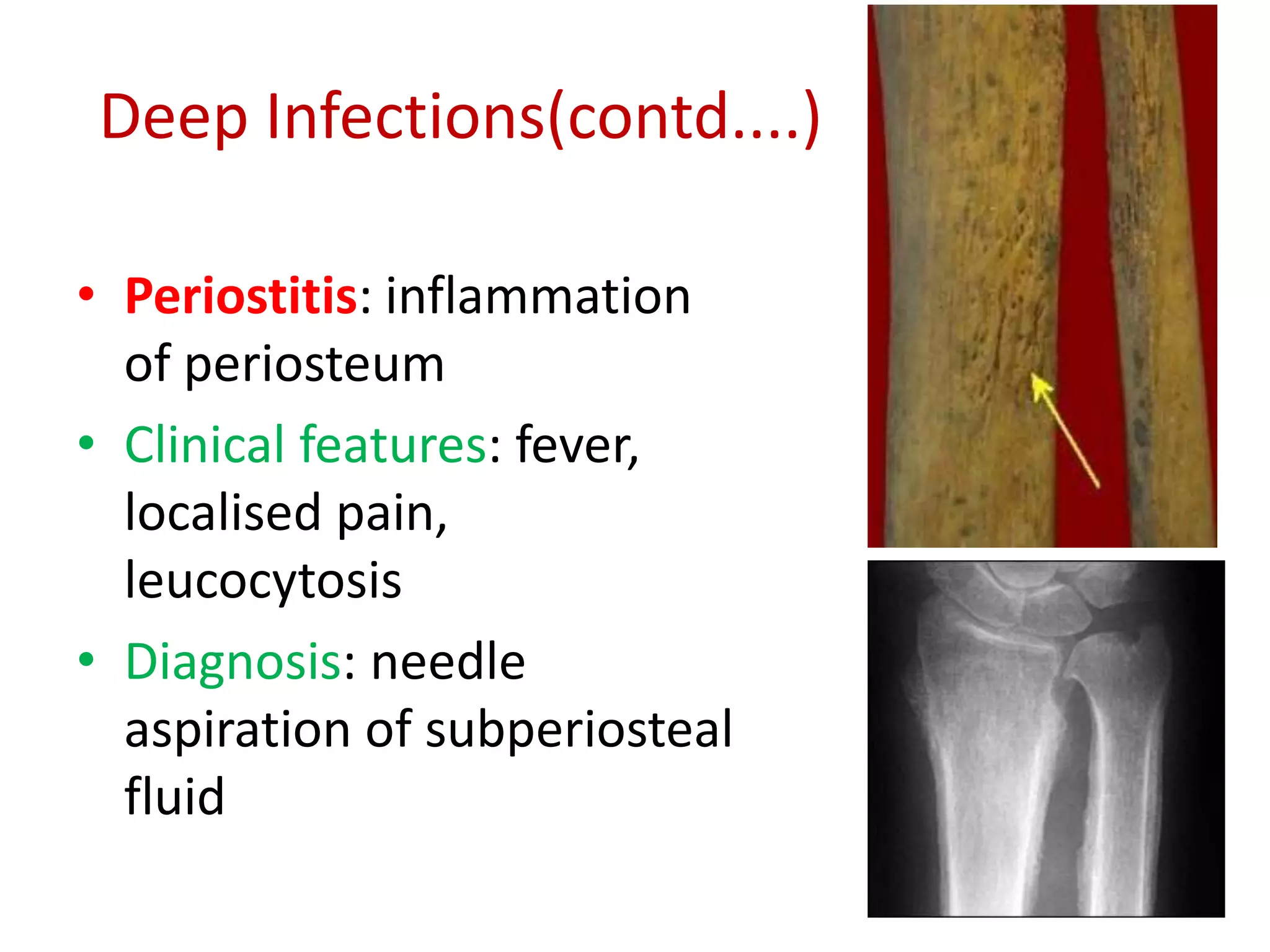
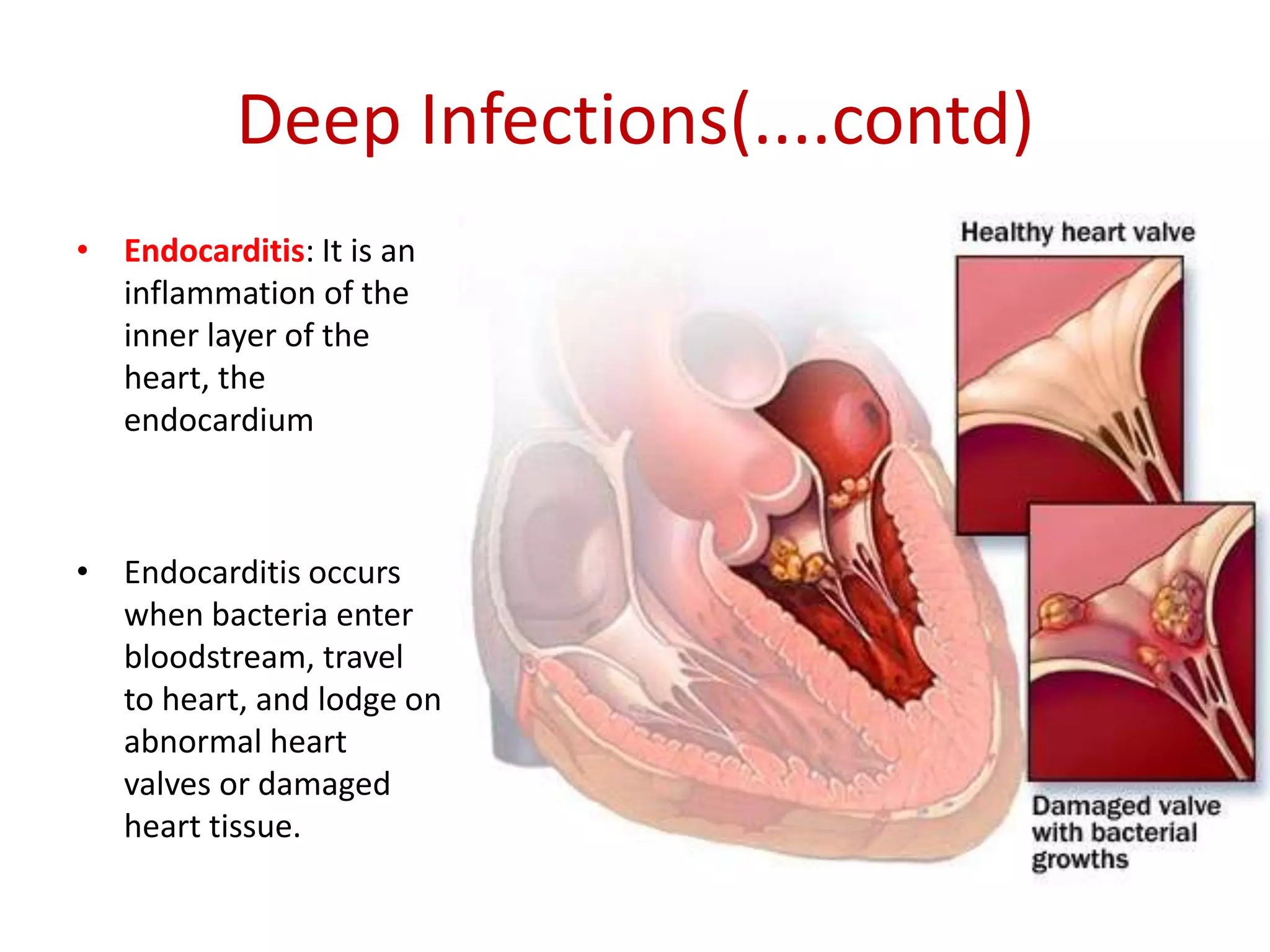
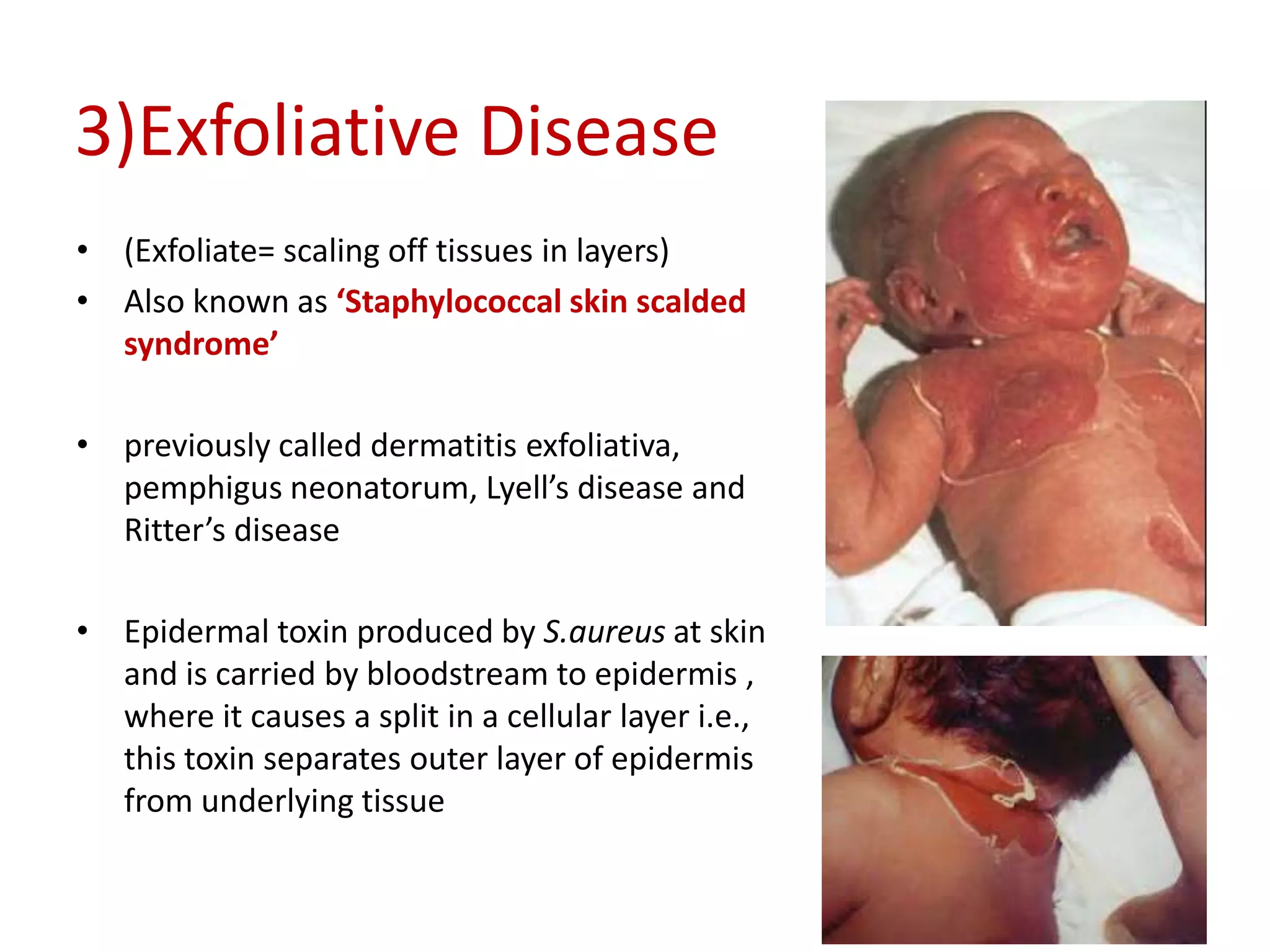
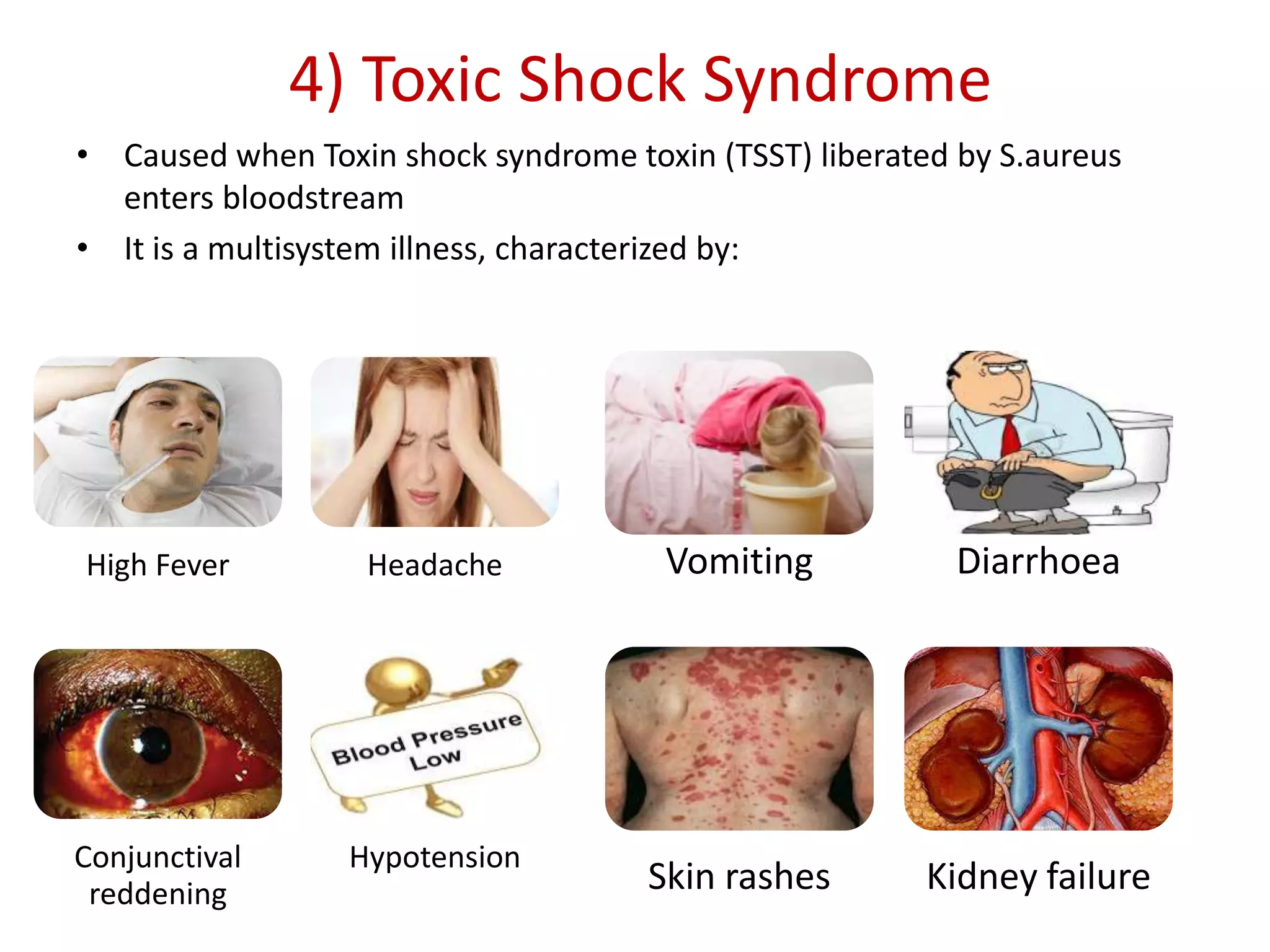
Staphylococcus is a genus of bacteria that can cause a variety of infections in humans. The most common pathogenic species is Staphylococcus aureus, which was first identified in the late 19th century. S. aureus produces toxins and enzymes that allow it to infect skin, blood, lungs, and other tissues. It commonly causes skin infections like boils and abscesses but can also lead to serious diseases like pneumonia, meningitis, or toxic shock syndrome. Methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA) infections are difficult to treat with many antibiotics. Laboratory tests are used to identify S. aureus from patient samples and test for antibiotic resistance.










![Laboratory Diagnosis (contd....)
B. Bacteriological
Investigation:
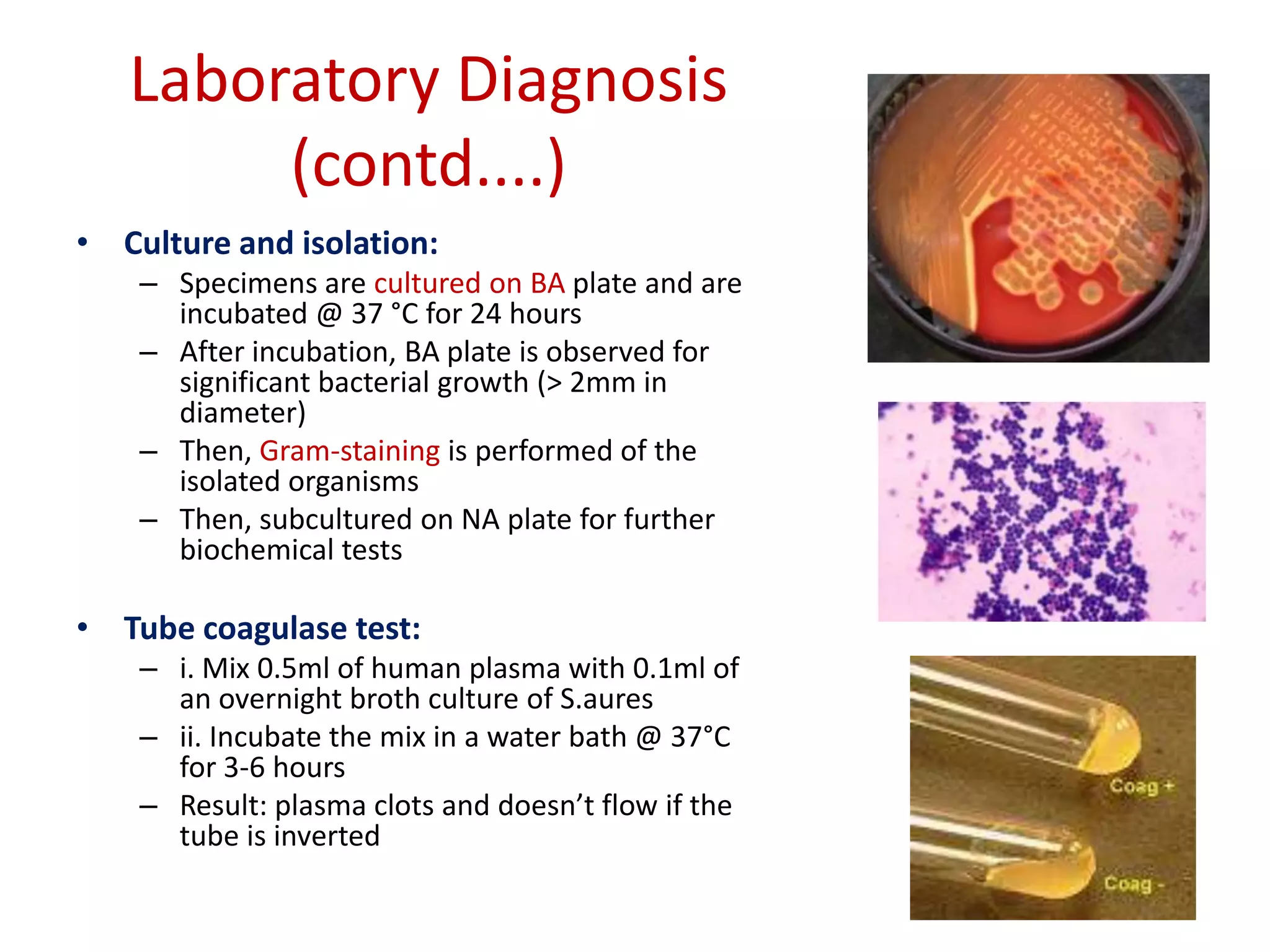
• Specimens:
– Pus: from wound or
abscess or burns]
– Nasal Swab: from
suspected carrier
– Food: to diagnose
staphylococcal intoxication
– Blood: to diagnose
endocarditis and
bacteremia
– Sputum: to diagnose lower
respiratory tract infection](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/staphylococcus-230928081257-d470d800/75/staphylococcus-pdf-32-2048.jpg)