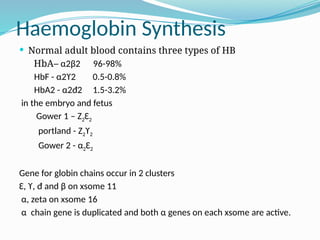
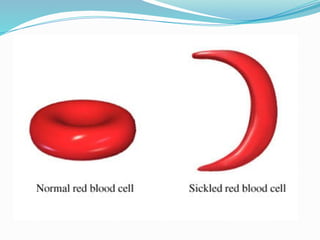
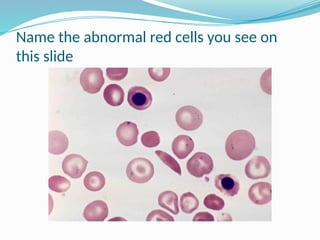
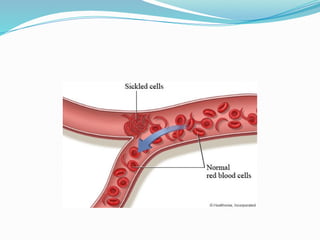
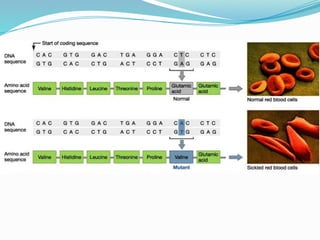
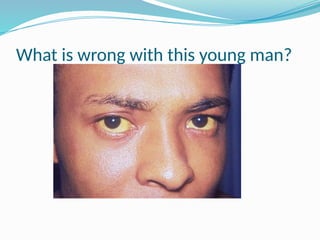
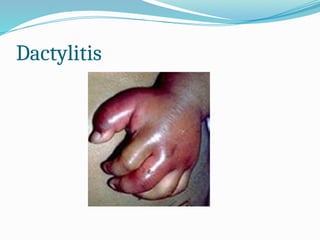
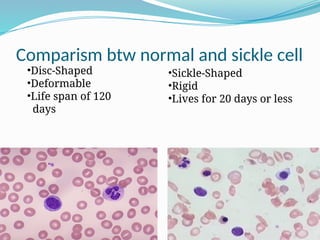
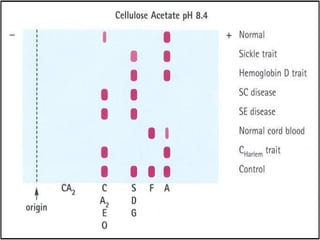
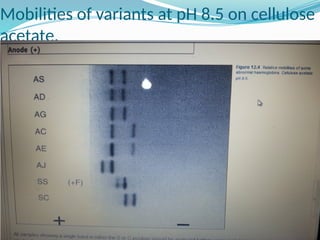
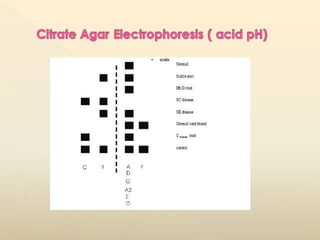
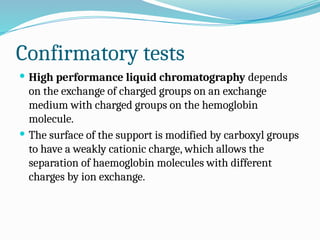
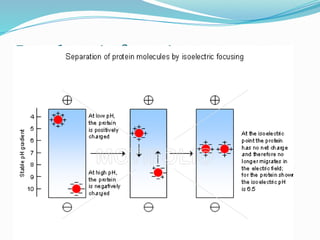
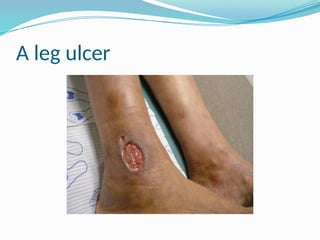
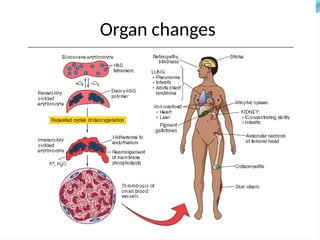
The document discusses sickle cell anemia, highlighting its genetic basis as a structural abnormality in the beta-globin chain of hemoglobin, its epidemiology, pathogenesis, clinical features, diagnosis, and management strategies. It details the various crises patients may experience, complications arising from the disease, and laboratory tests for diagnosis, emphasizing the importance of early identification and comprehensive care. The management includes prevention of infections, crisis management, and pharmacological treatments such as hydroxyurea to stimulate the production of fetal hemoglobin.