The document discusses various topics related to chemical kinetics including:
- Rate of reaction is defined as the change in concentration of reactants or products over time. Rate laws relate the rate of reaction to the concentrations of reactants.
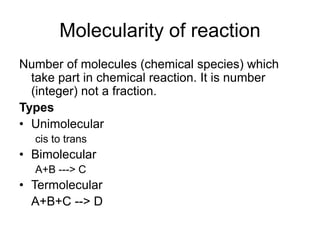
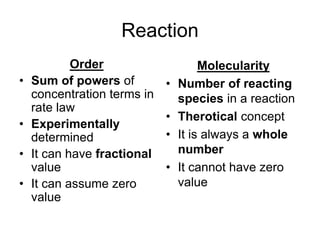
- Reaction order refers to the sum of powers in the rate law. Molecularity is the actual number of reacting species. Pseudo-orders occur when one reactant is in excess.
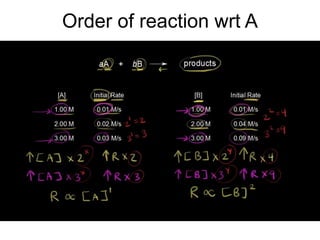
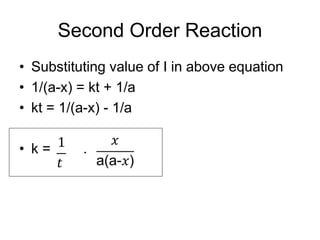
- Rate constants have different units for different reaction orders. Integrated rate laws and the half-life method can be used to determine the order of a reaction experimentally.
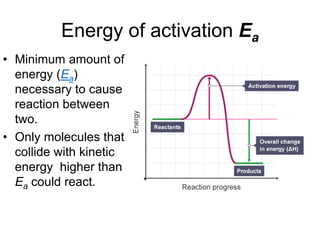
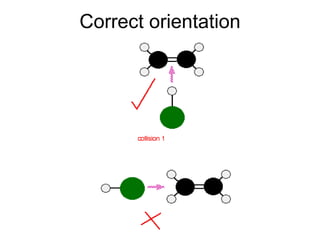
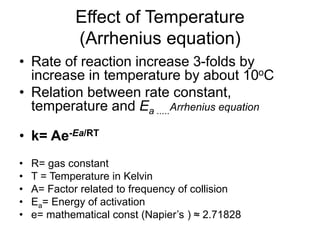
- Collision theory states that molecules must collide with sufficient energy and correct orientation to react. Physical factors like temperature, solvent, and


![Rate of reaction
• Rate of reaction = - d[A] /dt
• Rate of reaction = + d[B] /dt](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chemicalkineticsv2-200310142834/85/Chemical-kinetics-v2-3-320.jpg)
![Rate law
• The Equation which shows how rate is
related to concentration
Reaction
• 2NO + 2H2 → N2 + 2H2O
Rate Law
• Rate of reaction = k[H2] [NO]2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chemicalkineticsv2-200310142834/85/Chemical-kinetics-v2-4-320.jpg)
![Rate Law
• The rate of reaction is directly proportional
to the reactant concentration, each
concentration being raised to some power.
• 2A + B → Product
• Rate =k[A]m[B]n
(k = specific rate constant)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chemicalkineticsv2-200310142834/85/Chemical-kinetics-v2-5-320.jpg)
![Order of reaction
• Order of reaction is defined as sum of
powers of concentration in rate law.
• Rate =k[A]m[B]n
• Order of reaction in above case is (m+n)
• It is the number of concentration of
chemical species which determine the rate
of reaction depends.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chemicalkineticsv2-200310142834/85/Chemical-kinetics-v2-6-320.jpg)


![First Order Reaction
• dx/(a-x)= kdt …. (1)
• Integrating above equation..
• ∫dx/(a-x)= ∫kdt
• -ln (a-x) = kt + I …. (2)
If t=0, x=0 then I= -ln a
Substituting I in equation (2)
• ln [a/(a-x)]= kt or k = (1/t) ln [a/(a-x)]
• Converting it to common log
• k = log](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chemicalkineticsv2-200310142834/85/Chemical-kinetics-v2-12-320.jpg)



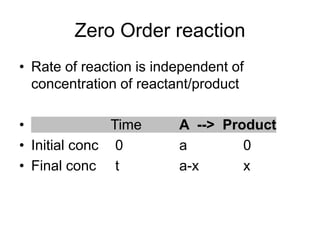
![Zero Order reaction
• Rate of reaction = -d[A]/dt= k0[A]0
• dx/dt= k0 (a-x)0
• x=k0t
• k0 is rate constant (or specific rate
constant) of zero order reaction
• Rate constant is the rate of reaction at all
concentrations x/t](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chemicalkineticsv2-200310142834/85/Chemical-kinetics-v2-18-320.jpg)
![Pseudo order reaction
• Experimental order of reaction which is not
actual is known as pseudo order
• Reaction A+B → Product
• If B is in excesses, its concentration will
practically constant and only concentration
of A will affect rate of reaction hence rate
law will be..
• Rate = k' [A]...](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chemicalkineticsv2-200310142834/85/Chemical-kinetics-v2-19-320.jpg)

![Units of rate constant
• Units of rate constant for different order
reaction are different
• For Zero order
• k= d[A]/dt
• k= mol/lit . 1/time
• k= mol lit-1 time-1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chemicalkineticsv2-200310142834/85/Chemical-kinetics-v2-21-320.jpg)
![Units of rate constant
• For first order
• k= 2.303/t . log a/(a-x)
• k= 2.303/t . log [A]0/[A]t
• k= 1/time
• k= time-1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chemicalkineticsv2-200310142834/85/Chemical-kinetics-v2-22-320.jpg)
![Units of rate constant
• For second order reaction
• k= 1/t . x/a(a-x)
• k= 1/t . x/[A]0([A]0-x)
• k= 1/time . concentration/concentration2
• k= 1/time . 1/concentration
• k= 1/time . 1/(mol/lit)
• k= mol-1 lit time-1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chemicalkineticsv2-200310142834/85/Chemical-kinetics-v2-23-320.jpg)

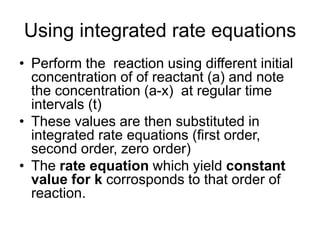
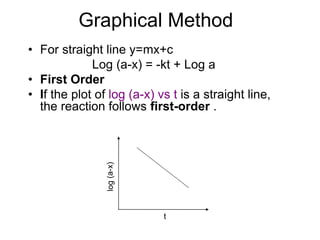
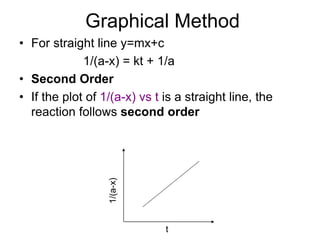


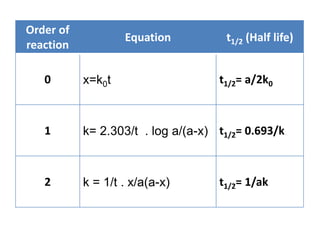
![Using Half life method
• Seperate experiments should be
performed using different initial
concentration. Let initial concentration be
A1 and A2 and corresponding half life t1
and t2
• Half life for nth order reaction is
• t1/2→ 1/ [A] n-1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chemicalkineticsv2-200310142834/85/Chemical-kinetics-v2-30-320.jpg)







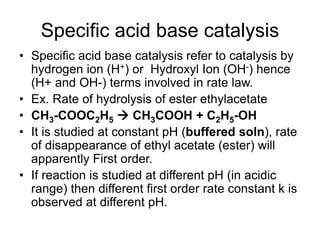
![Specific acid base catalysis
• Observed rate depend on concentration of
ester and [H+], therefore it is actually
second order reaction.
• Observed rate constant (kobs) at different
pH in acidic region, is proportional to [H+]
• kobs = kacid [H+]
• logkobs = log kacid + log [H+]
• logkobs = log kacid - pH](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chemicalkineticsv2-200310142834/85/Chemical-kinetics-v2-45-320.jpg)
![Specific acid base catalysis
• Log kobs = log kacid - pH
• It suggest log kobs vs pH is straight line
with slop -1 and y-intercept log kacid
• If we study same reaction in alkaline pH
then we observe different rate constant at
different pH
• log kobs = log kbase + log [OH-]
• kobs = kacid[H+] + kbase [OH-]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chemicalkineticsv2-200310142834/85/Chemical-kinetics-v2-46-320.jpg)
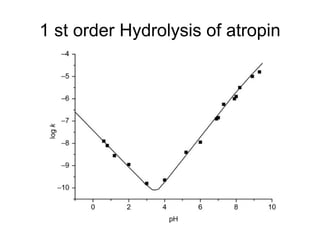
![General acid base catalysis
• Acid or base catalysis is not restricted to
effect of [H+] or [OH-]
• Other components of buffer (which is
generally used in pharma formulations)
may cause catalysis.
• Undissociated acid and base can often
produce catalytic effect
• Metal can also serve as catalyst
• Ex. Mutarotation of glucose in acetate
buffer is catalysed by [H+], [OH-], Acetate
ion [CH3COO-], undissociated acid
[CH3COOH] undissociated acetic acid.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chemicalkineticsv2-200310142834/85/Chemical-kinetics-v2-48-320.jpg)





