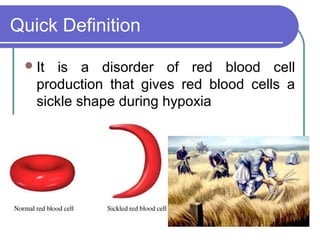
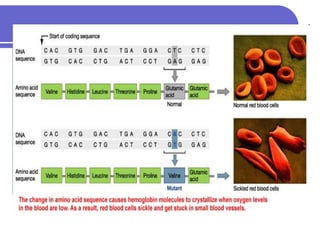
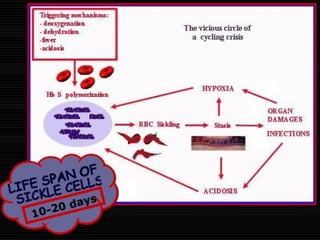
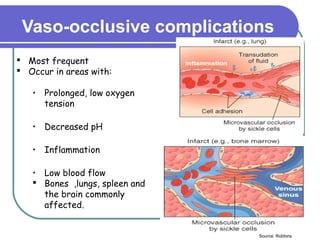
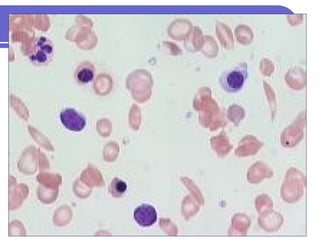
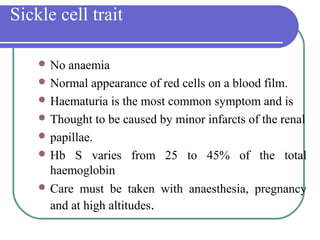
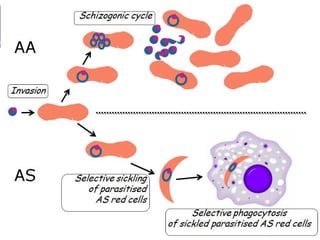
Sickle cell disease is a genetic disorder that causes red blood cells to take on a sickle shape during periods of low oxygen. It is most common among those of African descent and is caused by a mutation in the beta-globin gene. The sickling of red blood cells leads to hemolytic anemia, damage to blood vessels, and painful vaso-occlusive crises in the bones, lungs, and other organs. Treatments include blood transfusions, hydroxyurea to increase fetal hemoglobin levels, antibiotics to prevent infection, and pain management. Future treatments may involve stem cell transplants or gene therapy.