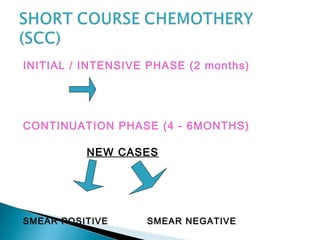
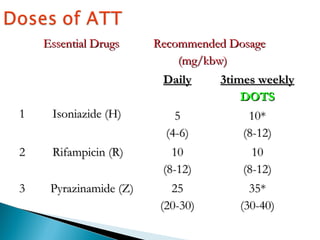
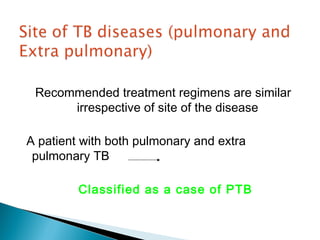
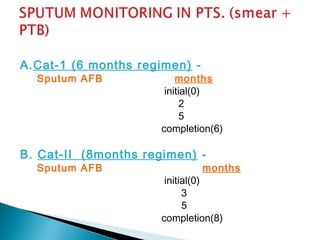
This document provides treatment guidelines for tuberculosis. It outlines the aims of TB treatment as curing the patient, preventing death from active or relapsed TB, decreasing transmission, and preventing drug resistance. It describes the initial and continuation phases of treatment for new and previously treated cases. It also defines different types of TB cases and provides recommended drug regimens and dosages depending on the category of TB patient. Isoniazid, rifampicin, pyrazinamide, and ethambutol are first-line oral drugs, while streptomycin and thioacetazone are also mentioned. BCG vaccination guidelines are also briefly covered.