Clostridium perfringens.pptx
- 1. By Dr. Rakesh Prasad Sah Associate Professor, Microbiology Clostridium Perfringens (Gas gangrene)
- 2. Clinical Based Question (LAQ) •A 25 year old man met with a road accident. He had crush injury and fracture of the right lower leg. He was admitted to the hospital. On loc al examination, there was oedema and pain at the site of injury. On p alpitation, crepitus was felt around the wound. •What is your provisional diagnosis? •Causative organisms? •Pathogenesis? •Lab diagnosis?
- 3. Introduction •Anaerobic bacteria do not have cytochrome system for oxyg en metabolism unable to neutralize toxic oxygen metabolites either can not grow in presence of oxygen (obligate anaero bes) or do not utilize oxygen but tolerate its presence of (aerotol erant anaerobes). •Needs special requirements for their growth in culture (Anaero bic Conditions)
- 4. •Needs special requirements for their growth in culture (Anaero bic Conditions) • McIntosh and Filde’s anaerobic Jar • GasPak system •Medium with low redox potential: by adding reducing substances to media e.g. •Unsaturated fatty acid •Ascorbic acid •Glutathione •Cysteine •Glucose •Sulfites •Metallic iron
- 5. Clostridium •Consists of anaerobic, spore forming, Gram positive bacilli. •Name Clostridium derived from the word “Kloster” spindle. •Spores wider than bacterial bodies swollen appearance resembling a “spindle”.
- 6. •Genus contains bacteria causes 3 major ds. due to powerful exotoxins. • Tetanus • Gas gangrene • Food Poisoning
- 7. Classification S. No Disease Organisms 1 Tetanus Cl. tetani 2 Gas gangrene A) Established Pathogens Cl. perfringens (Cl. welchii), Cl. novyi (Cl. oed ematiens), Cl. septicum B) Less Pathogenic Cl. histolyticum, Cl. fallax C) Doubtful pathogens Cl. bifermentans, Cl. sporogens 3 Food Poisoning A) Gastroenteritis Cl. perfringens (Type A) B) Necrotising Enteritis Cl. perfringens (Type C) C) Botulism Cl. botulinum 4 Acute colitis Cl. difficile
- 8. Cl. perfringens (Cl. welchii) •Cultivated by Achalme (1891) and was first described in detail by Welch and Nuttal (1892). •Cl. Perfringens most common & impt etiological agent of gas gangren e (60%), followed by Cl. Novyi (30-40%) and Cl. Septicum (10-20%). •Cl. Perfringens also produces food poisoining and necrotising enteritis in man. •Commensals of large intestine and spores are found in soil and dust. •Is invasive as well as toxigenic
- 9. Morphology •Large, stout, Gram positive bacillus wit h sub terminal spores. •Occurs single or in chains and is pleomorphic. •Capsulated and non-motile. •Spore formation induce on special media.
- 10. Culture •Grows on • Blood agar • Cooked meat broth (CMB) • Thioglycollate broth •Grows best in media containing carbohydrate e.g. glucose blood agar •Anaerobic, PH 5.5-8.0, tempr 20- 500C, Opt tempr 370C
- 11. Blood Agar •Most strains targeted hemoly sis narrow zone of complete h emolysis theta toxin and much wider zone of incomplete haemol ysis alpha toxin Cooked Meat broth •Meat pieces pink colour but are not digested.
- 12. Biochemical Reactions •Saccharolytic and mild proteolytic action (gelatin liquefaction). •Ferments • glucose • Lactose • Sucrose • Maltose •Litmus milk lactose fermentation acid colour of litmus blue to red. •Coagulates casein (acid clot) clotted milk disrupted due to vigorous gas production stormy fermentation. •Indole Negative •MR Positive •VP Negative •Reduces Nitrates
- 14. Classification •Produces 12 distinct toxins •On the basis of production of 4 major toxins (alpha, beta, epsilon and iota) classified into five types A to E. S. No. Strain Type Toxin Produced 1 Type A Alpha toxin 2 Type B Alpha, beta and epsilon toxins 3 Type C Alpha and beta toxins 4 Type D Alpha and epsilon toxins 5 Type E Alpha and iota toxins Type A causes Gas gangrene and some strains causes enterotoxins
- 15. Alpha (α) Toxin •Produced by all types of Cl. Perfringens most abundantly by type A strai ns. •Chemically it is a phospholipidase (lecithinase C) and is responsible for toxaemia in gas gangrene. •Is heat stable, lethal, dermonecrotic and hemolytic. •Hemolysis is best seen incubation at 370C followed by chilling at 40C. •Splits “lecithin” an impt constituents of mammalian cell membrane. •Used for rapid detection of Cl. perfringens in clinical specimens (Nagler reactio n).
- 16. Cl. Perfringens grown on medium containing 6% agar,5% Fildes peptic digest of sheep blood and 20% human serum or 5% egg yolk with Neomycin sulphate anti-toxin is spread to one half of the culture plate incubated at 370C for 24hrs Colonies on the half of the plate without antitoxin surrounded by opacity while colonies around other half with antitoxin shows no opacity due to neutralisation of alpha toxin. Nagler Reaction
- 17. Alpha Toxin (Lecithinase C) Lecithin Diglyceride Phosphoryl Choline Deposits around the colony Opacity
- 18. Reverse CAMP Test •Is similar to the CAMP tests for identifying group B streptococci •Except that Clostridium sp. Is inoculated in place of Staph. aureus and a known group B streptococcus is used. •Group B streptococci show enhanced hemolysis with other clostridia but only Cl. Perfringens exhibits accenentuated zone of hemolysis as butterfly appearance.
- 19. Other Minor Toxins S.no. Toxin Actions 1 Gamm () and eta () minor lethal actions 2 Delta () lethal and hemolytic 3 Theta () oxygen labile Agenically related to streptolysin O. 4 Kappa () collagenase 5 Lambda () proteinase and gelatinase 6 Mu () hyaluronidase 7 Nu () deoxyribonuclease •Beta (), epsilon (), and iota () toxins lethal and necrotizing pr operties.
- 20. Enterotoxin •Some strains of type A enterotoxin diarrhoea & other symptoms of food poisoning. Other Soluble Substances • Haemagglutinins • Neuraminidase • Fibrinolysin • Haemolysin • Histamine
- 21. Clinical Manifestations •Polymicrobial involving other clostridia species. 1. Simple wound contamination • Involves wound surface contamination without invasion of underlying tissue occurs in absence of devitalized tissue Clostridial Wound infections
- 22. 2. Anaerobic cellulitis •Involves facial plane with minimal toxin release, without muscle inv asion. 3. Anaerobic myositis (gas gangrene) •Muscle invasion occurs leads to gas in the muscle compartment with abundant toxin release.
- 23. Clostridial Enteric infections •Caused by C. perfringens type A enterotoxin. •Occurs consumption of impro perly cooked contaminated meat. •Enterotoxin acts by forming pores in the intestinal mucosal membrane. 1. Food Poisoning
- 24. Clostridial Enteric infections •A life threatining condition •Characterized by • Ischemic necrosis of the Jejunum And • Gas in the tissue. •Caused by C. perfringens type C strains β-toxin. Enteritis necroticans (gas gangrene of the bowel)
- 25. Necrotizing enterocolitis •Resembles enteritis necroticans but associated with C. perfringens type A. •Gangrenous appendicitis.
- 26. Other Clostridial infections •Bacteremia (C. perfringens, C. tertium and C. septicum) •Skin and soft tissue infections • C. perfringens, C. histolyticum, C. septicum, C. novyi and C. sord ellii cause necrotizing infections of skin and soft tissues • Infection of the endometrium toxic shock syndrome • Meningitis and brain abscess • Panophthalmitis (C. sordellii or C. perfrngens) (rapidly progressing (choroid, retina, vitreous fluid, aqueous fluid, cornea, sclera, and conjunctiva) with extension into the orbital structures.)
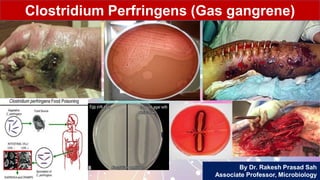
- 27. Gas Gangrene Definition •A rapidly spreading, edematous myone- crosis occuring in association with severly crushed wounds contaminated with pathogenic clostridia, particularly with C. perfringens. •Previously the disease was called Malignant edema or Clostridial myonecrosis.
- 28. Pathogenesis Anaerobic Environment Contamination of wounds Non-traumatic Gas gangrene
- 29. Development of gas gangrene requires RTA (Road traffic accident) Crushing injuries of muscles lead to interruption in blood supply and tissue ischemia causing liberation of large or medium sized arteries open fractures of long bones or foreign bodies (bullet injuries) or devitalized tissues Anoxic muscle Anaerobic environment Starts utilizing pyruvate anaerobically to produce lactic acid
- 31. Contamination of wound •Contamination of wound with Clostridial spores present In the s oil or clothes. •Rarely non-traumatic gas gangrene hematogenous seeding of normal muscle with bowel clostridia occurs in people with GIT pathologies (e.g. colonic malignancy)
- 32. Clinical Manifestations of Gas Gangrene •I.P. 10-48hrs for C. perfringens • 2-3 days for C. septicum • 5-6 days for C. novyi •Various manifestation include • Sudden onset of excruciating pain at the affected site. • Rapid development of a foul-smelling thin serosanguineous discharge. • Gas bubbles (Crepitus) in the muscle planes
- 34. Clinical Manifestations of Gas Gangrene Continue…. •Various manifestation include • Brawny edema and induration. • Gangrenous tissues become liquefied and sloughed off. • Shock and organ failure develop later. • High mortality rate (50%).
- 35. Laboratory Diagnosis •Specimens • Necrotic tissues • Muscle fragments • Exudates from deeper parts of the wound
- 36. Laboratory Diagnosis •Direct Microscopy • Thick, stubby, boxcar-shaped grampositive bacilli without spore are suggestive of C. perfringens.
- 37. Laboratory Diagnosis •Culture • Media RCM (Robertson cooked meat broth, egg yolk, agar etc) • Incubation anaerobically by GasPak
- 38. Identification Target hemolysis (double zone hemolysis) Nagler’s reaction: Opalescence surrounding the streak line on egg yolk agar
- 39. Identification Reverse CAMP test: Positive Heat tolerance test: Positive In litmus milk: Produces stormy clot reaction.
- 40. Treatment Early surgical debridement - most crucial step in the management o f gas gangrene. All devitalized tissues should be widely resected so as to remove con ditions that produce anaerobic environment. Closure of wounds – delayed for 5–6 days until the sites are free from infection.
- 41. Antibiotics: Combination of penicillin and clindamycin is recom mended for 10–14 days Hyperbaric oxygen: It may kill the obligate anaerobic clostridia - C. perfringens; however, it has no effect on aerotolerant clostri dia (C. septicum) Passive immunization with anti-α-toxin antiserum.
- 42. Prophylaxis •Surgery •Antibiotics: Metronidazole, penicillin, sulphonamide, tetracycl ine, and amoxycillin. •Antitoxin •Hyperbaric oxygen •Active immunisation Toxoids.
- 43. Clinical Based Question (LAQ) •A 25 year old man met with a road accident. He had crush injury and fracture of the right lower leg. He was admitted to the hospital. On loc al examination, there was oedema and pain at the site of injury. On p alpitation, crepitus was felt around the wound. •What is your provisional diagnosis? •Causative organisms? •Pathogenesis? •Lab diagnosis?
