This document discusses pH determination methods. It defines pH as the negative logarithm of hydrogen ion concentration and describes how Sorensen developed the pH scale in 1909. A pH of 7 is neutral as hydrogen and hydroxide ion concentrations are equal. The document outlines that the glass electrode method measures potential difference using a pH meter to determine pH electrometrically. It also describes colorimetric determination where pH is estimated by comparing color changes of indicators like phenolphthalein in solutions of known pH.

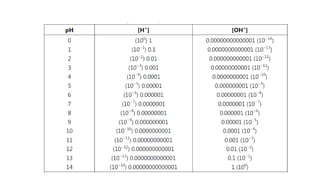
![Dissociation constant (Kw)
• In any aqueous solution at a given temperature (Dissociation
constant = Kw)
• [H+] = [OH-] = 1.0 x 10-7 M
• [1.0 x 10-7][1.0 x 10-7] = 1.0 x 10-14
• Kw = [H+] [OH-]
• Acids
• [H+] increases and [OH-] decreases
• Bases
• [OH-] increases and [H+] decreases](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/phsb-201106130603/85/Sorensen-s-pH-scale-SB-2-320.jpg)
![Sorensen’s pH scale
• pH = − log [H+]
• where, log is a base −10 logarithm and [H+] is the
concentration of hydrogen ions in moles per litre of solution.
• pOH = − log [OH-]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/phsb-201106130603/85/Sorensen-s-pH-scale-SB-4-320.jpg)
![Sorensen’s pH scale
• Danish biochemist Soren Sorensen in 1909 developed the pH scale and
introduced pH definition as minus (−) logarithm of [H+] to the base 10.
• A pH of 7 is considered as “neutral”, because the concentration of
hydrogen ions is exactly equal to the concentration of hydroxide (OH−)
ions produced by dissociation of the water.
• The hydrogen ion concentration in pure water at room temperature is
about 1 × 10−7 M .
• Increasing the concentration of hydrogen ions above 1 × 10−7 M produces
a solution with a pH of less than 7, and the solution is considered as
“acidic”.
• On other hand decreasing the concentration of hydrogen ions below 1 ×
10−7 M produces a solution with a pH above 7, and the solution is
considered “alkaline” or “basic”.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/phsb-201106130603/85/Sorensen-s-pH-scale-SB-5-320.jpg)