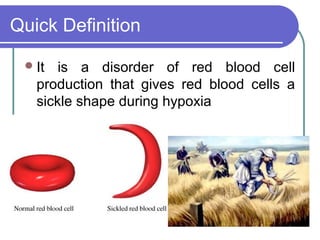
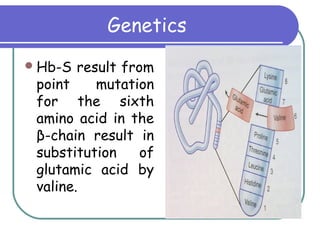
Sickle cell disease is a genetic disorder that causes red blood cells to become sickle shaped and break down during periods of low oxygen. It results from a mutation that substitutes one amino acid for another in the beta chain of hemoglobin. This causes red blood cells to form rigid, sickle shapes that can clog small blood vessels. Sickle cell disease primarily affects those of African descent and results in complications like painful sickle cell crises, infections, strokes, and damage to organs like the lungs, bones, and spleen. Diagnosis involves blood tests that identify the presence of hemoglobin S. Treatment focuses on pain management, antibiotics, blood transfusions, and hydroxyurea which can reduce symptoms by increasing fetal hem