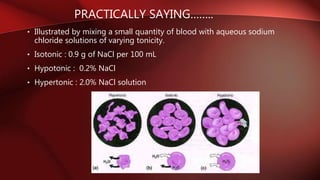
Buffer solutions maintain a fairly constant pH even when small amounts of acid or base are added. There are isotonic, hypotonic, and hypertonic solutions depending on their solute concentration compared to blood or other fluids. Buffer solutions are important for intravenous injections, which should be isotonic with blood plasma. Tonicity can be measured using haemolytic or colligative methods. The colligative method involves measuring properties like freezing point depression, which should be -0.52°C for a solution to be considered isotonic with blood plasma. Calculating tonicity is important for parenteral and ophthalmic preparations.