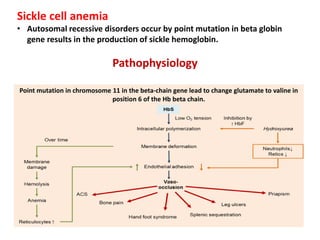
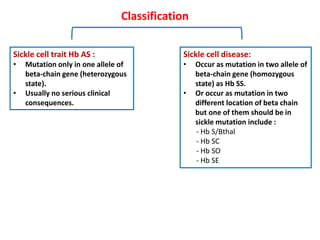
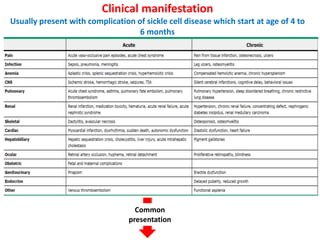
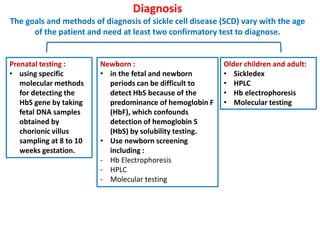
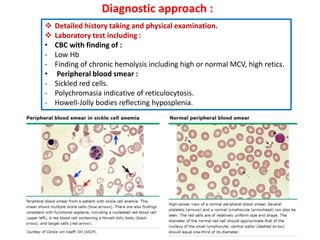
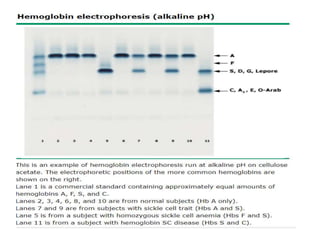
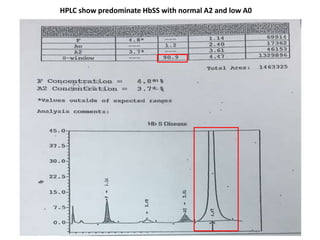
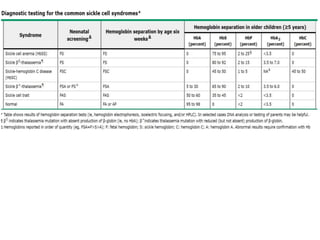
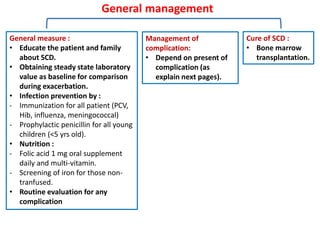
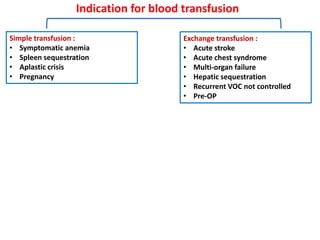
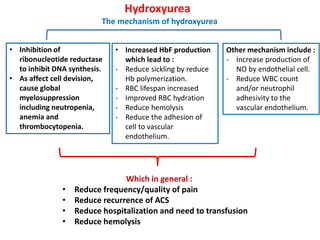
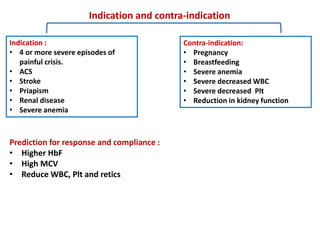
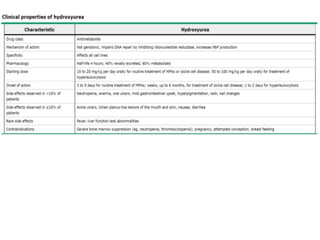
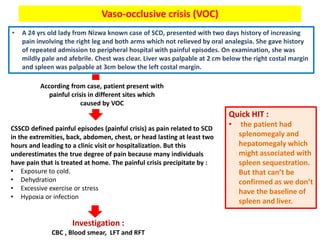
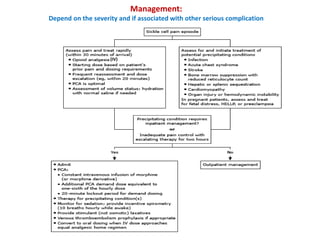
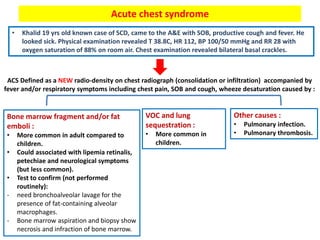
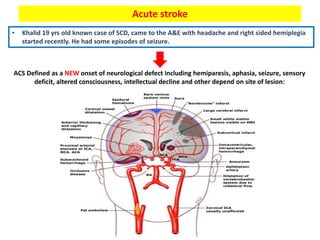
1. The patient presented with headache and right-sided hemiplegia, consistent with an acute stroke.
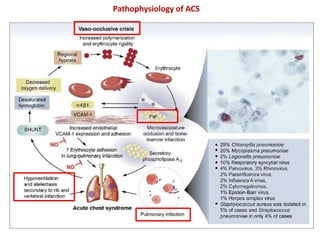
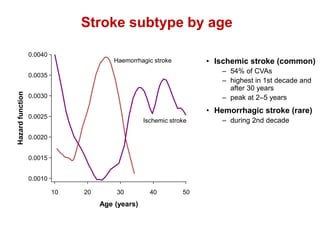
2. Strokes in sickle cell disease are most commonly ischemic and occur bimodally, peaking in younger children and those over 30 years old. Hemorrhagic strokes are rarer and peak during the second decade.
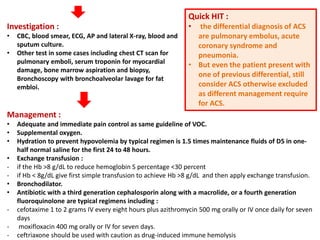
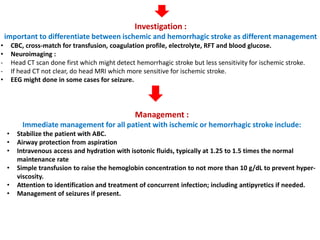
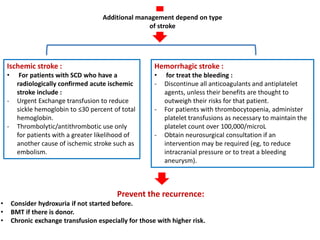
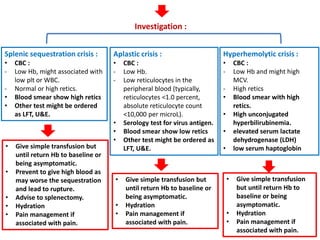
3. Diagnostic workup includes blood tests and neuroimaging to determine if the stroke is ischemic or hemorrhagic, as management differs between the two.