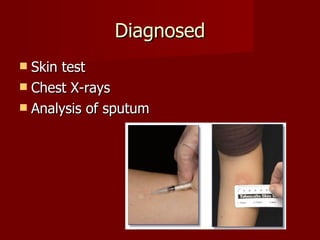
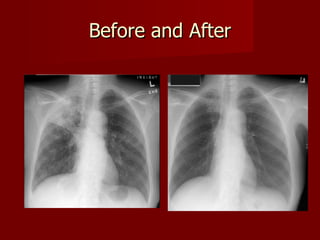
Tuberculosis (TB) affects over 9 million people globally, leading to approximately 2 million deaths annually, with 10-15 million individuals infected in the U.S. alone. Caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis, it primarily infects the lungs and is highly contagious, spreading through airborne bacteria. Diagnosis involves skin tests and chest X-rays, with treatment options including antibiotics and the BCG vaccine aimed at TB elimination.