This document discusses pH, buffers, and isotonic solutions. It begins by defining pH as a measure of hydrogen ion concentration in water using Sorensen's pH scale. It then describes two methods for determining pH: the calorimetric method which compares a solution's color to standard buffers and indicators, and the electrometric method which uses a pH meter. The document also discusses buffers and their importance in biological and pharmaceutical systems like blood, tears, and injections to maintain optimal pH levels. Factors that can influence a buffer's pH like temperature, dilution, and ionic strength are also covered.




![Sorensen’s pH Scale….
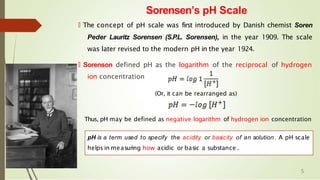
🠶 Based on the pH values and different concentrations of H+ ions, a scale has been
devised and named after Sorensen.
🠶 The scale starts with zero pH, i.e, hydrogen ion
concentration is 100. It means the solution is strongly
acidic .
🠶 At the other end of the scale, pH is 14. i.e, hydrogen
ion concentration is 10-14. It means the solution is
strongly alkaline .
🠶 The central point pH in the scale is 7.0, because [H+] is
equal to [OH+], i.e., hydrogen ion concentration is10-
7
🠶 Solutions with a pH less than 7 are acidic and solutions with a pH greater than 7
are basic. Pure water neutral, being neither an acid nor a base.
🠶 pH Applications: Enhancing solubility, Increasing stability, improving purity, Optimizing
biological activity and storage of products.
6](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/phbuffersisotonicsolutions-220607131628-65c30984/85/pH-BUFFERS-ISOTONIC-SOLUTIONS-pptx-6-320.jpg)




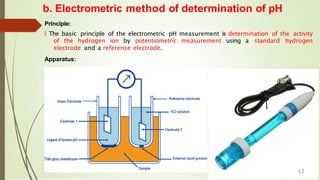
![b. Electrometric method of determination of pH..
Method:
🠶 Before use, remove electrode from storage solution, rinse, and blot, dry with a soft tissue
paper.
🠶 Calibrate the instrument with standard buffer solution. [Ex: pH 4.0, 7.0 and 10]
🠶 Once the instrument is calibrated remove the electrode from standard solution; rinse,
blot and dry.
🠶 Dip the electrode in the sample whose pH has to be measured.
🠶 Stir the sample to ensure homogeneity.
🠶 Note down the reading (pH) from the pH meter.
Advantages
• Sensitivity of the electrometric method is high. Hence, accurate measurements can be
obtained.
• The solution is uncontaminated , because the addition of indicators is avoided.
• The pH range of measurement islarge.
Disadvantages
• Electrometric method isnot suitable for viscous solutions and gels, because of poor ionic
mobility.
• Initial cost of pH meter is high compared to the colourimetric method.
13](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/phbuffersisotonicsolutions-220607131628-65c30984/85/pH-BUFFERS-ISOTONIC-SOLUTIONS-pptx-13-320.jpg)




























![For Acid Buffers:
T
he pH of acid buffer can be calculated
dissociation constant, Ka of the weak acid
from the
and the
concentrations of the acid and salt used.
🠶T
he dissociation expression of the weak acid can be
represented as:
🠶HA ↔ H+ + A-
🠶Ka =[H+] [A-
] / [HA]
🠶Or
🠶[H+] = Ka [HA] / [A-] -
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
- (1)
47](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/phbuffersisotonicsolutions-220607131628-65c30984/85/pH-BUFFERS-ISOTONIC-SOLUTIONS-pptx-47-320.jpg)

![🠶 [H+] = Ka. [Acid] / [Salt] --------- (2)
🠶 Taking log on both sides, we get:
🠶 log[H+] = logKa + log [Acid] / [Salt]
🠶 multiplying both sides by –ve sign,
🠶 -log[H+] = -logKa - log [Acid] / [Salt]
🠶 As -log[H+] = pH & -logKa = pka
🠶 pH = pka - log[Acid] / [Salt] OR
pH = pka + log[Salt] / [Acid] ---------- (3)
Eq. (3) is called as Henderson – Hasselbalch equation.
It helps in calculating the pH value of buffer solution,
if the concentrations of acid as well as that of the salt are known.
49](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/phbuffersisotonicsolutions-220607131628-65c30984/85/pH-BUFFERS-ISOTONIC-SOLUTIONS-pptx-49-320.jpg)
![For Basic Buffers
Buffer equation for basic buffer can be calculated in same way as that
for acidic buffers.
Consider a basic buffer composed of a mixture of weak base (BOH)
and its salt (BA). The dissociation constant for base can be written as,
BOH ↔ B+ + OH-
Kb = [B+] [OH-] / [BOH]
OR
[OH-] = Kb [BOH] / [B+] ------------- (1) 50](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/phbuffersisotonicsolutions-220607131628-65c30984/85/pH-BUFFERS-ISOTONIC-SOLUTIONS-pptx-50-320.jpg)

![[OH-] = Kb. [Base] / [Salt] --------- (2)
Taking log on both sides, we get:
log[OH-] = logKb + log [Base] / [Salt]
multiplying both sides by –ve sign,
-log[OH-] = -logKb - log [Base] / [Salt]
As -log[OH-] = pOH & -logKb = pkb
pOH = pkb – log [Base] / [Salt]
Or
pOH = pkb + log[Salt] / [Base] ---------- (3)
52](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/phbuffersisotonicsolutions-220607131628-65c30984/85/pH-BUFFERS-ISOTONIC-SOLUTIONS-pptx-52-320.jpg)











