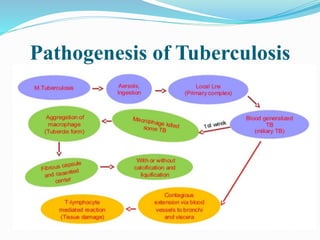
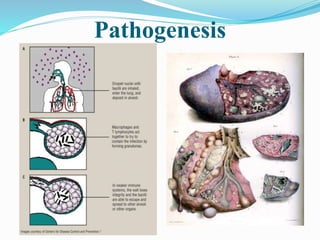
1) Tuberculosis is caused by mycobacteria, mainly Mycobacterium tuberculosis, and commonly affects the lungs. It can also affect other body systems when the immune system is weakened.
2) TB spreads through air when a sick person coughs or sneezes, expelling dried bacteria. Close and household contacts are most at risk of infection through inhalation or ingestion.
3) Diagnosis involves tests like chest x-rays, sputum smears, tuberculin skin tests, and culture of bacteria. Treatment requires taking multiple antibiotics like rifampin and isoniazid daily for 6-12 months to fully eliminate the bacteria.