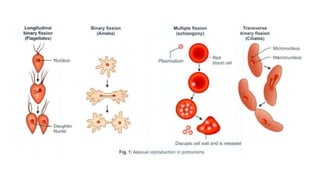
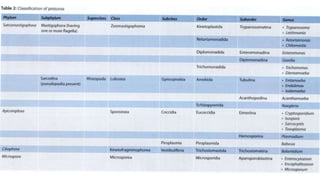
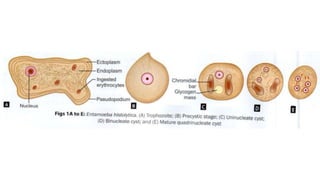
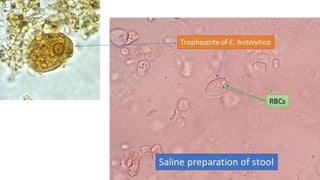
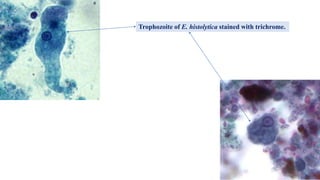
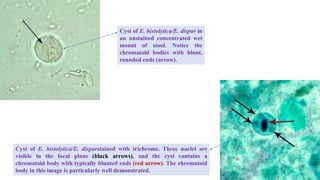
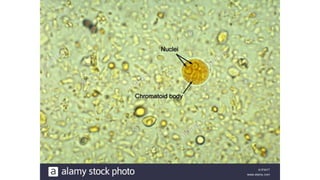
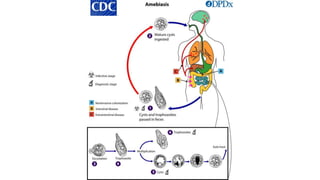
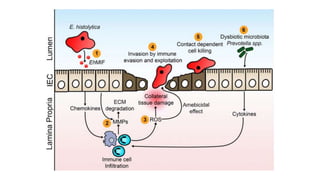
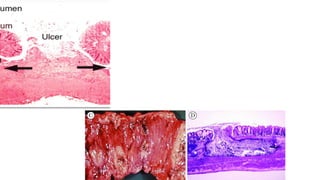
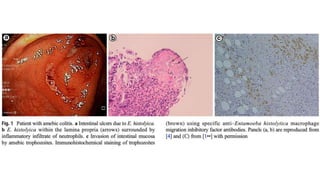
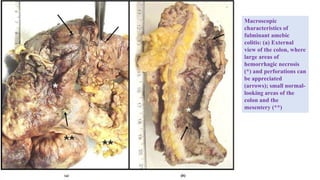
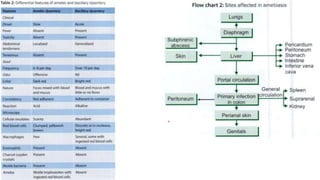
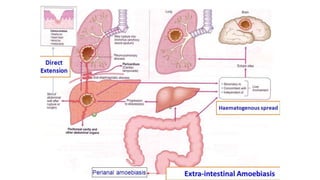
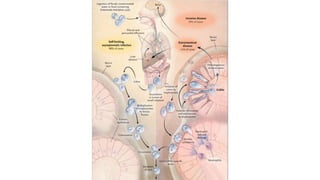
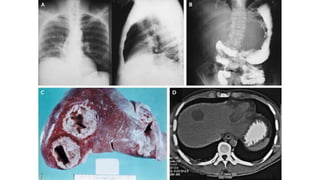
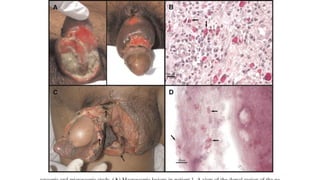
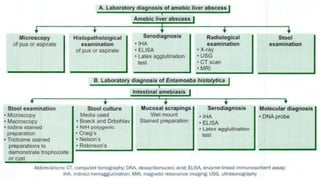
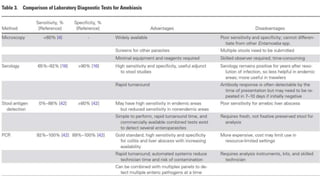
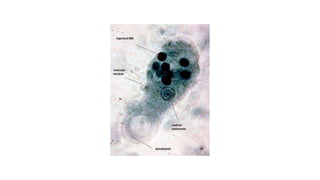
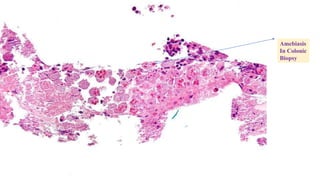
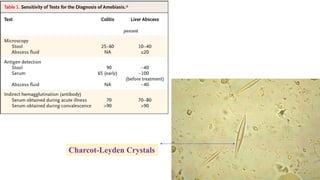
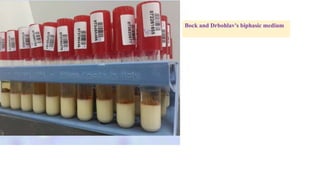
E. histolytica causes a range of diseases in humans. It can cause asymptomatic intestinal infection or symptomatic amebic colitis characterized by diarrhea, abdominal cramps and pain. Rarely, it can cause a severe, fulminant colitis with toxic megacolon. It is also known to cause amebic liver abscess when trophozoites spread from the intestine to the liver via the portal vein. E. histolytica exhibits a complex life cycle alternating between the infective cyst form and the invasive trophozoite form.