Embed presentation
Downloaded 17 times


![BUFFER EQUATION-
• Buffer equation for Acidic buffers-
CH3COOH CH3COO- + H+
CH3COONa CH3COO- + Na+
We can also write it like this-
HA H+ + A-
BA B+ + A-
Ka = [H+][A-]/[HA]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bufferbufferequations-200215155813/85/Buffer-buffer-equations-5-320.jpg)
![[H+ ] = Ka [HA]/[BA] = K [HA]/[BA]
Taking negative logarithms of both sides of the above equation gives-
-log ([H+]) = -log (Ka ) – log ([HA]/[BA])
or pH = pKa – log ([HA]/[BA])
It can also be written as-
pH = pKa + log ([BA]/[HA])
This form of the ionization or dissociation constant expression is called the
Henderson-Hasselbalch equation.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bufferbufferequations-200215155813/85/Buffer-buffer-equations-6-320.jpg)
![Buffer equation for Basic buffers-
NH4OH NH4+ + OH-
NH4Cl NH4+ + Cl-
We can also write it like this-
BOH B+ + OH-
BA B+ + A-
Kb = [OH-][B+]/[BOH]
[OH- ] = Kb [BOH]/[B+] = K [BOH]/[BA]
Taking negative logarithms of both sides of the above equation gives-](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bufferbufferequations-200215155813/85/Buffer-buffer-equations-7-320.jpg)
![-log ([OH-]) = -log (Kb ) – log ([BOH]/[BA])
or pH = pKa – log ([BOH]/[BA])
It can also be written as-
pH = pKb + log ([BOH]/[BA])
This form of the ionization or dissociation constant expression is called the
Henderson-Hasselbalch equation.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bufferbufferequations-200215155813/85/Buffer-buffer-equations-8-320.jpg)


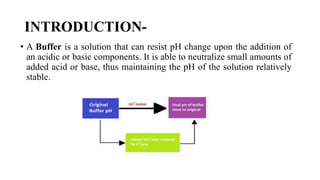
Buffers resist changes in pH upon the addition of acids or bases. There are two types of buffers: acidic buffers contain a weak acid and its salt, while alkaline buffers contain a weak base and its salt. The buffer equation, also called the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation, relates the pH of a buffer solution to the pKa of the acid or base and the ratio of the concentrations of the conjugate base and acid or base and conjugate acid. Specifically, for acidic buffers the pH equals the pKa plus the log of the ratio of the conjugate base to acid concentrations, and for alkaline buffers the pH equals the pKb plus the log of the ratio of the base to conjugate acid concentrations.




![BUFFER EQUATION-
• Buffer equation for Acidic buffers-
CH3COOH CH3COO- + H+
CH3COONa CH3COO- + Na+
We can also write it like this-
HA H+ + A-
BA B+ + A-
Ka = [H+][A-]/[HA]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bufferbufferequations-200215155813/85/Buffer-buffer-equations-5-320.jpg)
![[H+ ] = Ka [HA]/[BA] = K [HA]/[BA]
Taking negative logarithms of both sides of the above equation gives-
-log ([H+]) = -log (Ka ) – log ([HA]/[BA])
or pH = pKa – log ([HA]/[BA])
It can also be written as-
pH = pKa + log ([BA]/[HA])
This form of the ionization or dissociation constant expression is called the
Henderson-Hasselbalch equation.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bufferbufferequations-200215155813/85/Buffer-buffer-equations-6-320.jpg)
![Buffer equation for Basic buffers-
NH4OH NH4+ + OH-
NH4Cl NH4+ + Cl-
We can also write it like this-
BOH B+ + OH-
BA B+ + A-
Kb = [OH-][B+]/[BOH]
[OH- ] = Kb [BOH]/[B+] = K [BOH]/[BA]
Taking negative logarithms of both sides of the above equation gives-](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bufferbufferequations-200215155813/85/Buffer-buffer-equations-7-320.jpg)
![-log ([OH-]) = -log (Kb ) – log ([BOH]/[BA])
or pH = pKa – log ([BOH]/[BA])
It can also be written as-
pH = pKb + log ([BOH]/[BA])
This form of the ionization or dissociation constant expression is called the
Henderson-Hasselbalch equation.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bufferbufferequations-200215155813/85/Buffer-buffer-equations-8-320.jpg)
