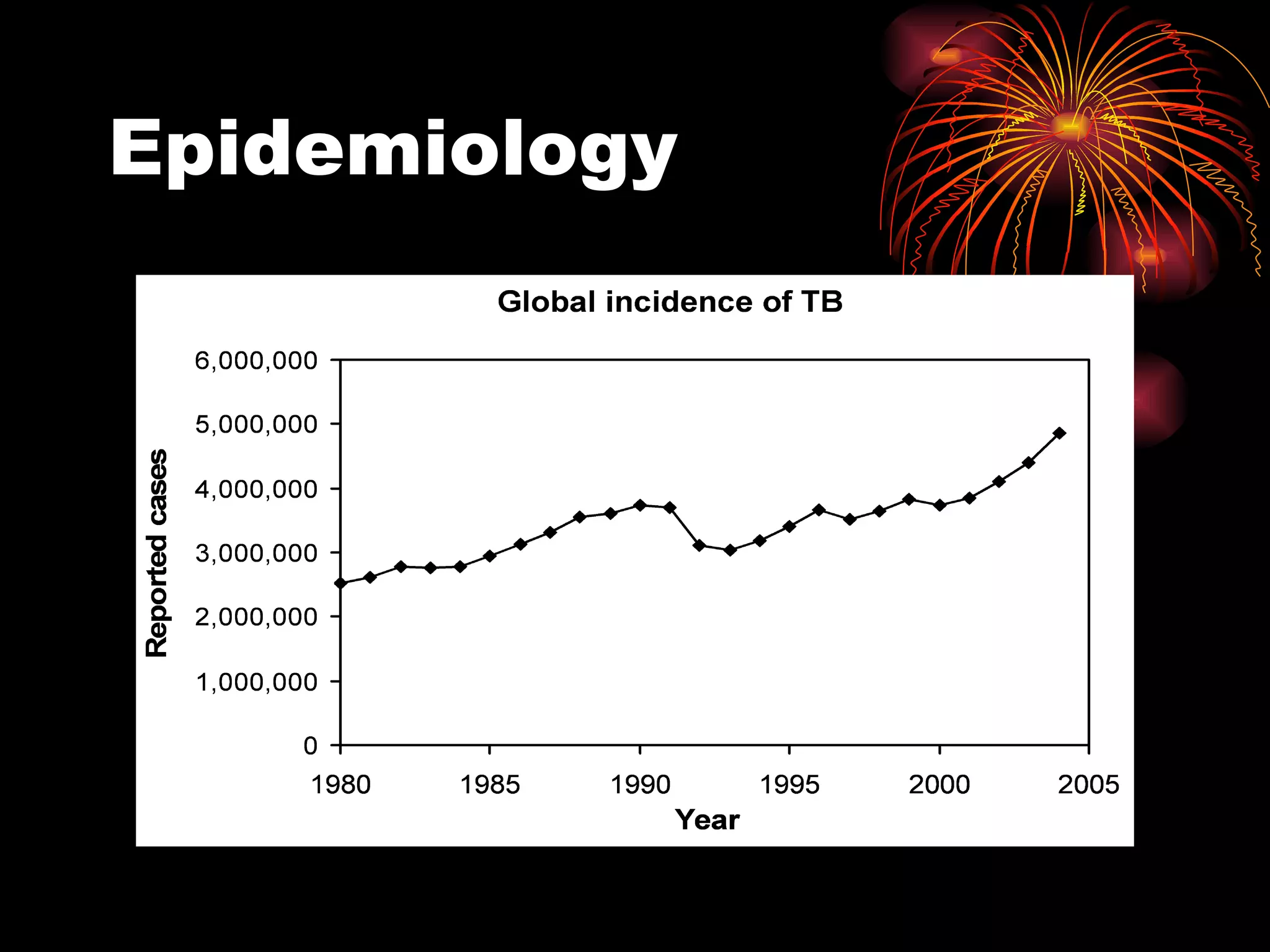
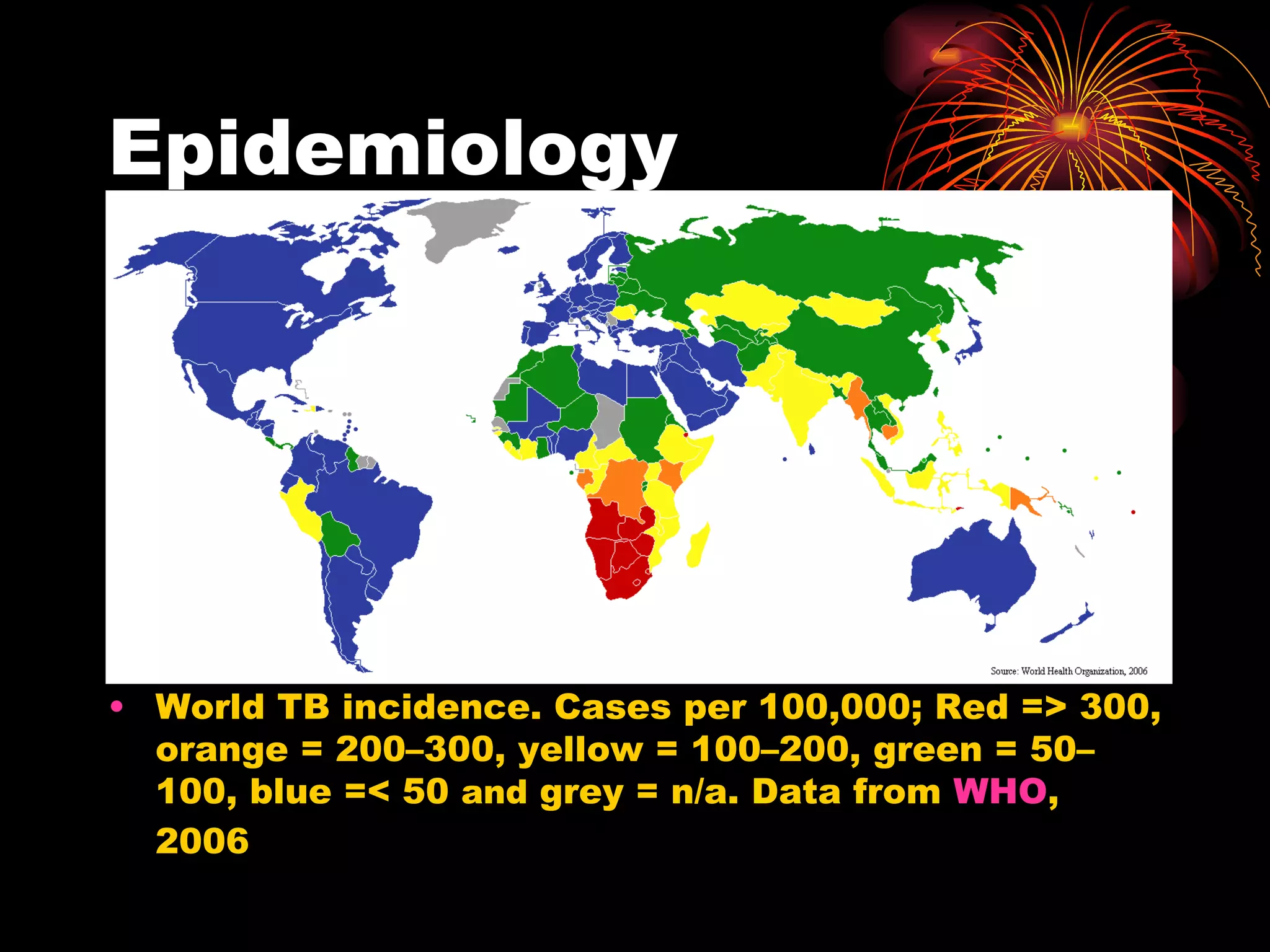
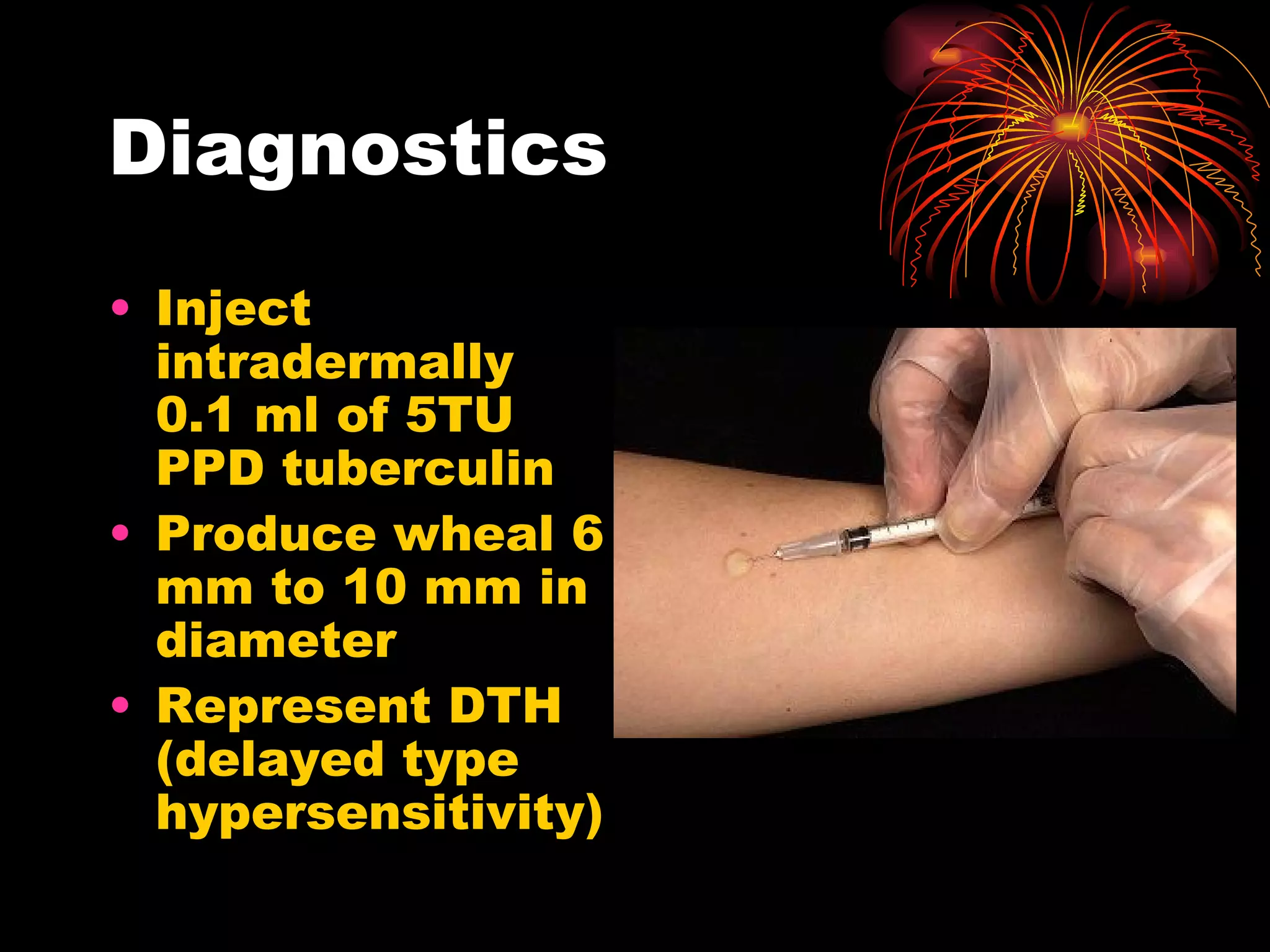
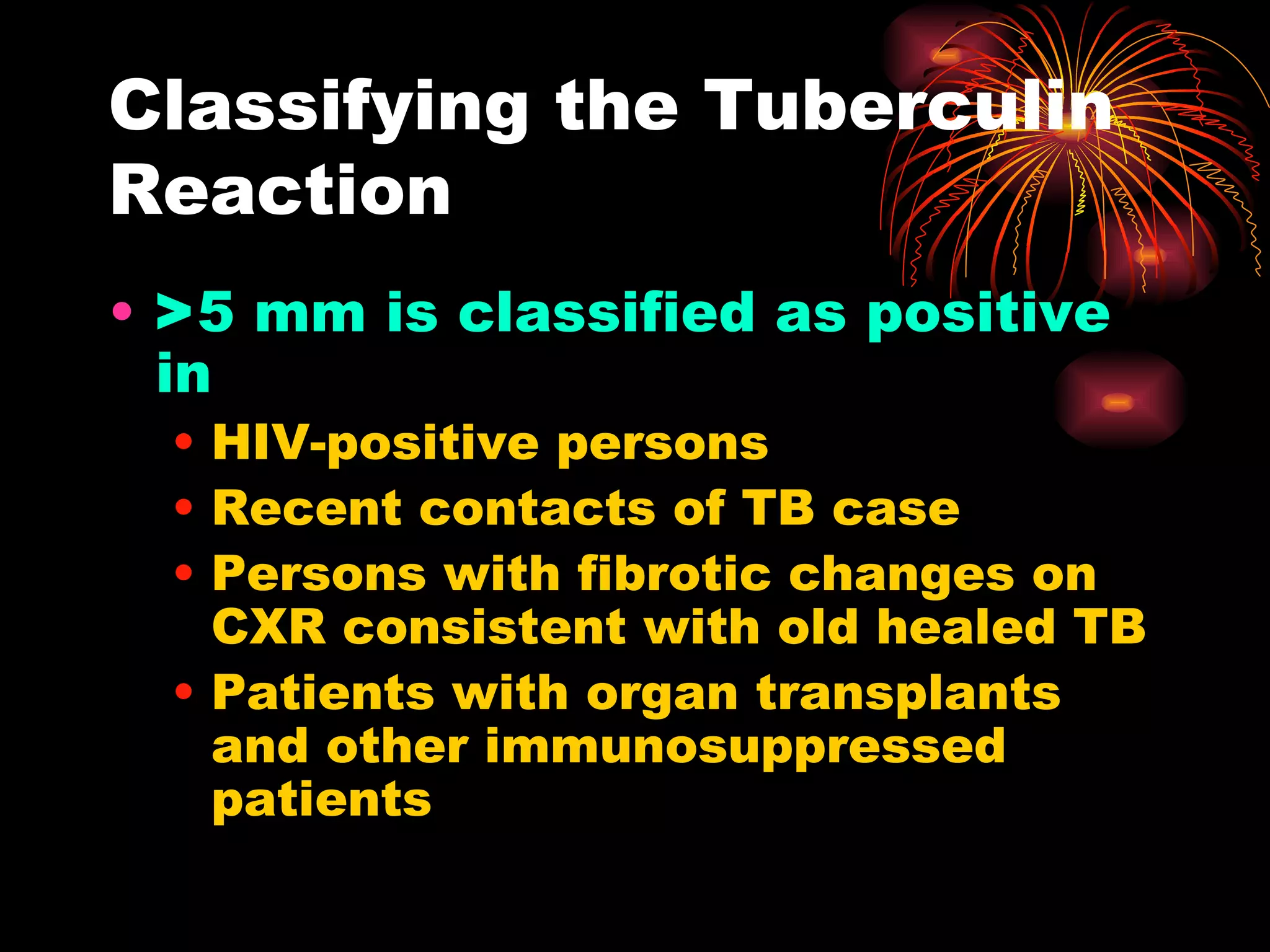
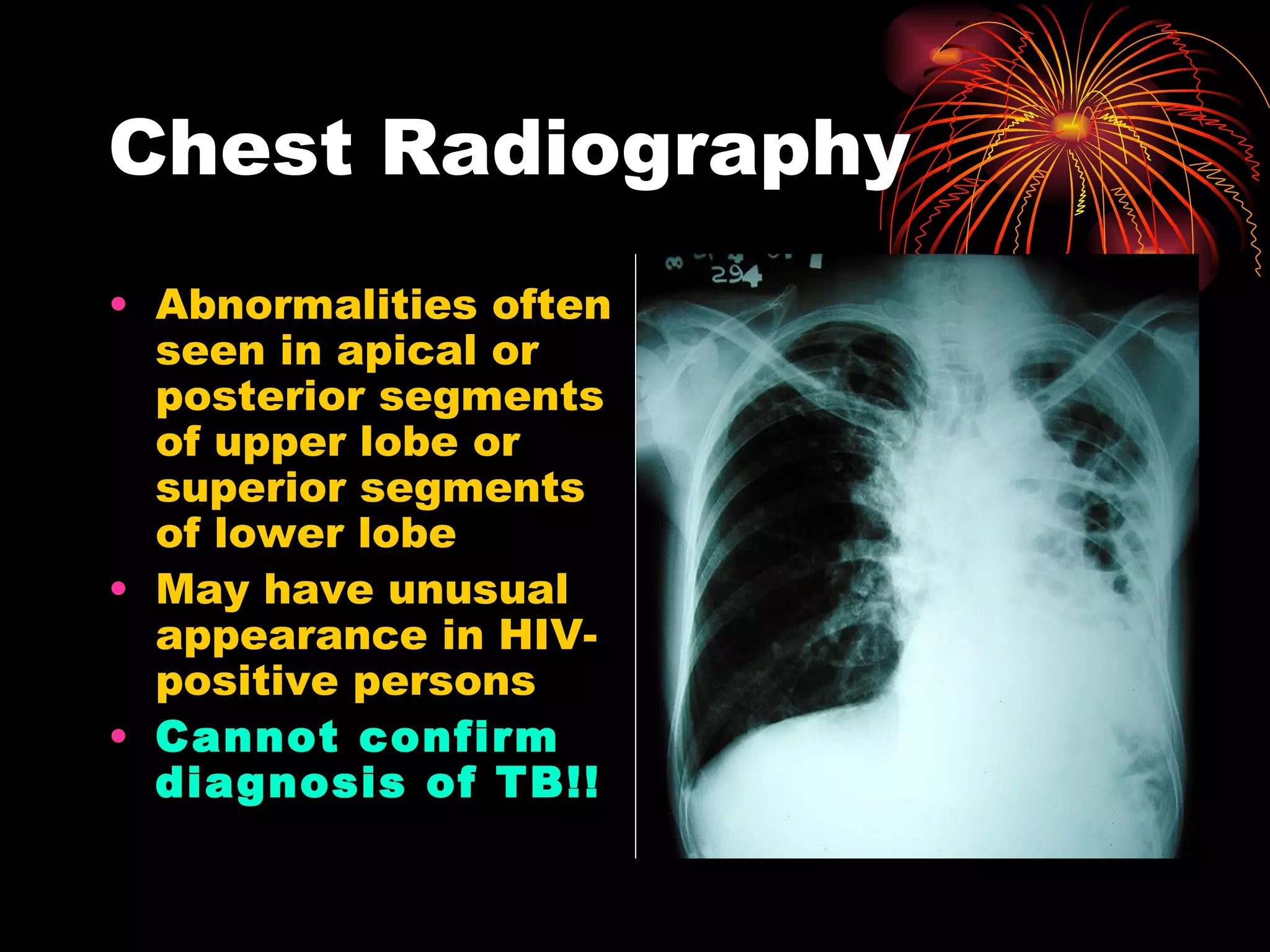
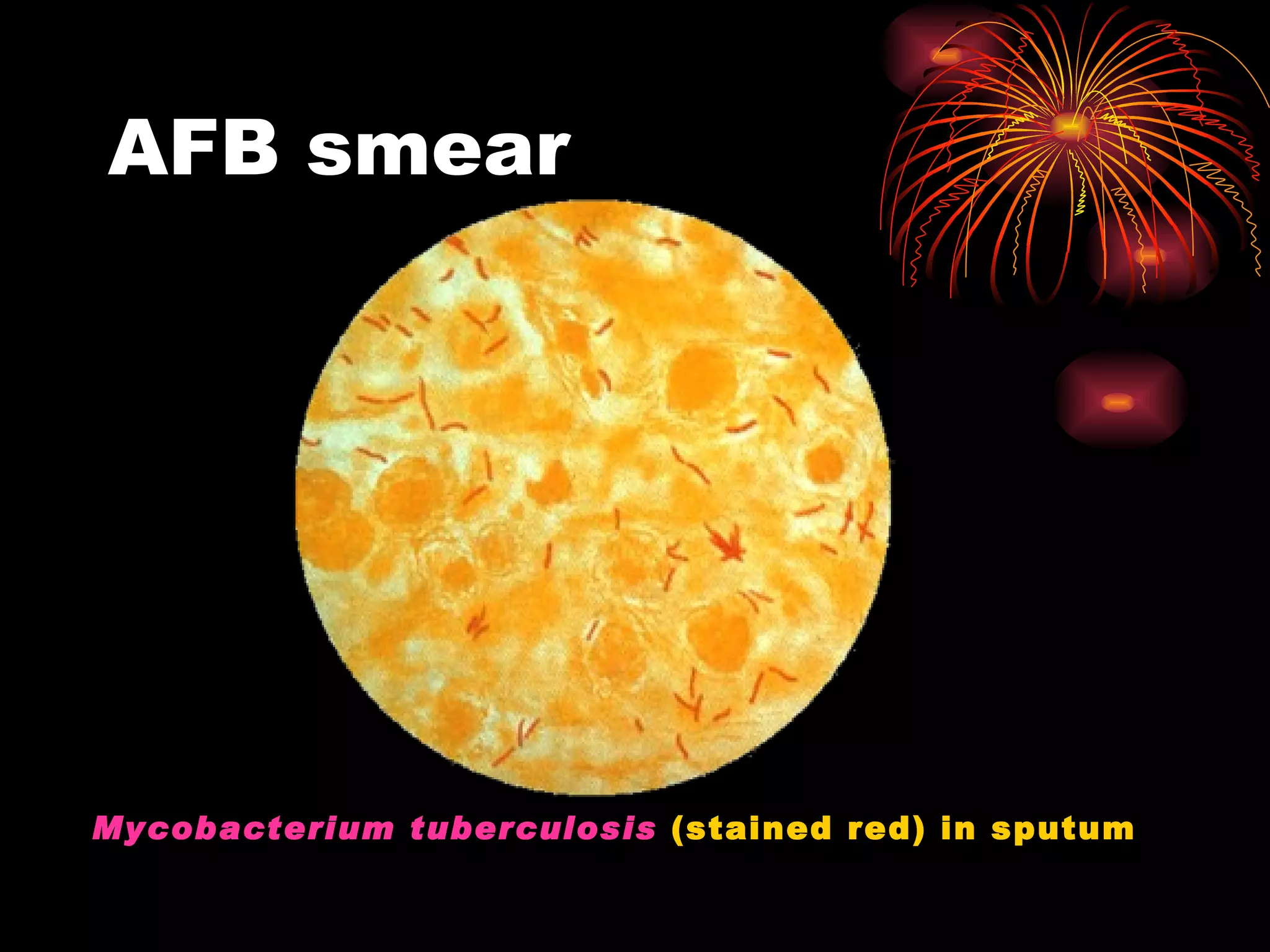
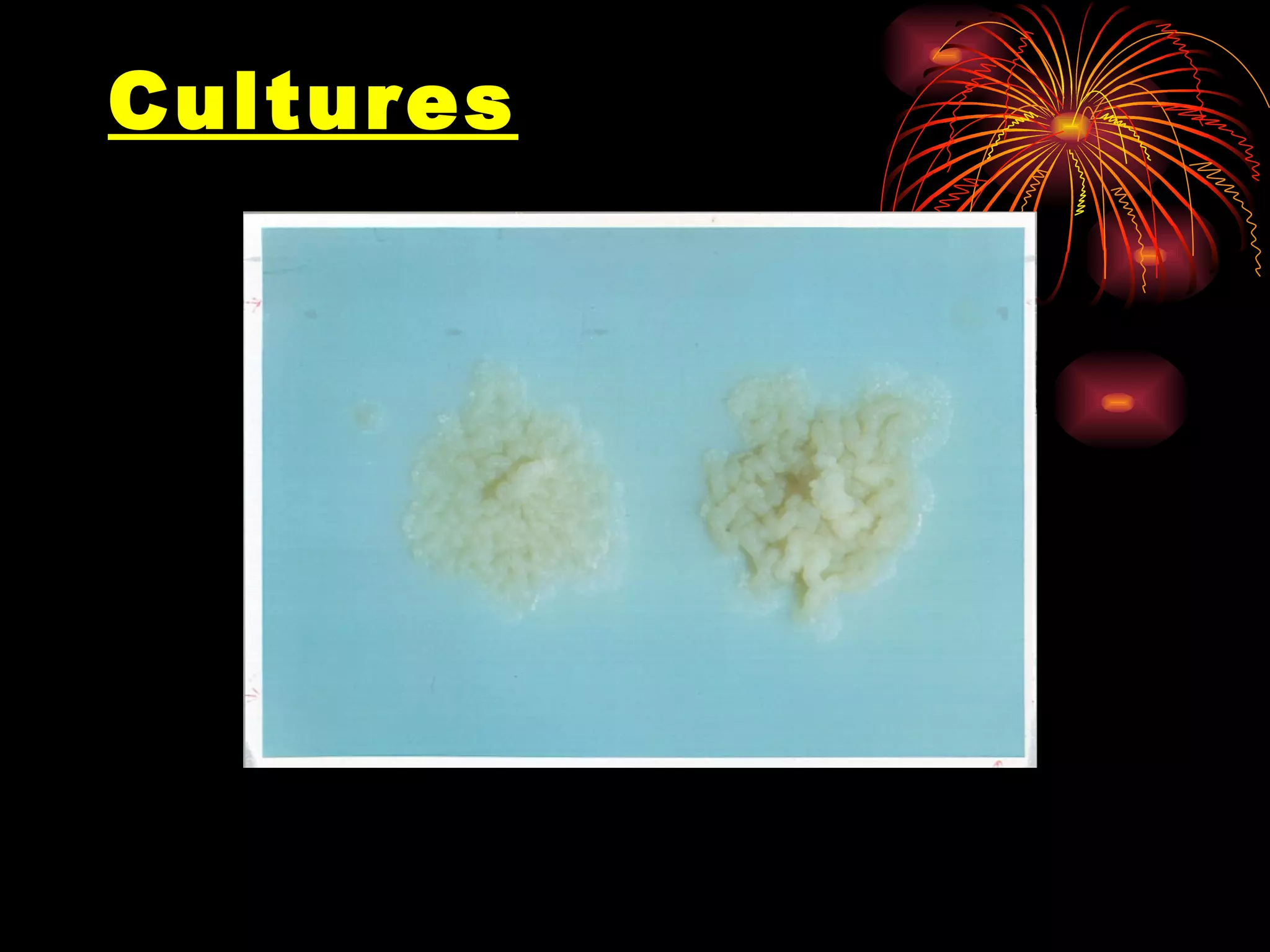
Pulmonary tuberculosis (TB) is a contagious disease caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis, primarily affecting the lungs and is responsible for millions of deaths annually worldwide. The WHO estimates around 2 billion people have been exposed to TB, with high incidence rates in certain populations, particularly those involved with HIV/AIDS and low socioeconomic status. Standard treatment involves a combination of first-line anti-tuberculosis drugs, with an urgent need for improved vaccination and surgical interventions for cases resistant to conventional treatment.