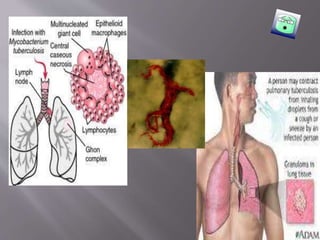
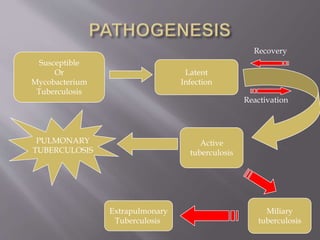
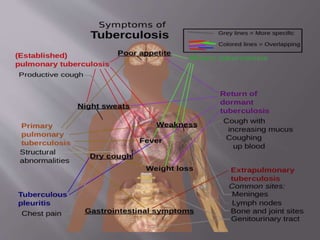
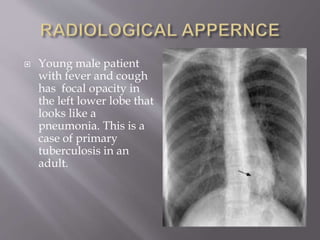
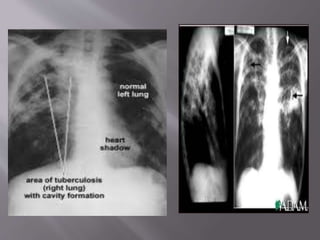
Robert Koch identified Mycobacterium tuberculosis in 1882 and received the Nobel Prize for this discovery. In 1906, Calmette and Guerin developed the BCG vaccine for tuberculosis. The vaccine was first used in humans in 1921 in France but did not become widely used in places like the US, UK, and Germany until after World War II. Tuberculosis is caused by the bacterium M. tuberculosis and spreads through airborne droplets when infected people cough, sneeze, or talk. It affects mostly the lungs but can spread to other organs, and if left untreated it can be fatal.








![The two antibiotics most commonly used are isoniazid
and rifampicin, and treatments can be prolonged, taking
several months. Latent TB treatment usually employs a
single antibiotic
New onset
In 2010, is six months of a combination of antibiotics
containing rifampicin, isoniazid, pyrazinamide, and
ethambutol for the first two months, and only rifampicin
and isoniazid for the last four months.[11] Where
resistance to isoniazid is high, ethambutol may be added
for the last four months as an alternative.
Recurrent disease
If multiple drug-resistant TB is detected, treatment with
at least four effective antibiotics for 18 to 24 months is
recommended.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pulmonarytb-arun-170226172125/85/Pulmonary-tuberculosis-19-320.jpg)

