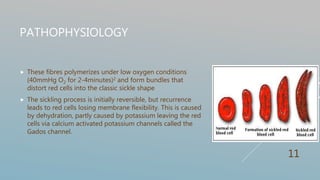
Hydroxyurea therapy increases fetal hemoglobin levels and reduces vaso-occlusive crises in sickle cell disease by inhibiting ribonucleotide reductase and altering cell adhesion molecules, with common side effects being leukopenia and neutropenia. Guidelines recommend hydroxyurea for patients with frequent pain episodes or a history of acute chest syndrome or anemia to reduce complications. Treatment involves monitoring blood counts and titrating dosage up or down based on response and side effects.