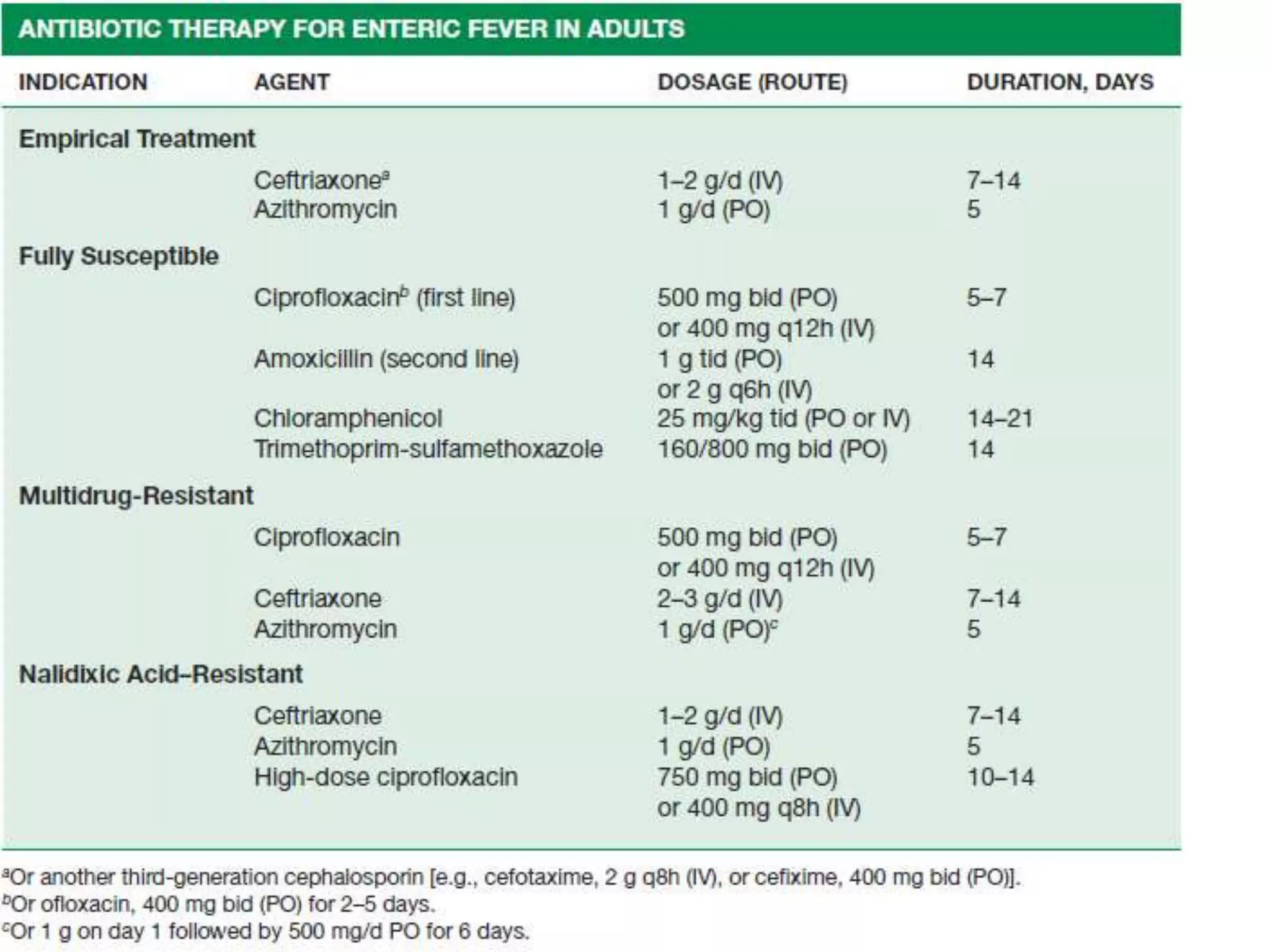
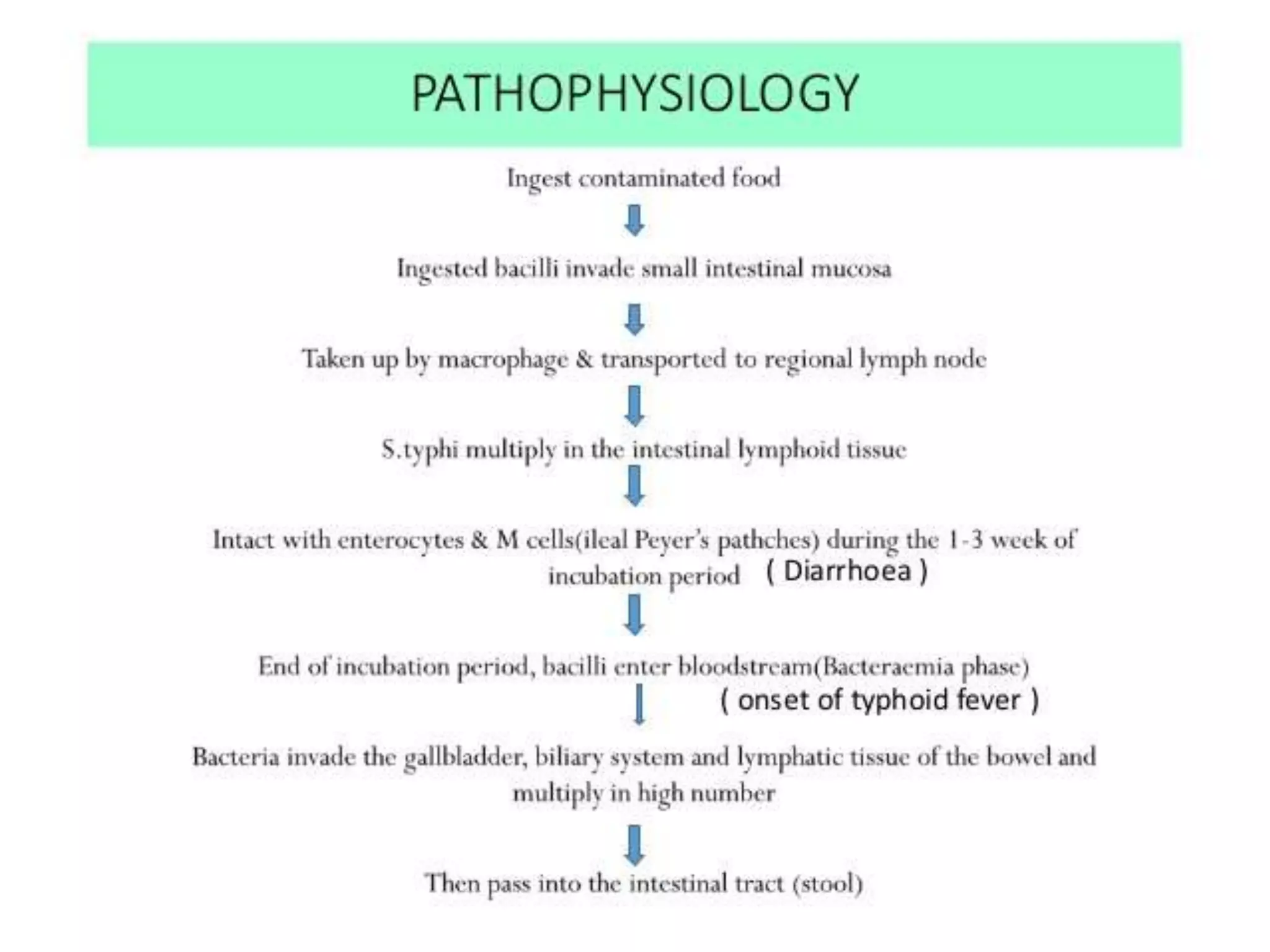
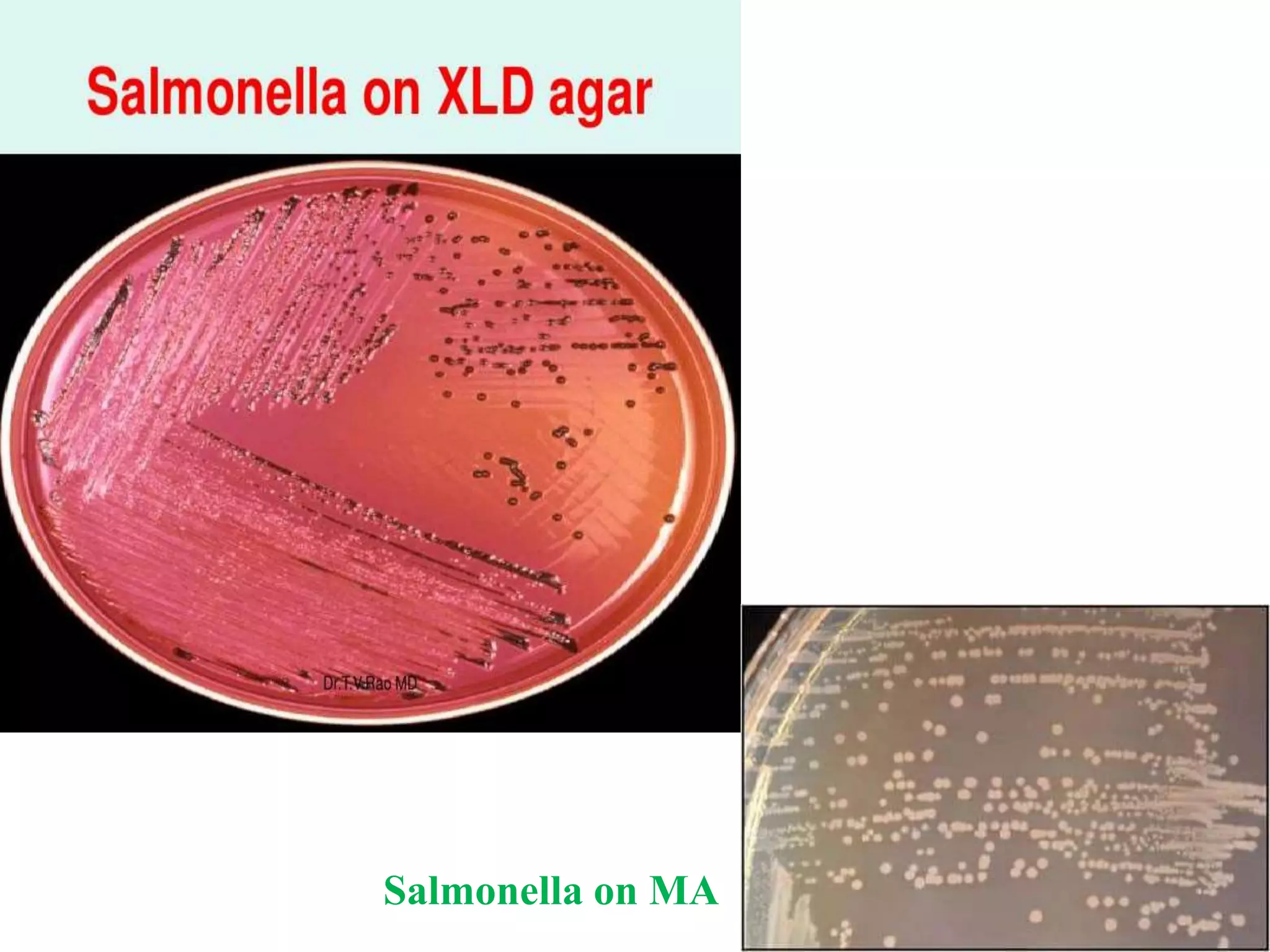
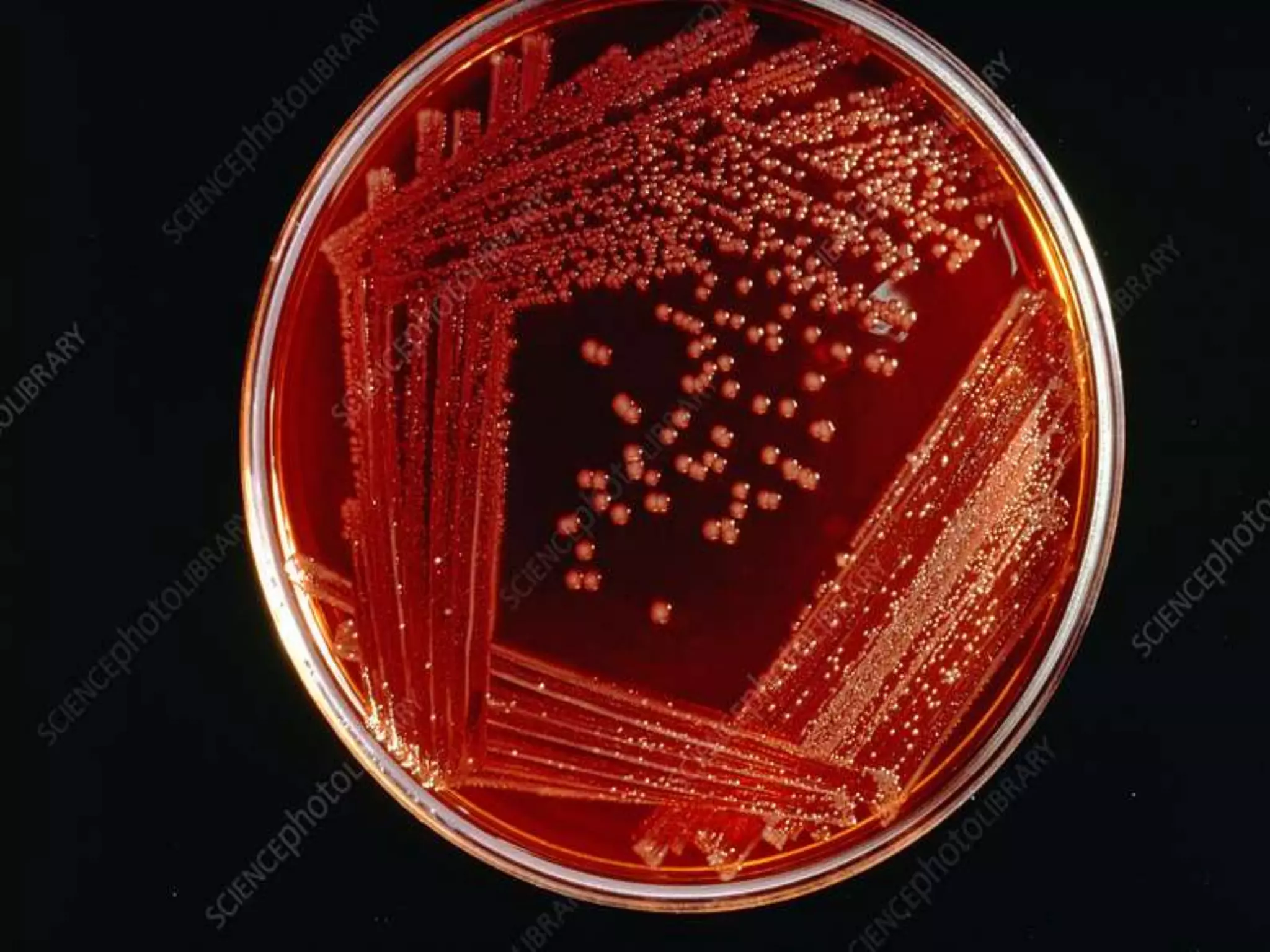
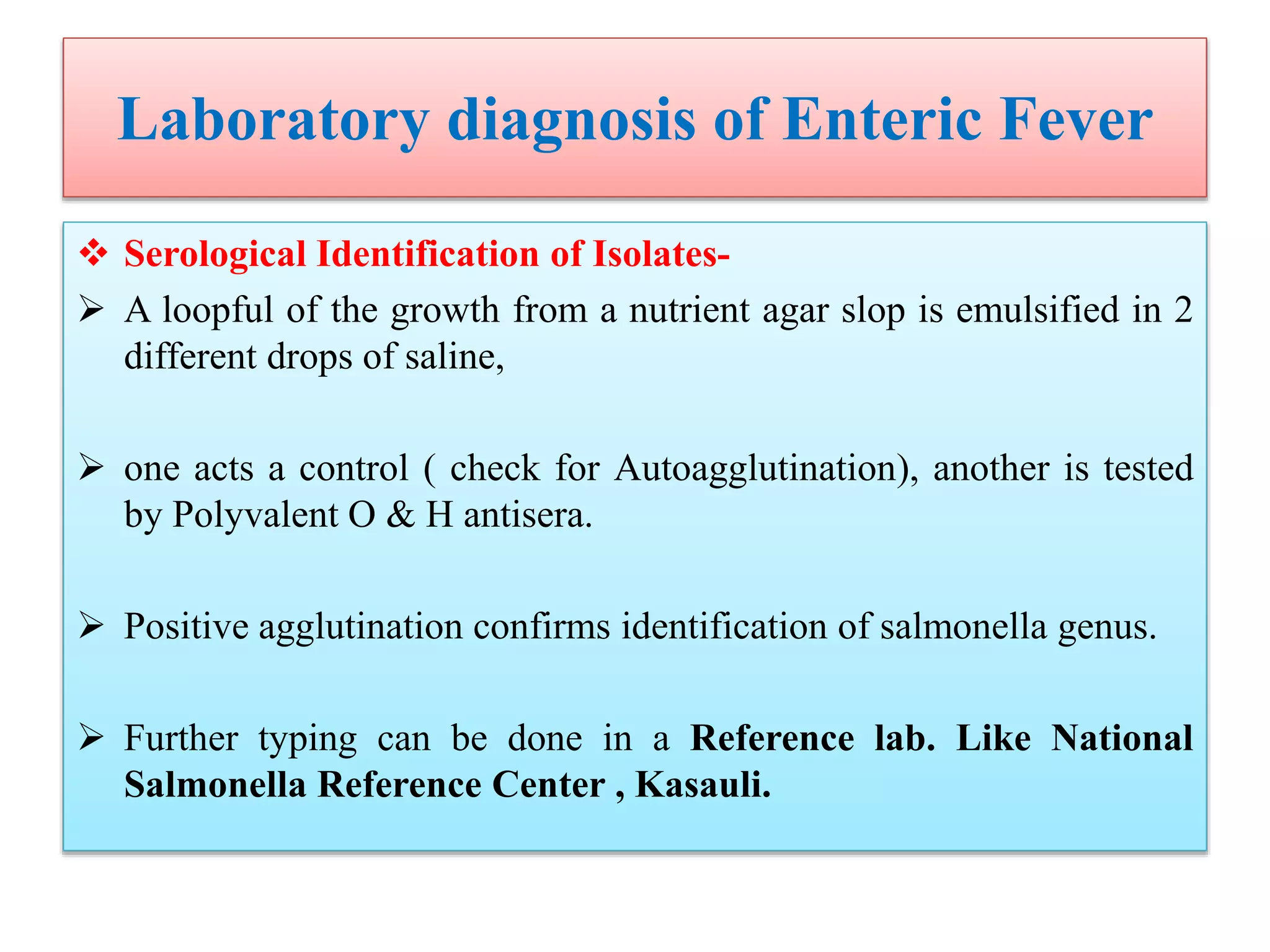
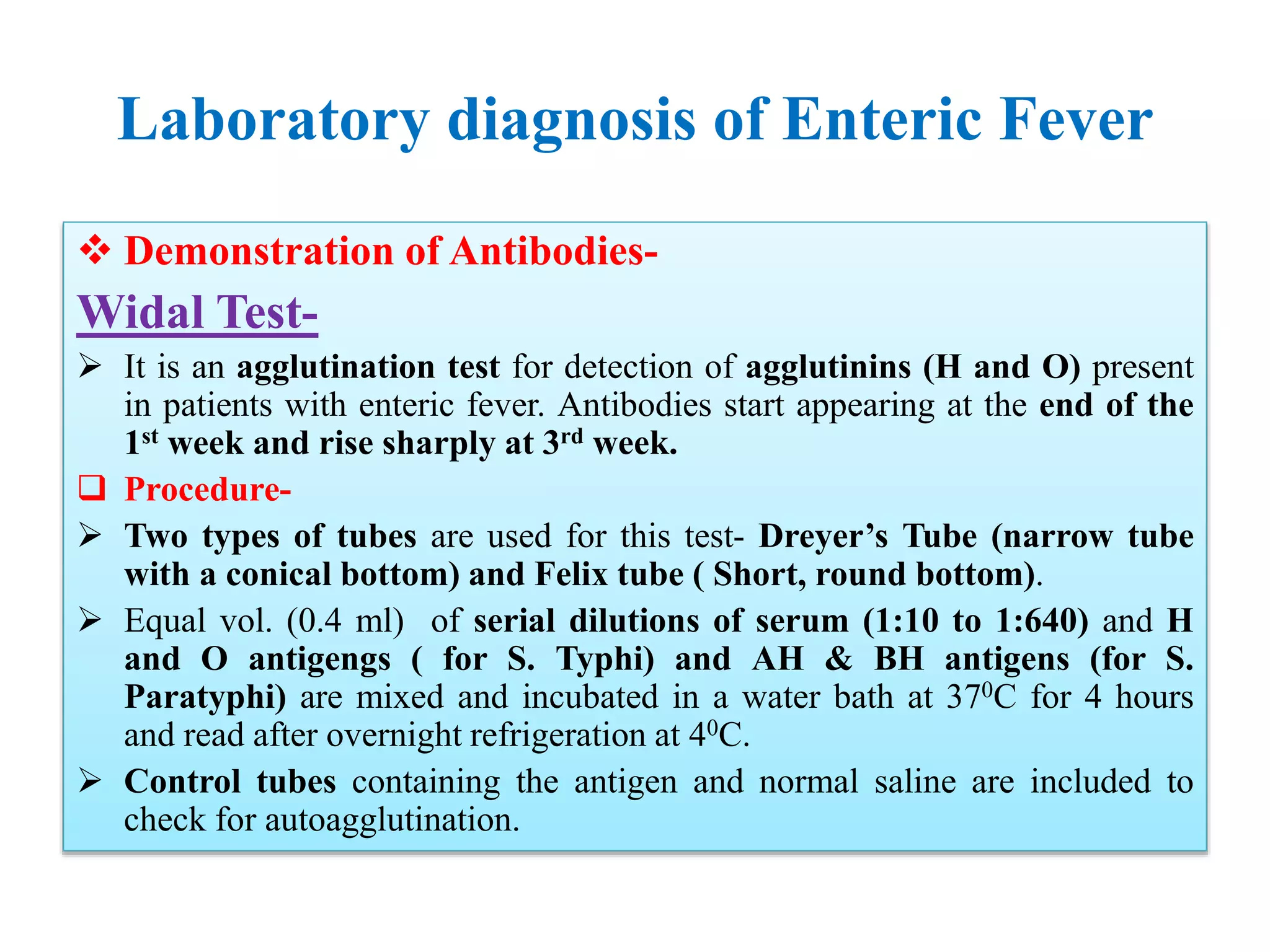
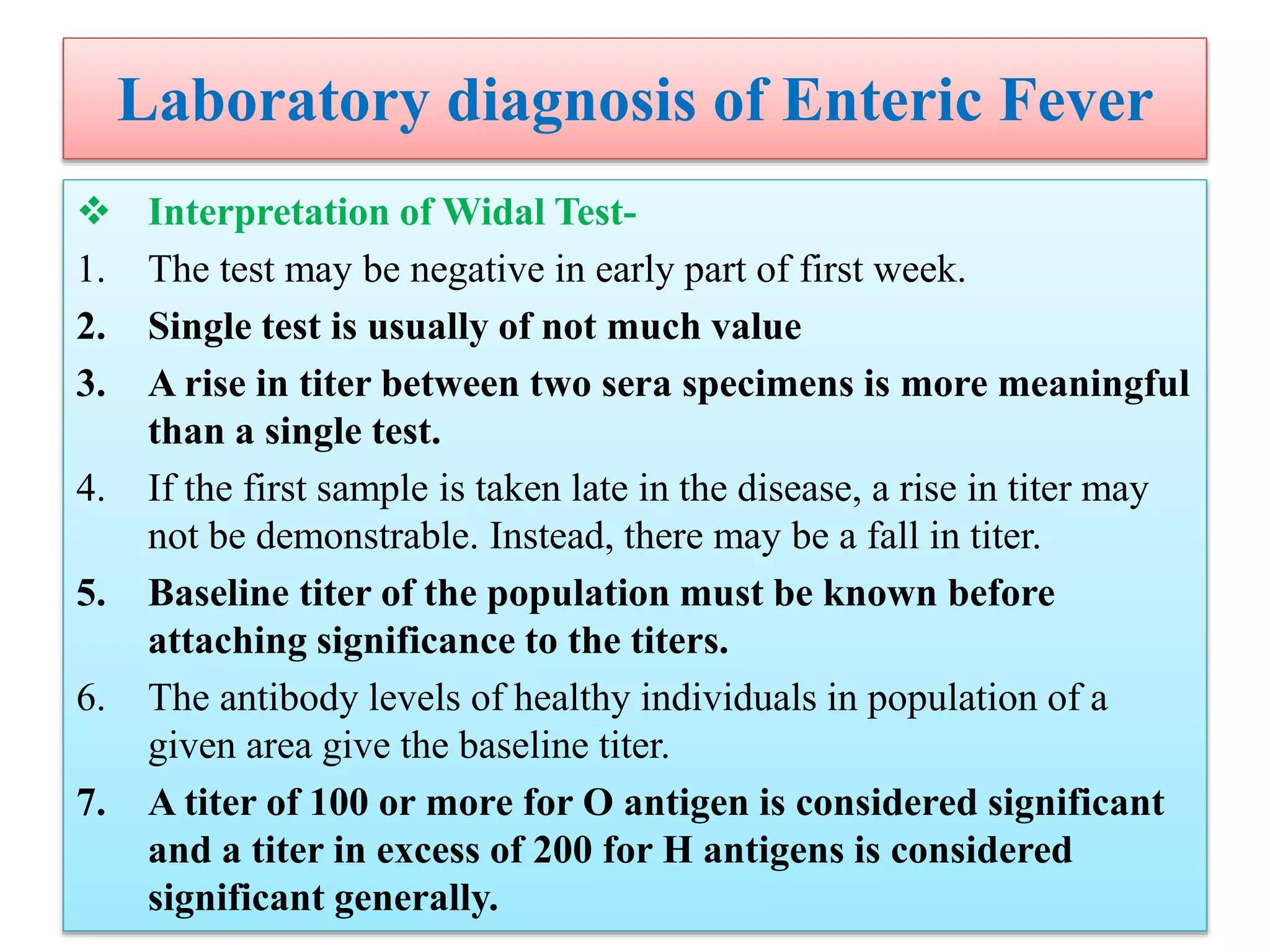
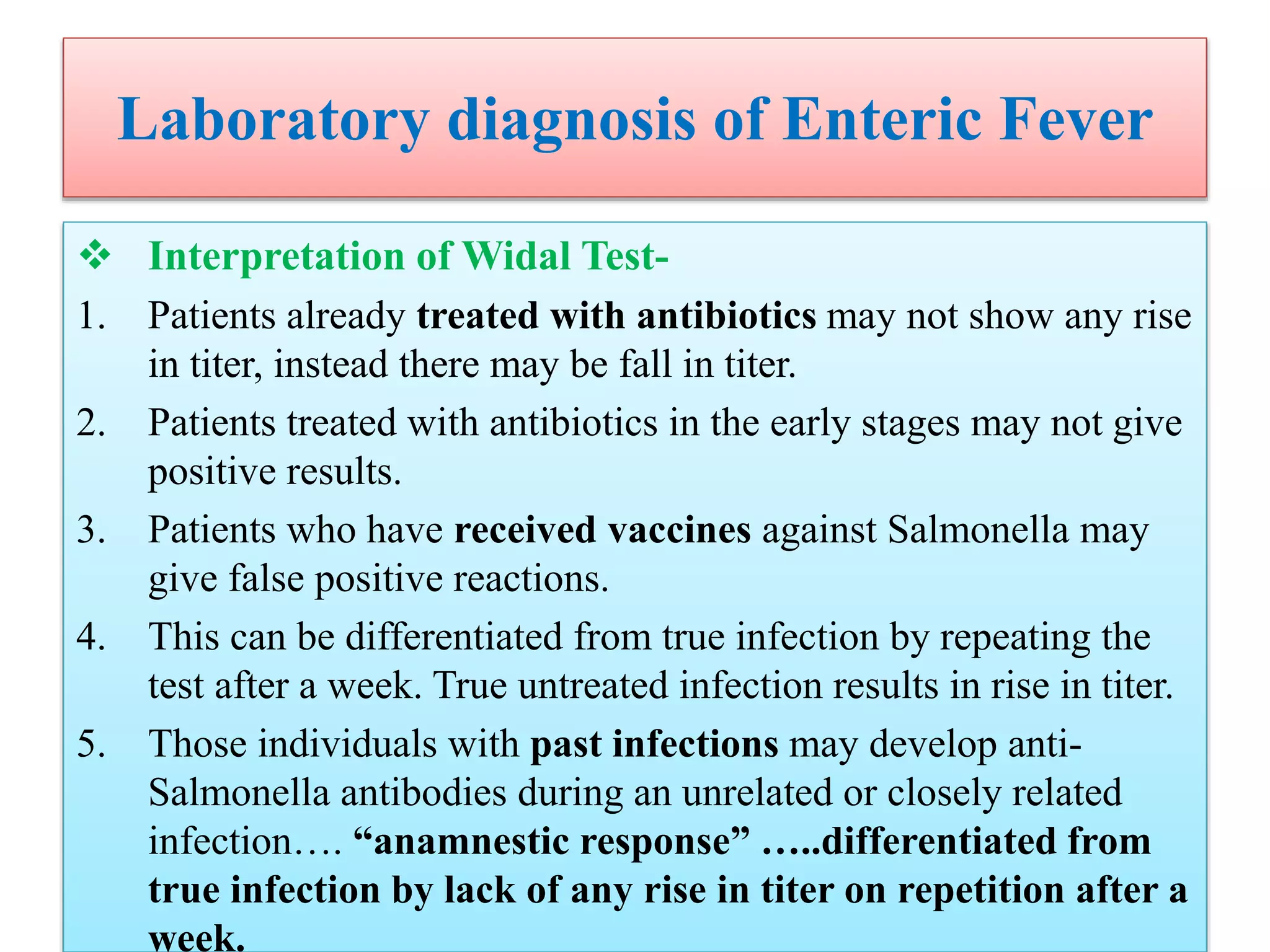
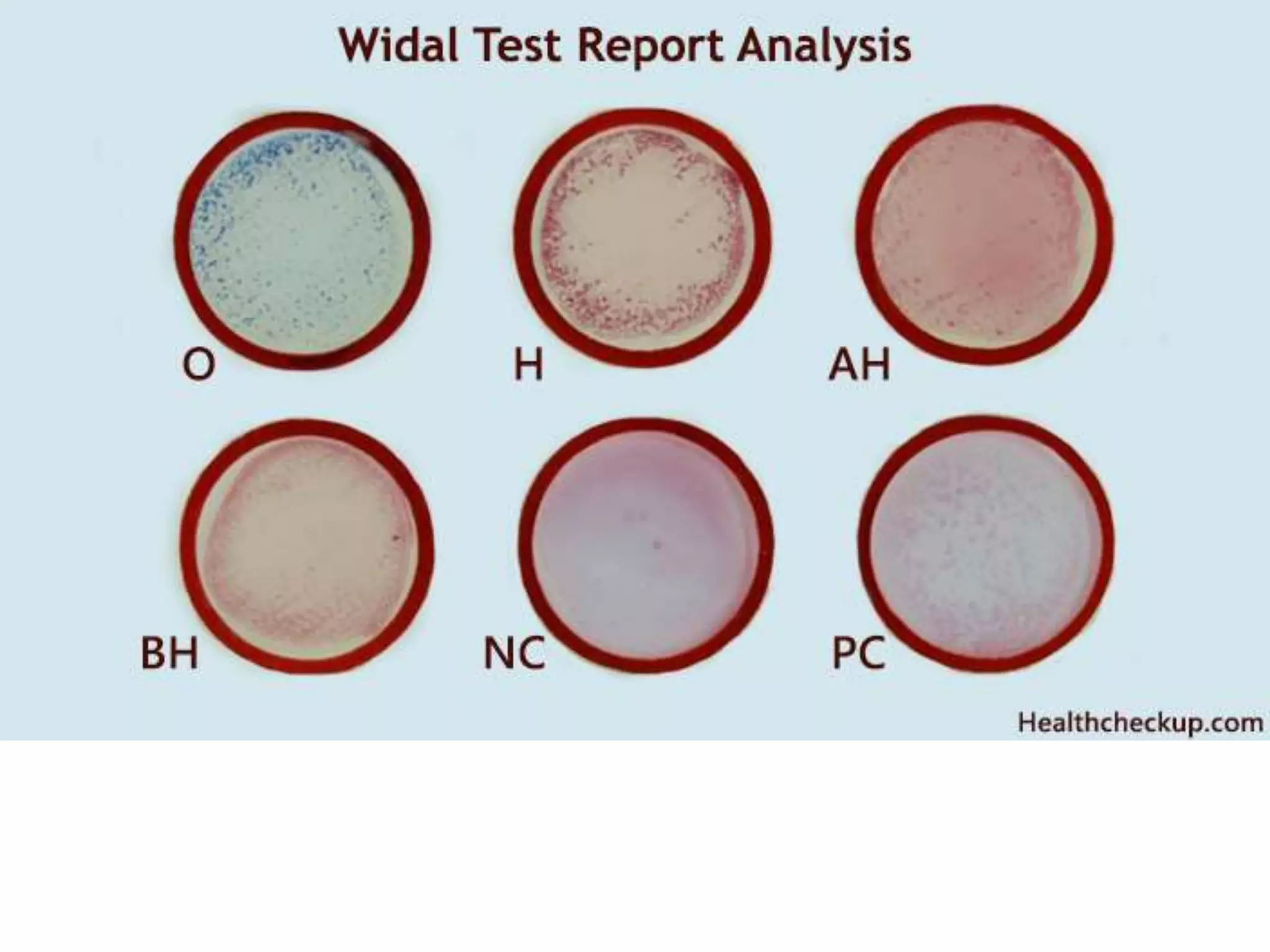
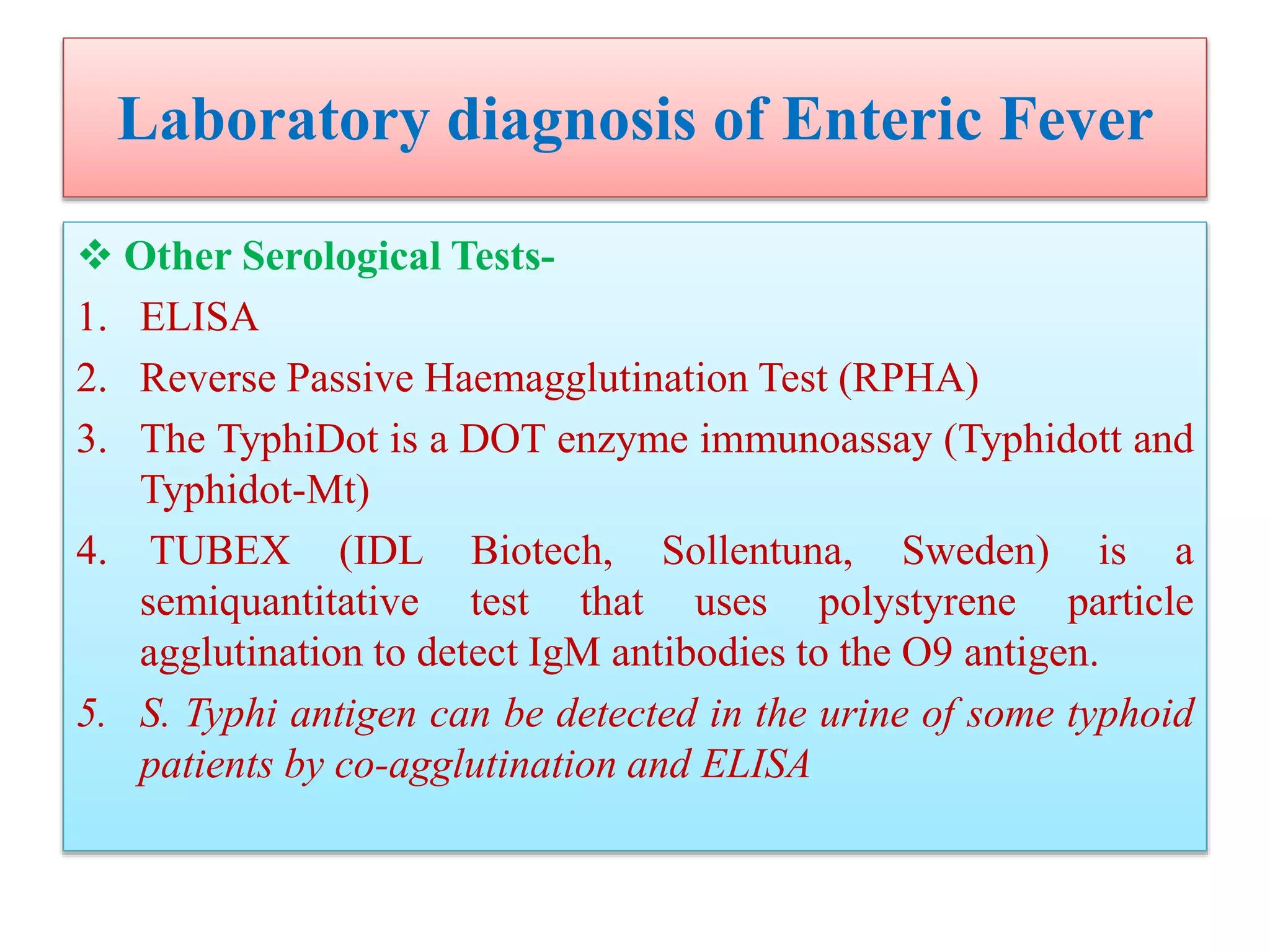
This document provides an overview of Salmonella, including Salmonella enterica and Salmonella bongori. It discusses Salmonella serotyping based on surface structures. The pathogenesis and immunity of Salmonella is described, noting how it attaches and invades the intestines. Two pathogenicity islands regulate these processes. Epidemiology sections explain the animal reservoirs and most common sources of human infections like poultry, eggs and dairy. Clinical diseases caused include gastroenteritis, septicemia, enteric fever and asymptomatic colonization. Laboratory diagnosis focuses on culturing Salmonella from blood, feces or bone marrow. Biochemical tests are used to identify isolates.



























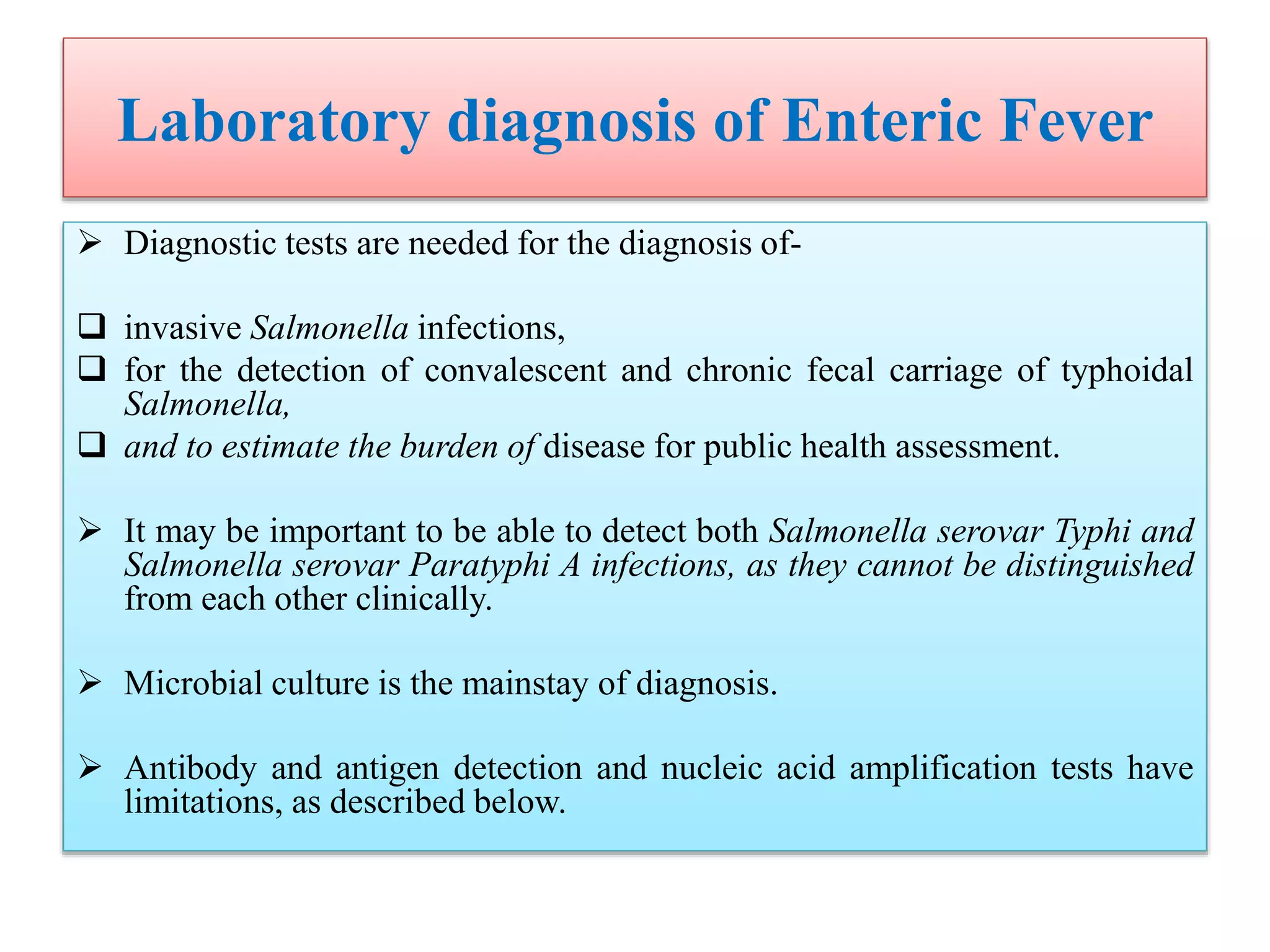













![Laboratory diagnosis of Enteric Fever
Molecular Diagnosis-
Targets for Salmonella serovar Typhi PCR-based assays have included
theHdflagellin gene fliC-d,
the Vi capsular gene viaB,
the tyvelose epimerase gene (tyv) (previously rfbE),
the paratose synthase gene (prt) (previously rfbS),
groEL,
the 16sRNA gene ,
hilA (a regulatory gene in Salmonella pathogenicity island 1 [SPI-1]), the gene
encoding the 50-kDa outer membrane protein ST50
The food industry has used PCR technology for several decades and guidelines
are published for quantitative detection of Salmonella in food by PCR.
Studies using single or nested PCR primers for fliC of S. Typhi have reported
good results from PCR.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/salmonellatyphi-200623072716/75/Salmonella-typhi-56-2048.jpg)