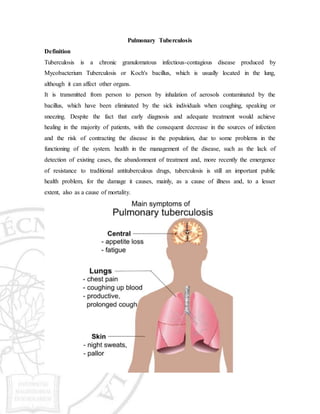
Pulmonary tuberculosis is a chronic infectious disease caused by the bacterium Mycobacterium tuberculosis, which is usually located in the lungs. It is transmitted through inhalation of aerosols from an infected individual when they cough, sneeze or speak. Symptoms include a persistent cough, bloody sputum, weight loss, fever and night sweats. Diagnosis involves physical examination, chest x-rays, sputum tests and cultures. Treatment requires a multi-drug regimen to prevent drug resistance, and patients should take precautions like covering coughs and staying home until non-contagious. Prevention includes testing high-risk groups and timely treatment of active cases to control spread.