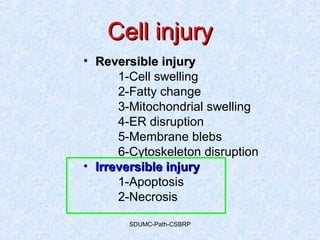
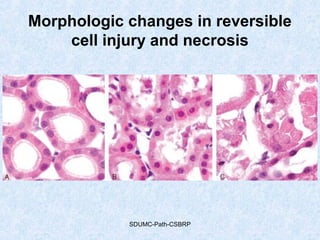
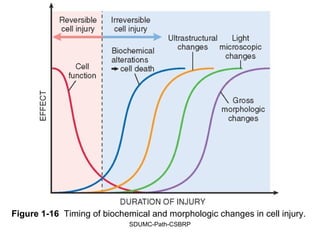
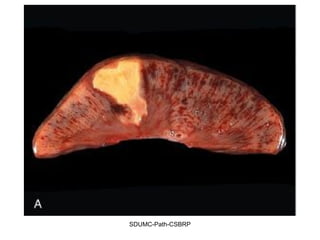
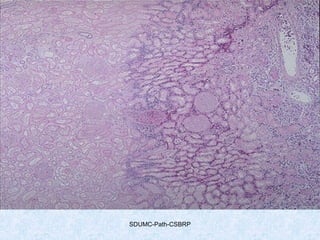
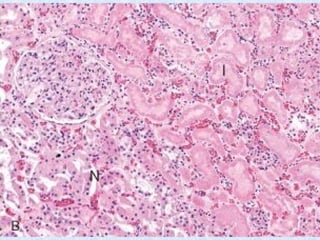
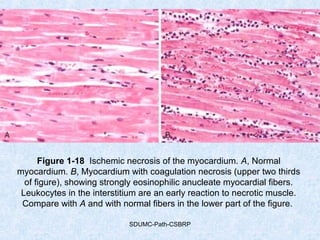
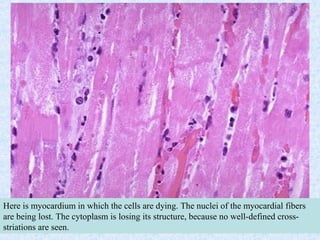
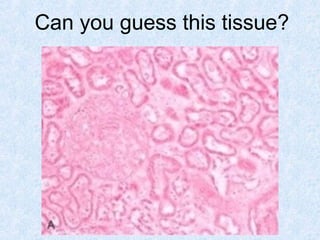
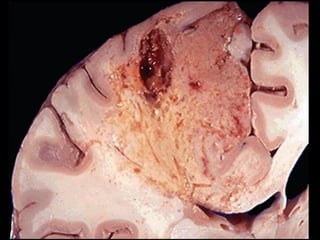
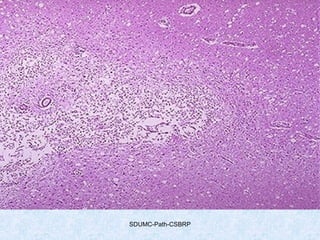
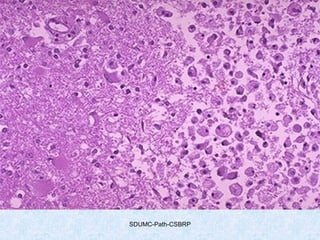
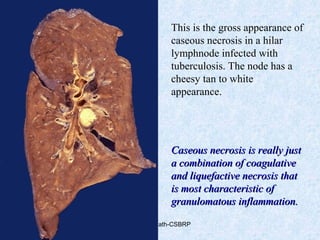
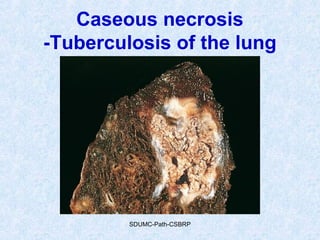
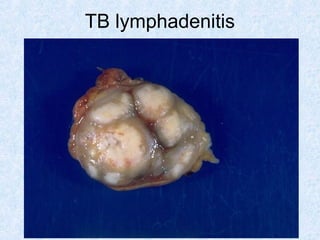
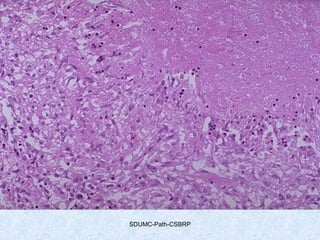
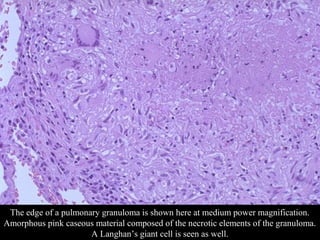
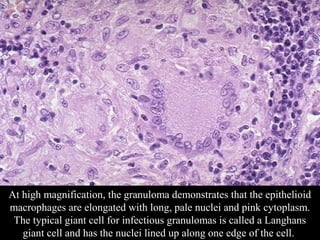
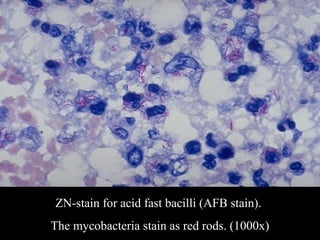
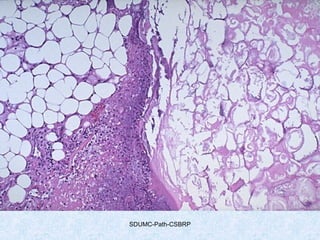
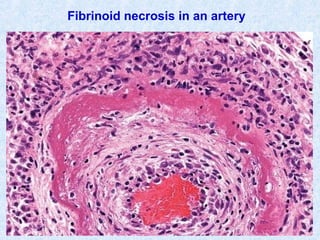
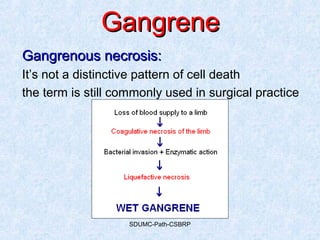
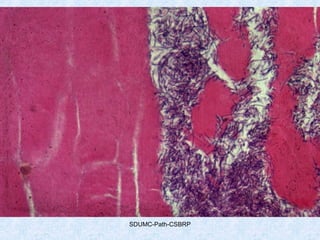
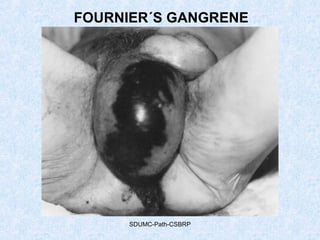
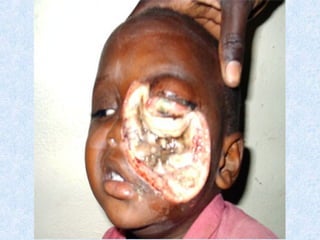
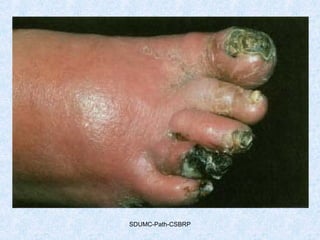
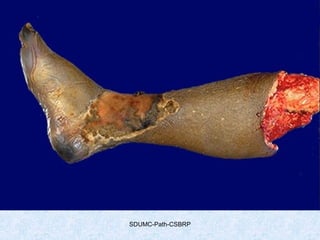
This document discusses various types of necrosis including coagulative, liquefactive, caseous, fat, and fibrinoid necrosis. Coagulative necrosis preserves cell outlines while liquefactive necrosis completely digests dead cells. Caseous necrosis is seen in tuberculosis and has a cheesy appearance. Fat necrosis occurs in pancreatitis. Fibrinoid necrosis involves fibrin deposition in blood vessels. Gangrene and primary gangrene are also described, with primary gangrene caused specifically by Clostridium bacteria. Overall, the document provides detailed information on the morphological and pathological features of different forms of cell death.