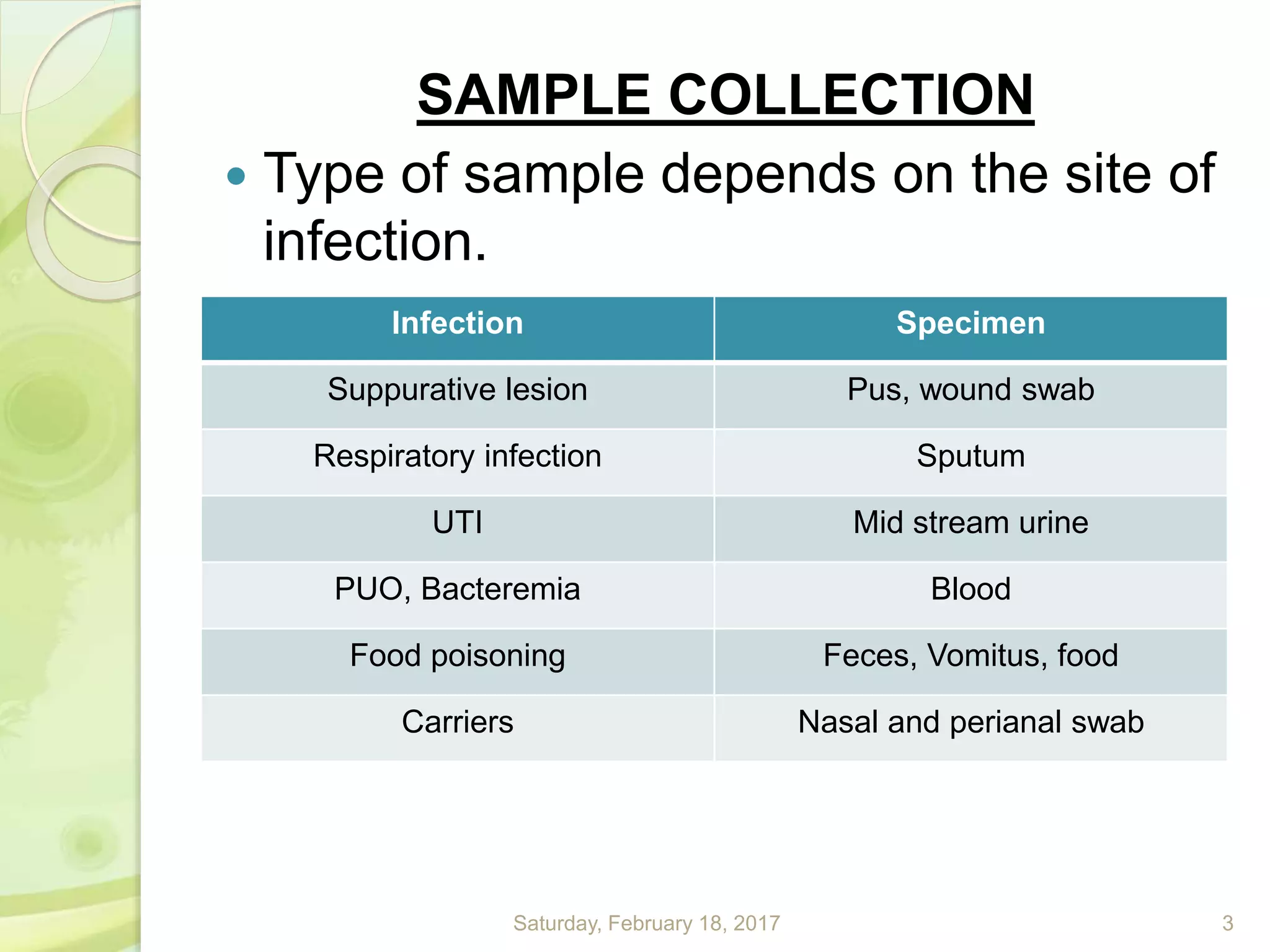
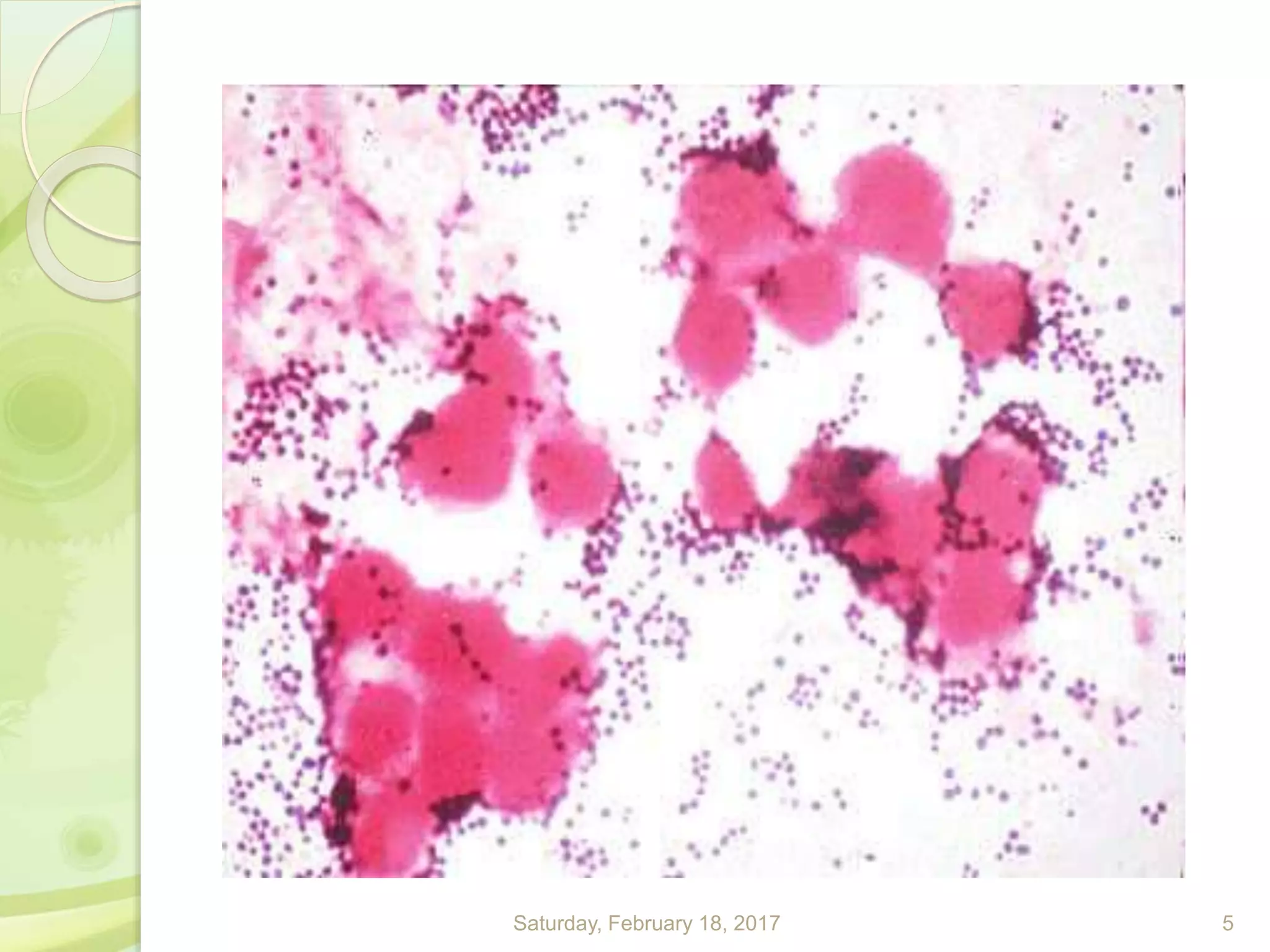
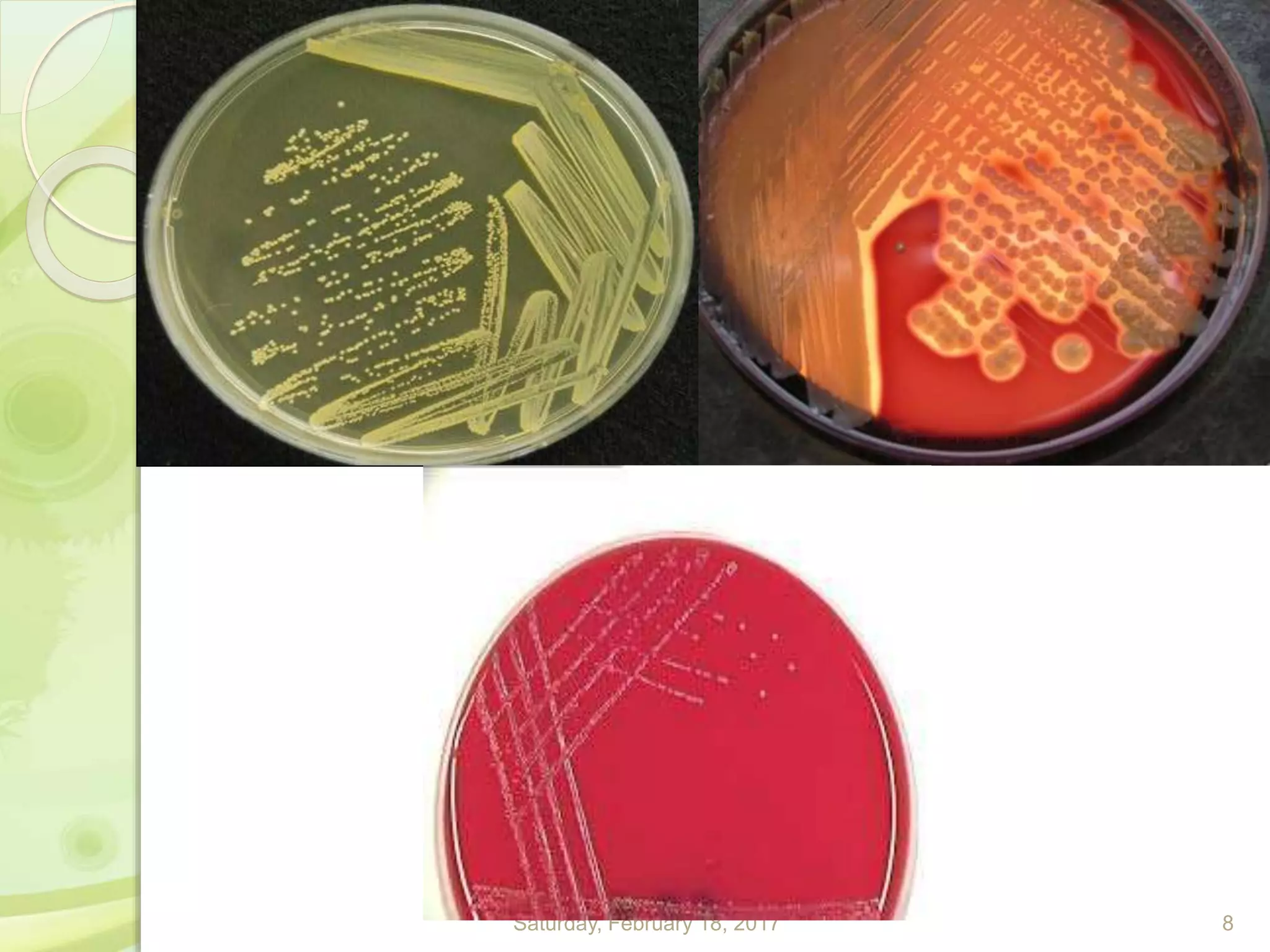
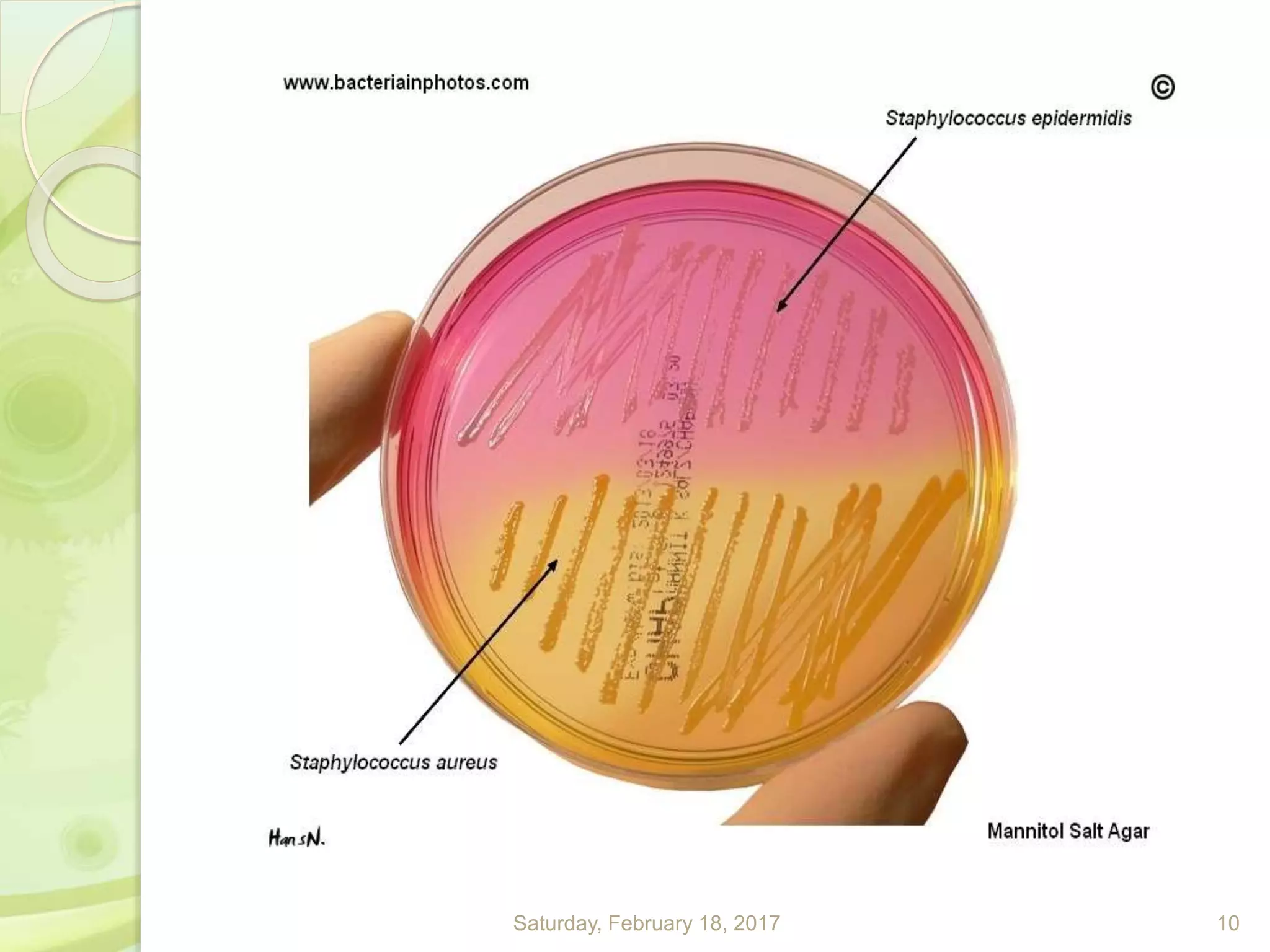
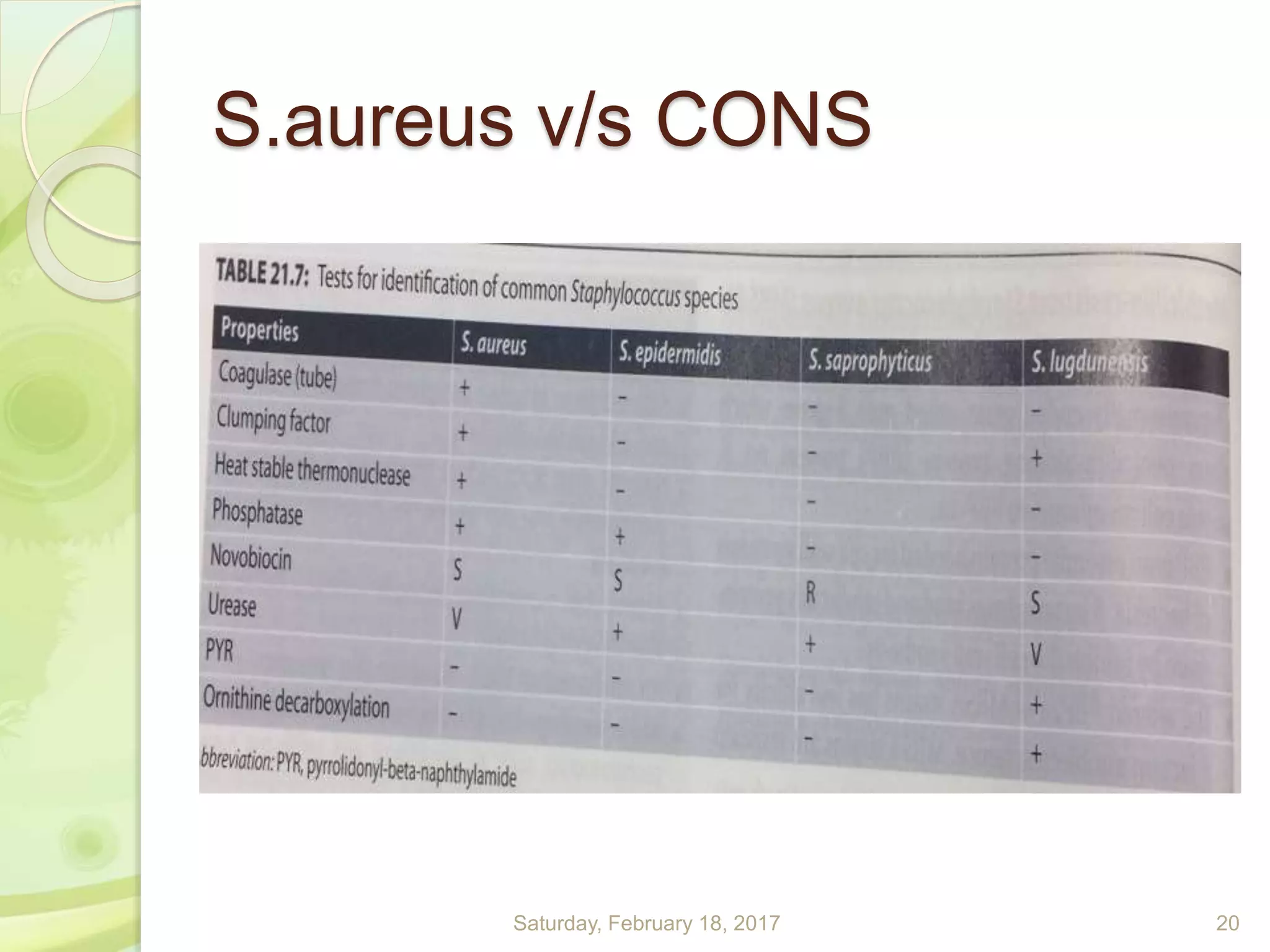
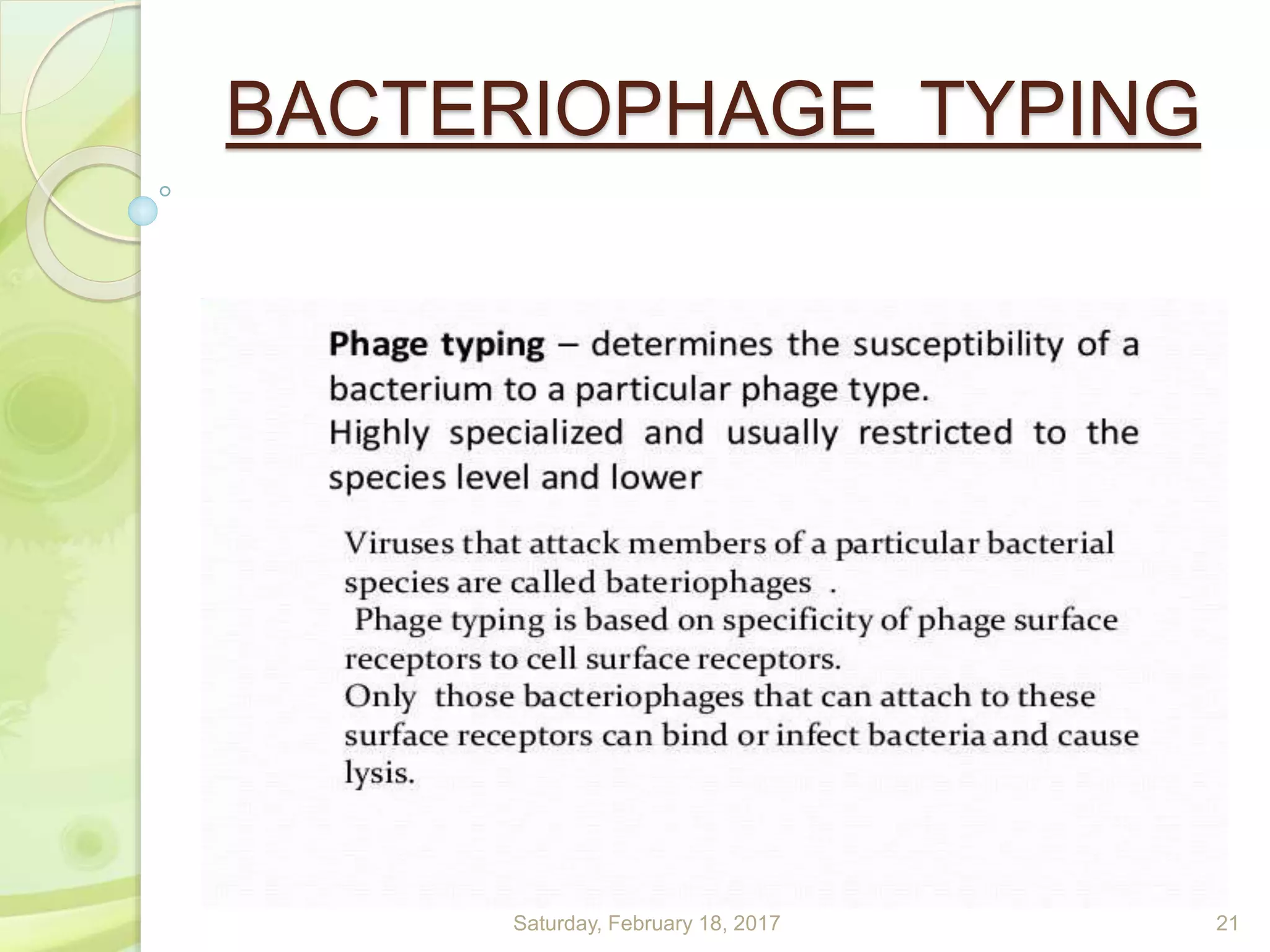
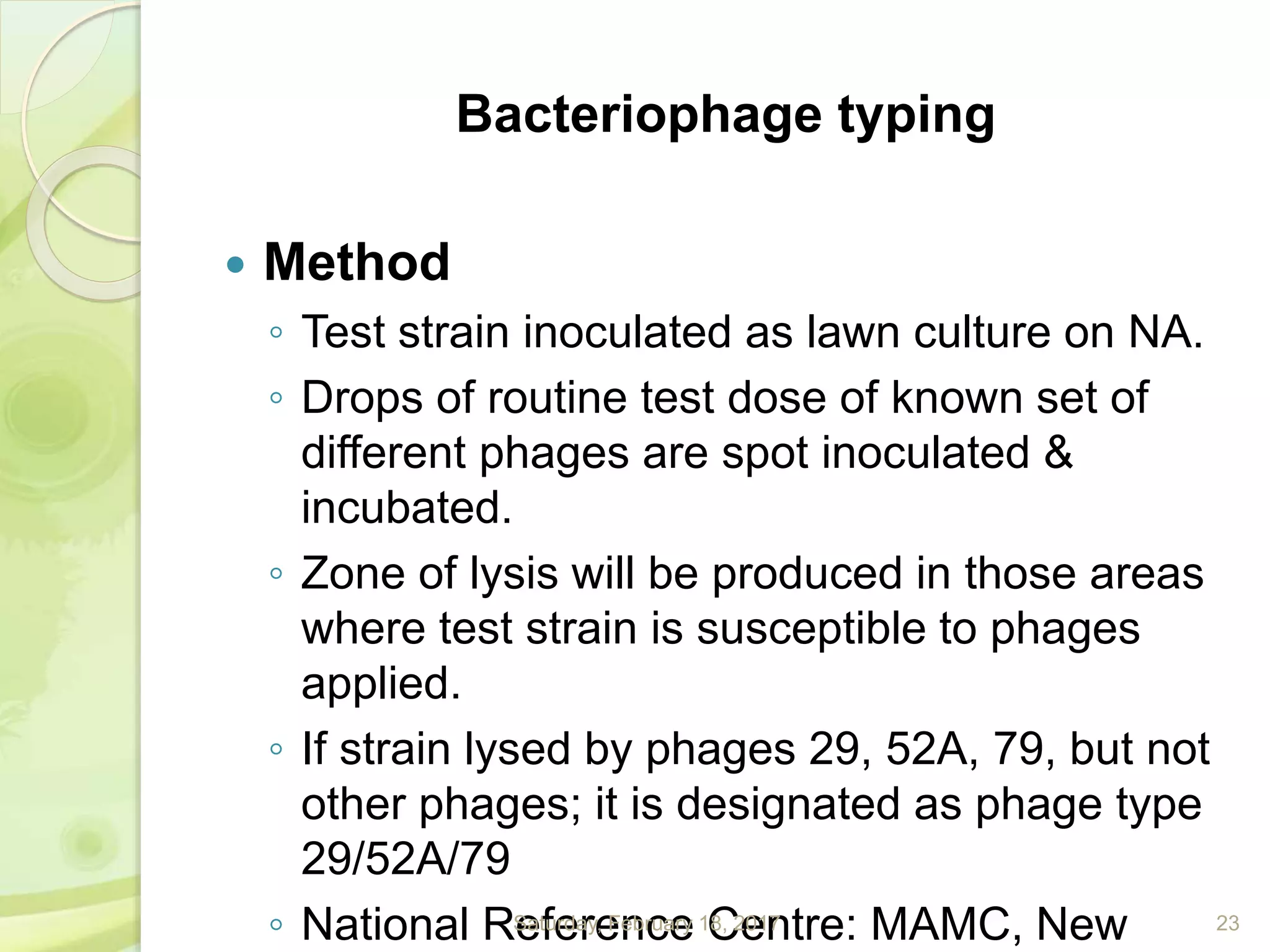
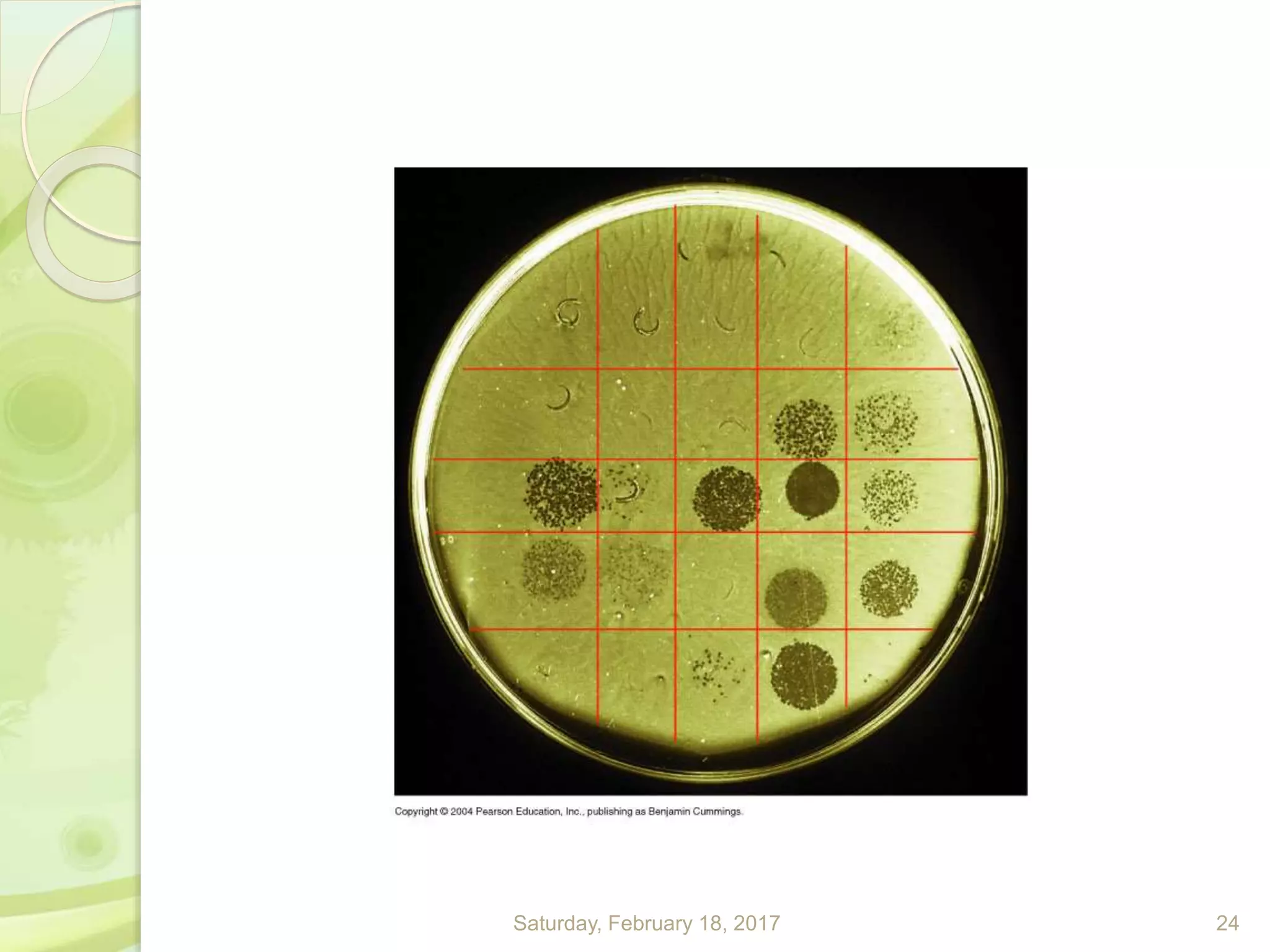
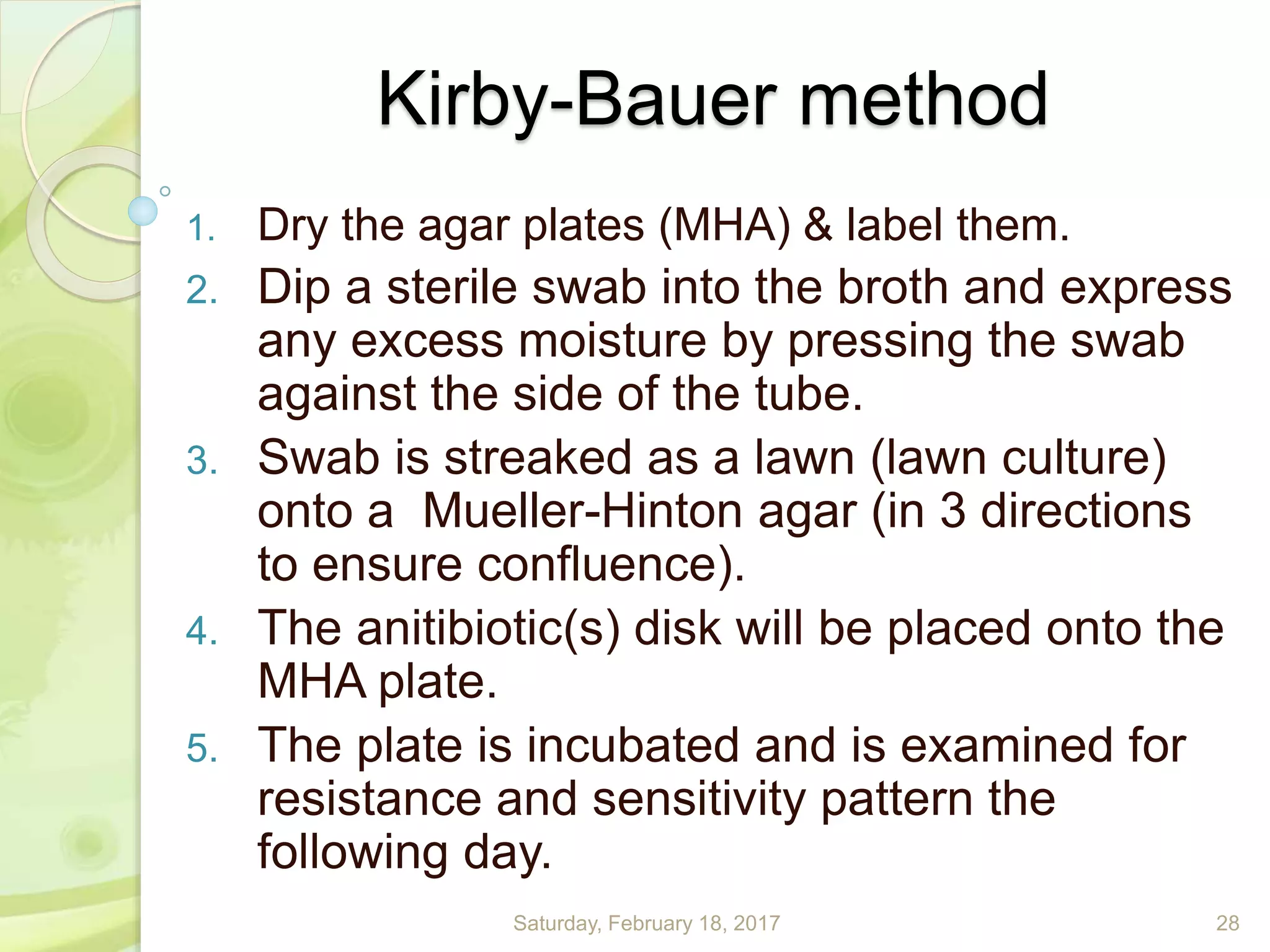
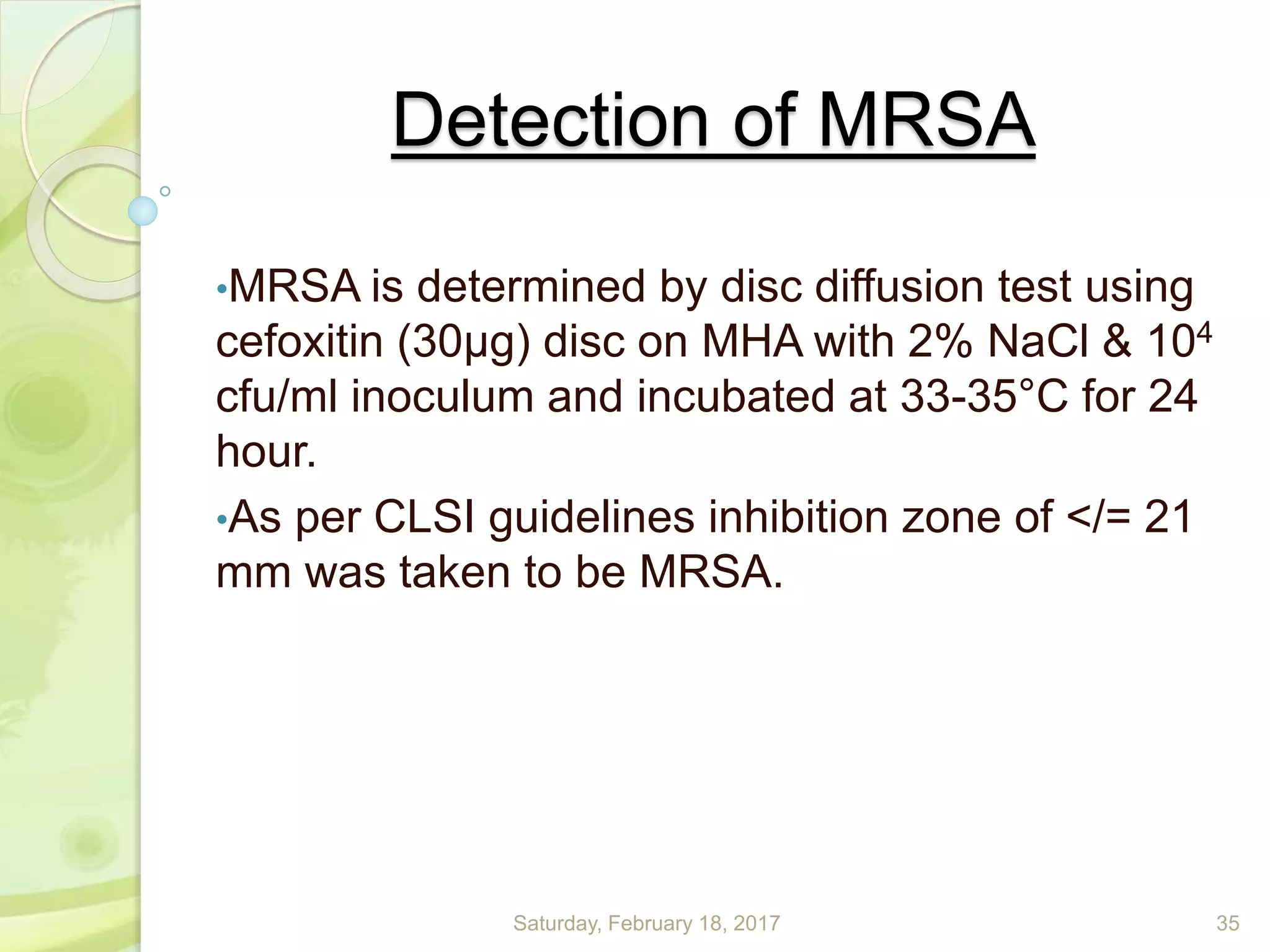
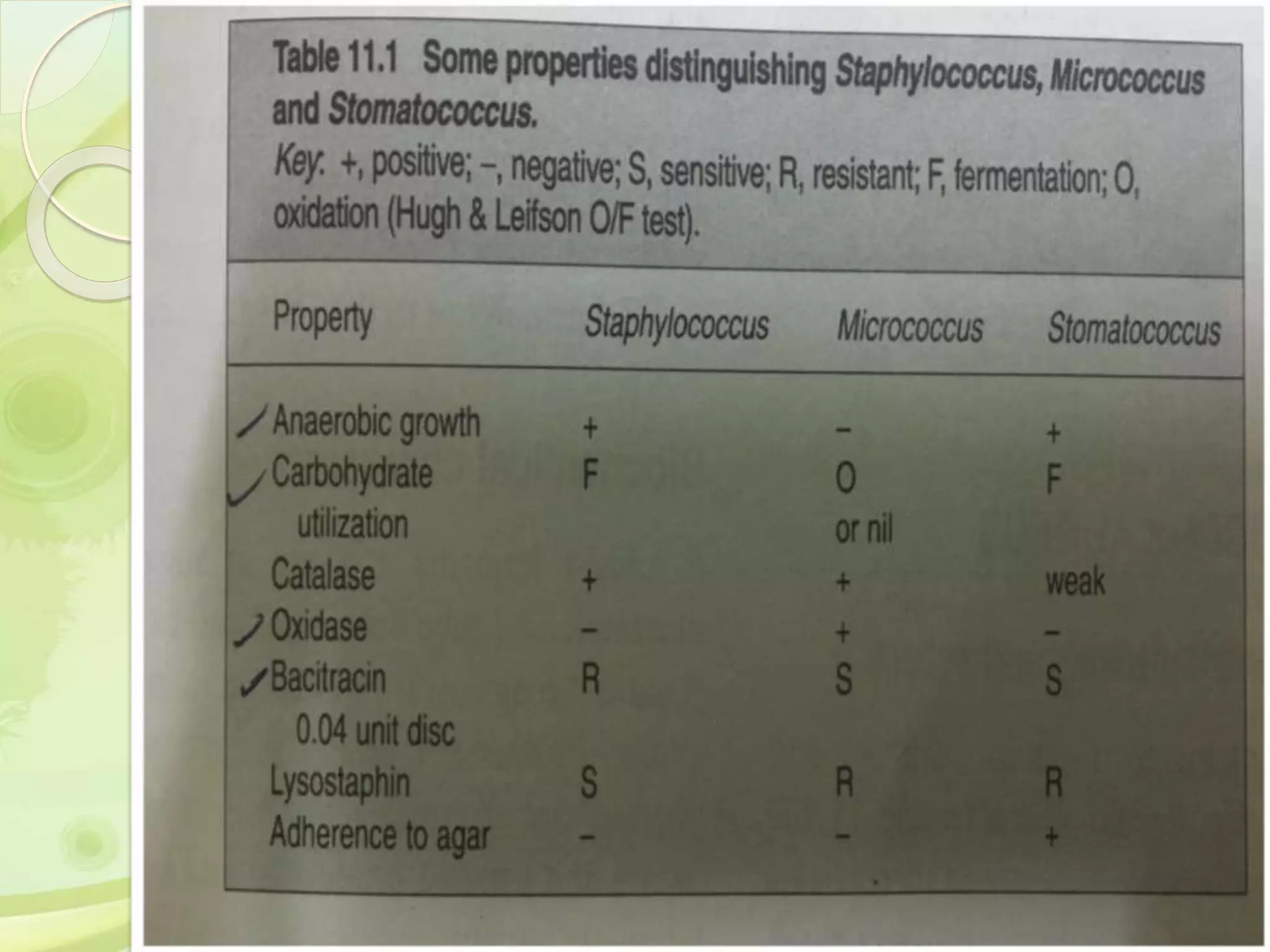
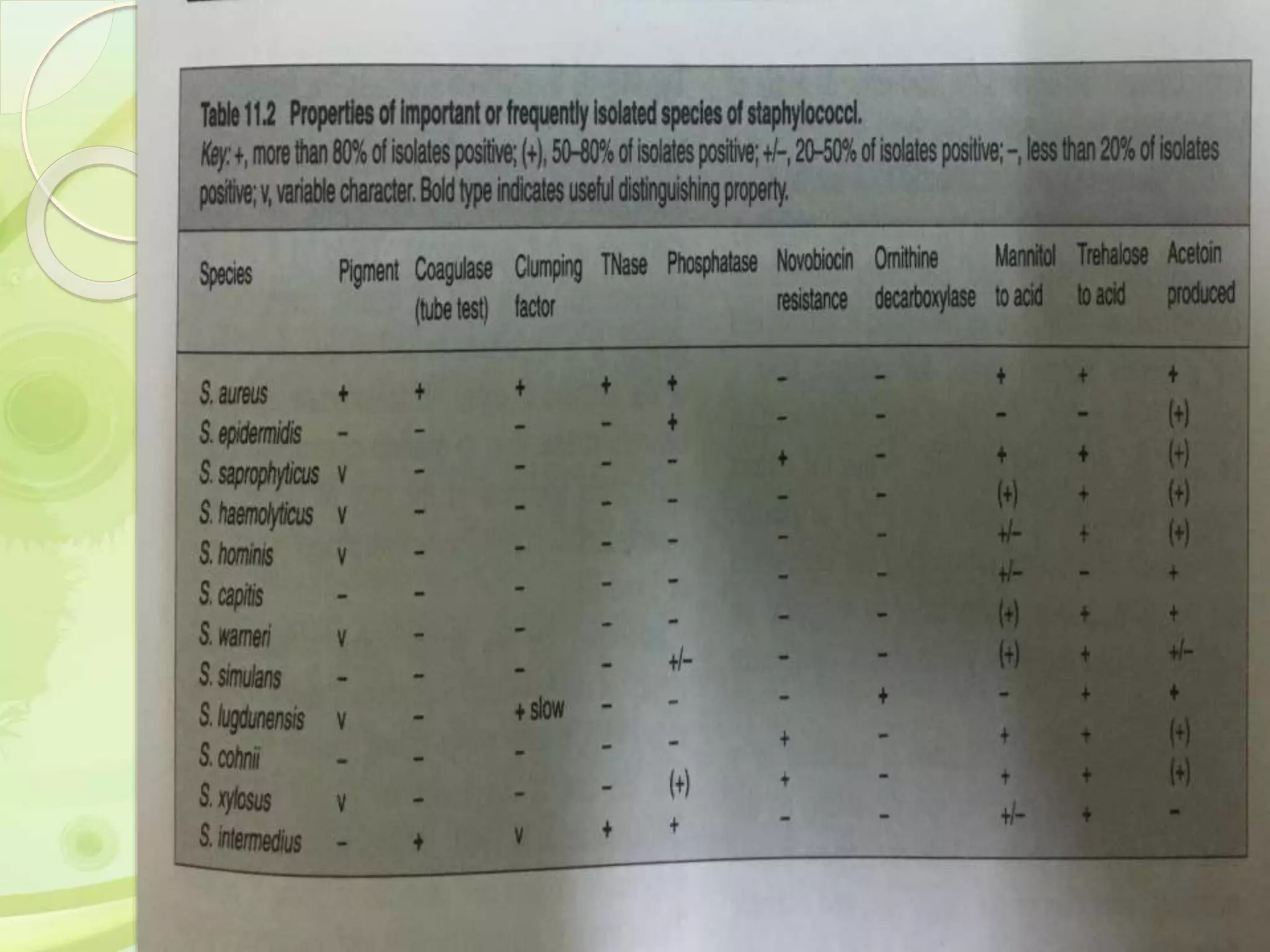
This document discusses the laboratory diagnosis of Staphylococcus, including sample collection, direct smear microscopy, culture techniques, biochemical reactions, antibiotic sensitivity testing, and typing of Staphylococcus aureus. Appropriate samples are collected based on the site of infection and transported to the laboratory for analysis. Direct smear microscopy can identify Gram-positive cocci clusters. Culture techniques help isolate and identify Staphylococcus colonies based on morphology and biochemical reactions provide further characterization. Antibiotic sensitivity testing determines effective treatment options and typing methods like bacteriophage typing are used for epidemiological purposes.