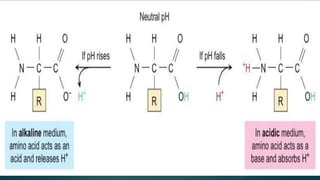
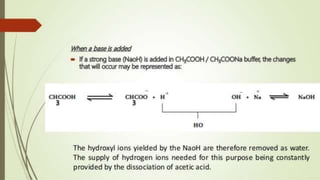
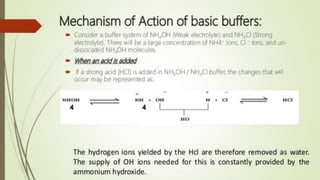
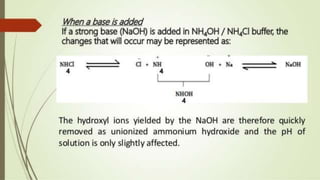
1. The document discusses buffers in pharmaceutical and biological systems. It describes various buffer systems that function in the human body to maintain blood pH, including bicarbonate-carbonic acid, phosphate, and protein buffers.
2. The bicarbonate-carbonic acid buffer system regulates blood pH through reactions involving sodium bicarbonate, carbonic acid, and water. The phosphate buffer system involves the conversion between sodium dihydrogen phosphate and sodium monohydrogen phosphate through reactions with strong acids and bases.
3. Hemoglobin and proteins also act as buffers, with hemoglobin buffering pH changes during the conversion of carbon dioxide to bicarbonate and proteins buffering pH in blood plasma and within