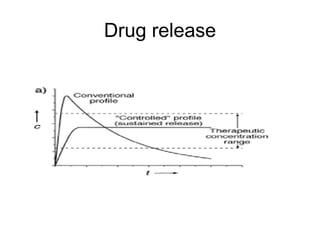
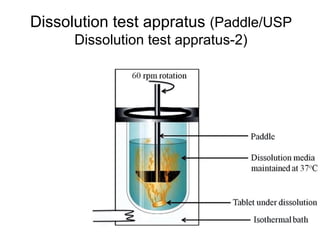
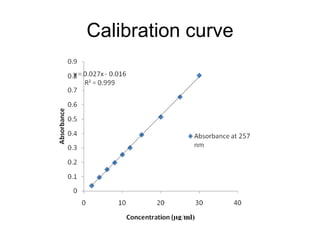
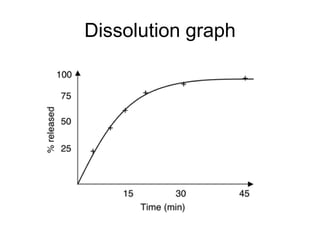
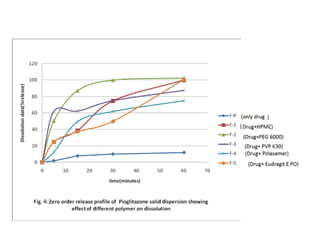
This document discusses drug dissolution and release from solid oral dosage forms. It provides 3 key points:
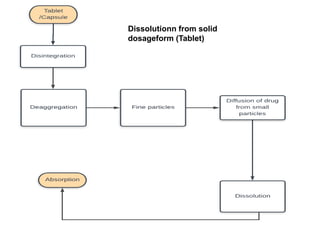
1) Dissolution is the process by which a solid drug forms a solution when it comes into contact with fluid in the body. The drug must dissolve before it can be absorbed and produce its pharmacological effects.
2) Several factors can impact the rate of drug dissolution including the drug's solubility, particle size, polymorphism, as well as formulation factors like excipients and manufacturing methods.
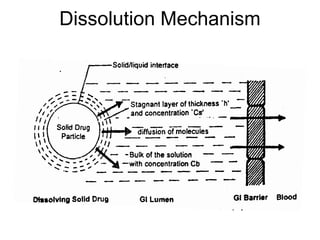
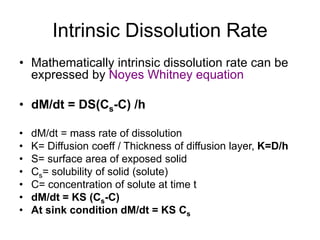
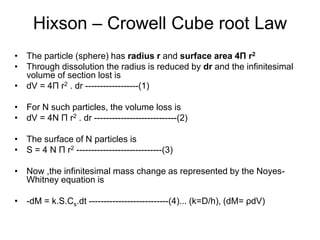
3) Common mathematical models like the Noyes-Whitney equation and Hixson-Crowell cube root law are used to describe and quantify drug dissolution kinetics based on assumptions like diffusion layer thickness and geometric














![• The drugs density is multiplied by the infinitesimal volume change ... ρ.dV = dM
....from eqn (4)
• -ρ.dV = k.S.Cs.dt --------------------------- (5)
• Equations (2) and (3) are substituted into equation (5) , to yield
• -4 ρ N Π r2 . dr = 4 N Π r2 . k .Cs .dt -------------(6)
• Equation (6) is divided through by 4 N Π r2 to give
• - ρ . dr = k Cs.dt -------------------------(7)
• Integration with r = ro at t= 0 produces the expression
• r = ro – (kCs . t/ ρ) -----------------------------(8)
• The radius of spherical particles can be replaced by the mass of N particles by
using the relationship of volume of sphere
• M = N ρ(Π/6)d3 ----------------------------(9)
• Taking cube root of the equation (9) yield,
• M1/3 = [ N ρ(Π/6)] 1/3 . d. ----------------------------(10)
• The diameter d from equation (10) ,is substituted for 2r into equation (8) to give...](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dissolutionv2-200310145732/85/Dissolution-v2-25-320.jpg)
![• M1/3 = [ N ρ(Π/6)] 1/3 . 2r
• Mo
1/3 - M 1/3 = kt
• Mo = Original mass of drug particles
• k = [ N ρ (Π/6) ]1/3.2 k Cs/ρ = Mo
1/3 /d . 2k Cs / ρ cube root
dissolution rate constant
• t = time
• M = Mass of N no. of particles Nρ(π/6)d3
• N= No. of particles
• ρ = Density of particles
• d = Diameter of particles
Hixson – Crowell Cube root Law](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dissolutionv2-200310145732/85/Dissolution-v2-26-320.jpg)
