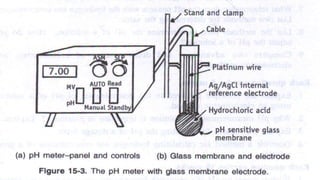
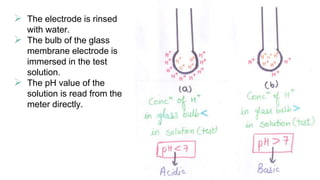
The document discusses the determination of pH using the electrometric method, specifically highlighting the use of glass electrodes. It explains the principles of pH measurement, the calibration process with standard buffer solutions, and lists advantages such as high sensitivity and rapid equilibrium establishment. However, it also notes disadvantages, including inapplicability to viscous solutions and higher initial costs compared to colorimetric methods.