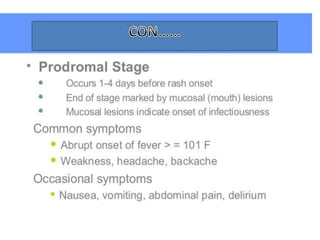
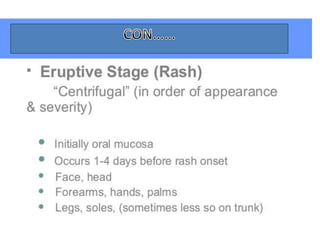
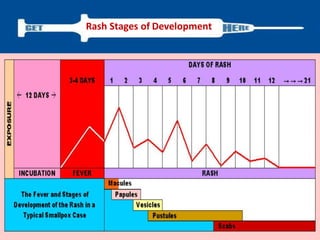
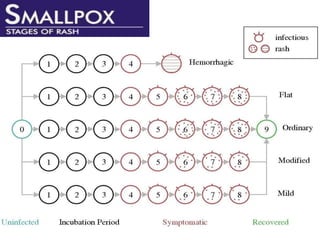
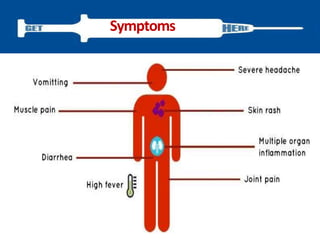
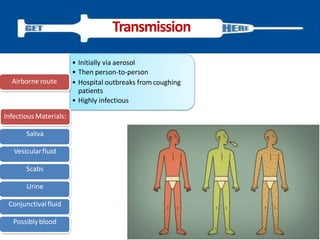
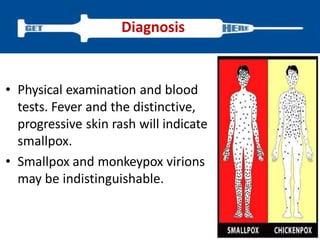
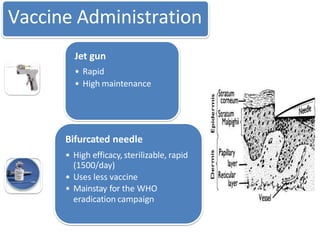
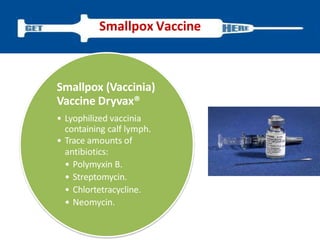
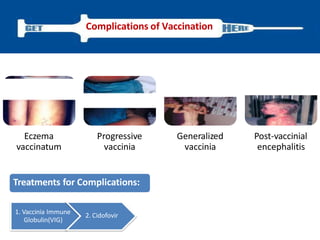
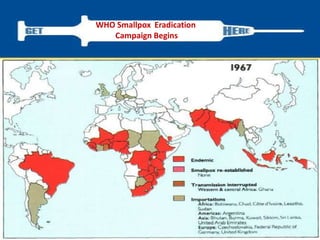
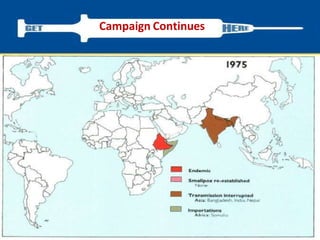
Variola virus causes the acute, contagious disease smallpox. It was effectively eradicated through global vaccination efforts led by the WHO between 1966-1979. Smallpox is characterized by an initial fever and flu-like symptoms followed by a distinctive pustular rash. It spreads through respiratory droplets or direct contact with infected individuals or contaminated objects. Vaccination provided effective immunity and was a major factor in eliminating smallpox worldwide by 1980, making it the only human infectious disease to be fully eradicated.