This document provides information on tuberculosis (TB), including:
- TB is a contagious bacterial infection that mainly affects the lungs, caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
- Over 9 million new cases and 2 million deaths occur worldwide each year, with 1/3 of the world's population infected.
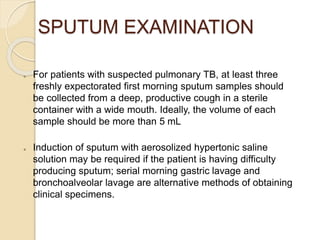
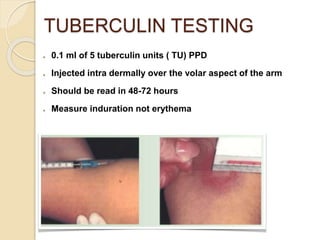
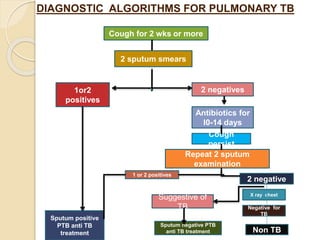
- Diagnosis involves sputum smear microscopy, culture, chest x-ray, and the tuberculin skin test. Standard treatment lasts 6-9 months using multiple antibiotic drugs.