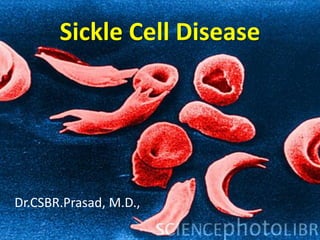
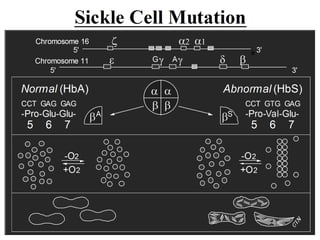
Sickle cell disease is a hereditary blood disorder caused by a mutation in the beta-globin gene that results in abnormal sickle hemoglobin molecules which polymerize and distort red blood cells into a sickle shape when deoxygenated, leading to chronic hemolysis, pain crises, organ damage, and infections. Common clinical manifestations include anemia, painful vaso-occlusive crises, acute chest syndrome, splenic sequestration, and susceptibility to infections. Management focuses on treatment of acute complications, prophylactic antibiotics, pain management, blood transfusions, and in severe cases hematopoietic stem