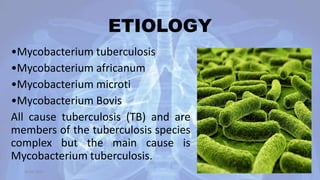
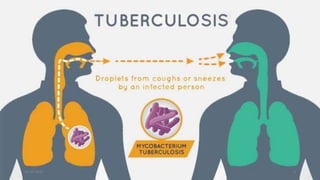
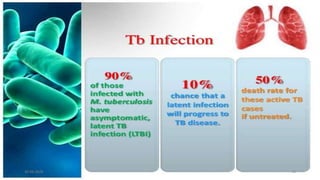
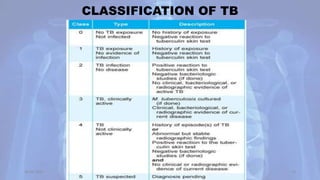
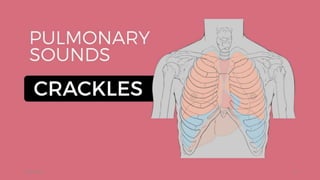
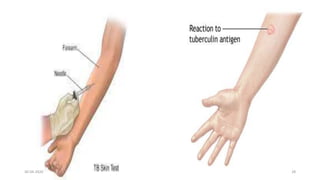
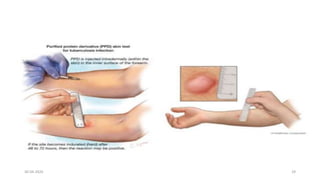
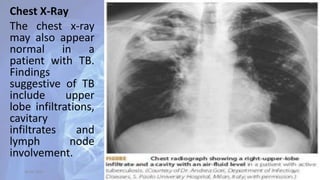
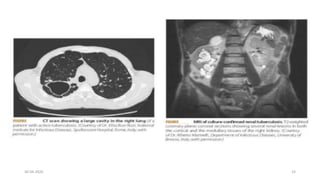
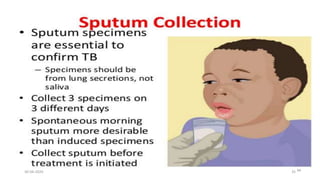
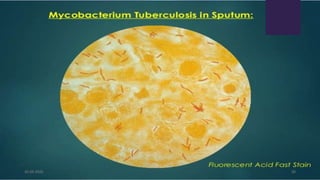
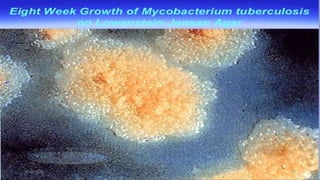
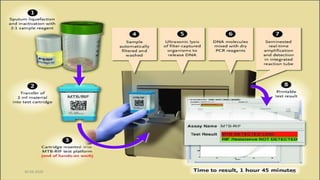
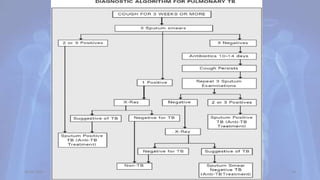
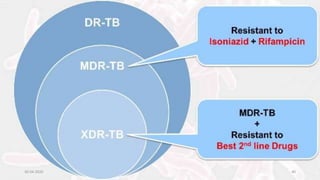
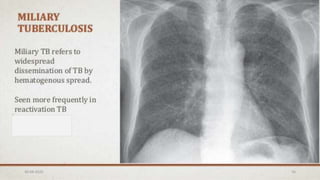
This document provides an overview of pulmonary tuberculosis and its management. It discusses the etiology, risk factors, pathophysiology, signs and symptoms, diagnostic evaluation including tuberculin skin test and chest x-ray, classification, medical management including DOTS therapy, complications, nursing assessment and interventions. Key points covered are that tuberculosis is caused primarily by Mycobacterium tuberculosis and affects the lungs. Diagnosis involves history, physical exam, skin test and chest x-ray. Treatment is with a combination of antibiotics over a period of 6-9 months to prevent drug resistance. Nursing care focuses on education, monitoring for side effects and preventing transmission.






































![REFERENCES
1.Janice L. Hinkle, Kerry H. Cheever. Brunner and Suddarth’s Textbook of Medical
Surgical Nursing. 2015. New Delhi. Wolters Kluwer.13th Edition. Volume 1. Pg. no.
586-591.
2.Joyce M. Black, Jane Hokanson Hawks. Medical Surgical Nursing Clinical
Management of Positive Outcomes.2015. New Delhi. Reed Elsevier India Private
Limited. Volume II. Pg. No.1604-1609.
3.Lewis. Medical Surgical Nursing Assessment and Management of clinical
problems.2015. New Delhi. Elsevier. 2nd Edition. Volume I. Pg. no. 553-559.
4.INDIA TB REPORT 2019. Available from
https://tbcindia.gov.in/WriteReadData/India%20TB%20Report%202019.pdf [cited 4
April 2020]
5.Feleke, B.E., Feleke, T.E. & Biadglegne, F. Nutritional status of tuberculosis
patients, a comparative cross-sectional study. BMC Pulm Med 19, 182 (2019).
https://doi.org/10.1186/s12890-019-0953-0.
6.PubMed. The Prevalence and Demographic Risk Factors for Latent Tuberculosis
Infection (LTBI) Among Healthcare Workers in Semarang, Indonesia. J Multidiscip
Healthc. 2020; 13: 197–206. doi: 10.2147/JMDH.S241972
30-04-2020 61](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tb-200430183237/85/Pulmonary-tuberculosis-and-its-management-61-320.jpg)